ATOMIC STRUacad test
... B. Atoms of the same element are identical C. Atoms are made of protons and electrons D. Atoms unite in definite ratios to form compounds 4. Which of the following ideas is NOT retained in the current theory of atomic structure? A. Electrons can absorb or emit energy B. Atoms have a central, positiv ...
... B. Atoms of the same element are identical C. Atoms are made of protons and electrons D. Atoms unite in definite ratios to form compounds 4. Which of the following ideas is NOT retained in the current theory of atomic structure? A. Electrons can absorb or emit energy B. Atoms have a central, positiv ...
Atomic Theory
... the periodic table. They are arranged in increasing order going from left to right. So Hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, Helium is 2 and so on. • The atomic number tells us how many protons an atom has. This also tells us how many electrons an atom has, because the number of protons and electrons ...
... the periodic table. They are arranged in increasing order going from left to right. So Hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, Helium is 2 and so on. • The atomic number tells us how many protons an atom has. This also tells us how many electrons an atom has, because the number of protons and electrons ...
ppt - Discover Earth Science
... Each electron does not swarm around the nucleus randomly, rather electrons move in definite orbits around the nucleus These orbits are located at specific distances from the nucleus These orbits are called energy ...
... Each electron does not swarm around the nucleus randomly, rather electrons move in definite orbits around the nucleus These orbits are located at specific distances from the nucleus These orbits are called energy ...
Introductory Chemistry, 2nd Edition Nivaldo Tro
... Mass Number is Not the Same as Atomic Mass • Atomic mass (or Atomic Weight) is an experimental number determined from all naturally occurring isotopes • Mass number refers to the number of protons + neutrons in one isotope natural or man-made When given the relative abundance of all isotopes, we c ...
... Mass Number is Not the Same as Atomic Mass • Atomic mass (or Atomic Weight) is an experimental number determined from all naturally occurring isotopes • Mass number refers to the number of protons + neutrons in one isotope natural or man-made When given the relative abundance of all isotopes, we c ...
Chemical Element
... Bang nucleosynthesis during the first 20 minutes of the universe[9] in a ratio of around 3:1 by mass (approximately 12:1 by number of atoms). Almost all other elements found in nature, including some further hydrogen and helium created since then, were made by various natural or (at times) artificia ...
... Bang nucleosynthesis during the first 20 minutes of the universe[9] in a ratio of around 3:1 by mass (approximately 12:1 by number of atoms). Almost all other elements found in nature, including some further hydrogen and helium created since then, were made by various natural or (at times) artificia ...
Chemistry Chapter 5 (Due Nov
... ____ 39. As changes in energy levels of electrons increase, the frequencies of atomic line spectra they emit ____. a. increase c. remain the same b. decrease d. cannot be determined ____ 40. The atomic emission spectra of a sodium atom on Earth and of a sodium atom in the sun would be ____. a. the ...
... ____ 39. As changes in energy levels of electrons increase, the frequencies of atomic line spectra they emit ____. a. increase c. remain the same b. decrease d. cannot be determined ____ 40. The atomic emission spectra of a sodium atom on Earth and of a sodium atom in the sun would be ____. a. the ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun. ...
... electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun. ...
Physics 1425: General Physics I
... What Holds the Nucleus Together? • The nucleons have a strong but very short range attraction, called the nuclear force, it’s like a thin layer of glue around each nucleon. • The electrostatic repulsion is longer range, and so is more important in bigger nuclei, unlike the nuclear “glue”, which onl ...
... What Holds the Nucleus Together? • The nucleons have a strong but very short range attraction, called the nuclear force, it’s like a thin layer of glue around each nucleon. • The electrostatic repulsion is longer range, and so is more important in bigger nuclei, unlike the nuclear “glue”, which onl ...
Introducing Charge - Galileo and Einstein
... What Holds the Nucleus Together? • The nucleons have a strong but very short range attraction, called the nuclear force, it’s like a thin layer of glue around each nucleon. • The electrostatic repulsion is longer range, and so is more important in bigger nuclei, unlike the nuclear “glue”, which onl ...
... What Holds the Nucleus Together? • The nucleons have a strong but very short range attraction, called the nuclear force, it’s like a thin layer of glue around each nucleon. • The electrostatic repulsion is longer range, and so is more important in bigger nuclei, unlike the nuclear “glue”, which onl ...
Chapter 3 Section 1 Notes
... of matter that could not be cut. What did people think of Democritus? People did not believe Democritus because he had no evidence to support his theory. ...
... of matter that could not be cut. What did people think of Democritus? People did not believe Democritus because he had no evidence to support his theory. ...
Student Expectation
... Key Concept 1: During a chemical reaction, the atoms of substances rearrange themselves into a new configuration forming new substances. The reactants (or the energy and atoms or molecules of the original substance) combine to produce products (or the energy, atoms, and molecules of the new substanc ...
... Key Concept 1: During a chemical reaction, the atoms of substances rearrange themselves into a new configuration forming new substances. The reactants (or the energy and atoms or molecules of the original substance) combine to produce products (or the energy, atoms, and molecules of the new substanc ...
atomic
... contains most of the mass of the atom oThis nucleus is made up of particles called protons, which have a positive charge oThe protons are surrounded by negatively charged electrons, but most of the atom is ...
... contains most of the mass of the atom oThis nucleus is made up of particles called protons, which have a positive charge oThe protons are surrounded by negatively charged electrons, but most of the atom is ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 81. How many lone pairs of electrons are in the Lewis dot structure for H2O? 82. Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following: CO, CO2, N2, and O2. 83. Define intermolecular forces and intramolecular forces. 84. Define London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole attractions, and hydrogen bonding. 85. ...
... 81. How many lone pairs of electrons are in the Lewis dot structure for H2O? 82. Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following: CO, CO2, N2, and O2. 83. Define intermolecular forces and intramolecular forces. 84. Define London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole attractions, and hydrogen bonding. 85. ...
Warm-up #11 Jan. 25
... Bohr got closer than we had been so far, but