Week 21 Lessons - Highline Public Schools
... - # of protons = Atomic Number - # of electrons = # of protons (this is a neutral atom.) - Mass number = # of protons + # of neutrons - # of neutrons = mass number - # of protons (Mass number must be a whole number!!!! You can’t have half a neutron. Use atomic mass and round up.) Exit Ticket: The nu ...
... - # of protons = Atomic Number - # of electrons = # of protons (this is a neutral atom.) - Mass number = # of protons + # of neutrons - # of neutrons = mass number - # of protons (Mass number must be a whole number!!!! You can’t have half a neutron. Use atomic mass and round up.) Exit Ticket: The nu ...
Honors Chemistry
... 27. Sodium metal has a first ionization energy of 496 kJ/mol. a. What wavelength of light, in nanometers, is sufficient to provide a photon with the necessary energy to remove 1 electron from an atom of sodium? ...
... 27. Sodium metal has a first ionization energy of 496 kJ/mol. a. What wavelength of light, in nanometers, is sufficient to provide a photon with the necessary energy to remove 1 electron from an atom of sodium? ...
Ppt
... • Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons when they are chemically combined with another element • Fluorine is the most electronegative • As you move away from Fluorine in any direction, the electronegativity decreases ...
... • Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons when they are chemically combined with another element • Fluorine is the most electronegative • As you move away from Fluorine in any direction, the electronegativity decreases ...
(electrons).
... He thought that if you were to cut up a material you would eventually come to a piece that is "uncuttable". He named this particle atom, which comes from the Greek word atomos for "indivisible" ...
... He thought that if you were to cut up a material you would eventually come to a piece that is "uncuttable". He named this particle atom, which comes from the Greek word atomos for "indivisible" ...
IPS Unit 8 – Periodic Table Review Worksheet
... 4. The inner transition metals include the a. alkali metals and halogens b. carbon group and noble gasses ...
... 4. The inner transition metals include the a. alkali metals and halogens b. carbon group and noble gasses ...
Introduction to Atoms
... Electrons move around the nucleus, which contains the protons and neutrons. This area is called an electron cloud because electrons may move anywhere within it. Comparing Particle Masses: Although electrons occupy most of an atom’s volume, they don’t account for much of its mass. A proton and ...
... Electrons move around the nucleus, which contains the protons and neutrons. This area is called an electron cloud because electrons may move anywhere within it. Comparing Particle Masses: Although electrons occupy most of an atom’s volume, they don’t account for much of its mass. A proton and ...
Name
... additional elements were identified by using their line spectra and about 65 elements had been identified. A. J.W. Dobereiner: Organized the elements into ______________ with similar _____________. He called these groups ________________. The middle element is often the ____________________ of the o ...
... additional elements were identified by using their line spectra and about 65 elements had been identified. A. J.W. Dobereiner: Organized the elements into ______________ with similar _____________. He called these groups ________________. The middle element is often the ____________________ of the o ...
"The Atom" Guided Notes
... Niels Bohr - Came up with a “___________________________________” of the structure of an atom , won Nobel prize in _______ Bohr Model Bohr discovered that ________________________________ move in orbitals _______________________the nucleus of an atom. Although, we don’t know exactly where electrons ...
... Niels Bohr - Came up with a “___________________________________” of the structure of an atom , won Nobel prize in _______ Bohr Model Bohr discovered that ________________________________ move in orbitals _______________________the nucleus of an atom. Although, we don’t know exactly where electrons ...
Review for the Physical Science Final
... extremely small. Ordinary-sized objects are made up of very large numbers of atoms. The mass number of an atom is the sum of the atom’s neutrons and protons. ...
... extremely small. Ordinary-sized objects are made up of very large numbers of atoms. The mass number of an atom is the sum of the atom’s neutrons and protons. ...
Chapter 3: Atomic Structure
... Calculation of average atomic mass Weighted average of all existing isotopes [(Percent abundance/100) * isotope mass] [(Percent abundance/100) * isotope mass] + [(Percent abundance/100) * isotope mass] ...
... Calculation of average atomic mass Weighted average of all existing isotopes [(Percent abundance/100) * isotope mass] [(Percent abundance/100) * isotope mass] + [(Percent abundance/100) * isotope mass] ...
04 Mass Spectrometer and Isotopes
... are atoms of the same element (same # protons) with a different # of neutrons. Therefore they have different atomic masses. Because isotopes have different atomic masses, this is usually indicated in the name. Example Hydrogen-2 This isotope has a mass of 2 g/mol. The atomic mass of an element i ...
... are atoms of the same element (same # protons) with a different # of neutrons. Therefore they have different atomic masses. Because isotopes have different atomic masses, this is usually indicated in the name. Example Hydrogen-2 This isotope has a mass of 2 g/mol. The atomic mass of an element i ...
The History of the Atom and Its Structure
... How small is the nucleus? • If the atom was the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be an ant or sitting on the 50 yard line and the electron an ants foot traveling around the stadium ...
... How small is the nucleus? • If the atom was the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be an ant or sitting on the 50 yard line and the electron an ants foot traveling around the stadium ...
n - Moodle @ FCT-UNL
... 1s22s2, respectively. The second ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous unipositive ion in its ground state. For the second ionization process, we write ...
... 1s22s2, respectively. The second ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous unipositive ion in its ground state. For the second ionization process, we write ...
Agenda 11/2/2016
... What kind of ion is a reactive element on right hand side of PT - a nonmetal, likely to form? Bromine if it gains an electron, now Br-, a bromide ion Notice complete octet of electrons in outermost energy level xx x x ...
... What kind of ion is a reactive element on right hand side of PT - a nonmetal, likely to form? Bromine if it gains an electron, now Br-, a bromide ion Notice complete octet of electrons in outermost energy level xx x x ...
History of Atomic Theory
... the electrons travel • Electrons in the same shell are approx. the same distance from the ...
... the electrons travel • Electrons in the same shell are approx. the same distance from the ...
Name Date Class Chapter 6 – The Periodic Table Guided Reading
... the properties of other elements in the periodic table. It also describes the use of electron configurations to classify elements. As you read Chapter 6 Section 2 define the following words: Alkali metals – ...
... the properties of other elements in the periodic table. It also describes the use of electron configurations to classify elements. As you read Chapter 6 Section 2 define the following words: Alkali metals – ...
Atom
... Atoms are too small to describe with everyday units of mass (grams, kilograms). Scientists use units known as Atomic Mass Units (AMU) to describe the mass of atoms and its particles. A proton or neutron has a mass equal to about one amu ...
... Atoms are too small to describe with everyday units of mass (grams, kilograms). Scientists use units known as Atomic Mass Units (AMU) to describe the mass of atoms and its particles. A proton or neutron has a mass equal to about one amu ...
PERIODIC TRENDS PRACTICE QUIZ
... the periodic table. b. Upper right-hand corner of the periodic table. c. Lower left-hand corner of the periodic table. d. Upper left-hand corner of the periodic table. 8. Of the following elements, which one would have the smallest ionization energy? a. Neon b. Lithium c. Boron d. Nitrogen 9. As one ...
... the periodic table. b. Upper right-hand corner of the periodic table. c. Lower left-hand corner of the periodic table. d. Upper left-hand corner of the periodic table. 8. Of the following elements, which one would have the smallest ionization energy? a. Neon b. Lithium c. Boron d. Nitrogen 9. As one ...
Atomic Structure
... Electrons can be located in a specific energy level Gain energy to move to a higher energy level. Lose energy to move to a lower energy level. ...
... Electrons can be located in a specific energy level Gain energy to move to a higher energy level. Lose energy to move to a lower energy level. ...
The Periodic Table
... Electron affinity does not change greatly as we move down a group. Electron affinity should become more positive (less energy released). Reason: Moving down a group the average distance between the added electron and the nucleus steadily increases, causing the electron-nucleus attraction to decrease ...
... Electron affinity does not change greatly as we move down a group. Electron affinity should become more positive (less energy released). Reason: Moving down a group the average distance between the added electron and the nucleus steadily increases, causing the electron-nucleus attraction to decrease ...
PERIODIC TRENDS PRACTICE QUIZ
... the periodic table. b. Upper right-hand corner of the periodic table. c. Lower left-hand corner of the periodic table. d. Upper left-hand corner of the periodic table. 8. Of the following elements, which one would have the smallest ionization energy? a. Neon b. Lithium c. Boron d. Nitrogen 9. As one ...
... the periodic table. b. Upper right-hand corner of the periodic table. c. Lower left-hand corner of the periodic table. d. Upper left-hand corner of the periodic table. 8. Of the following elements, which one would have the smallest ionization energy? a. Neon b. Lithium c. Boron d. Nitrogen 9. As one ...
Atomic Theory
... Using this tube he was able to cause nonradioactive atoms to produce streams of negatively charge particles that were later found to be electrons. ...
... Using this tube he was able to cause nonradioactive atoms to produce streams of negatively charge particles that were later found to be electrons. ...
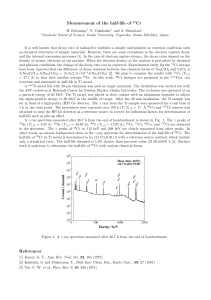
Measurement of the half-life of
... density of atomic electrons at the nucleus. When the electron density at the nucleus is perturbed by chemical and physical conditions, the change of the decay rate can be expected. Experimental study for the 51 Cr isotope have been reported that the difference of decay constant between two chemical f ...
... density of atomic electrons at the nucleus. When the electron density at the nucleus is perturbed by chemical and physical conditions, the change of the decay rate can be expected. Experimental study for the 51 Cr isotope have been reported that the difference of decay constant between two chemical f ...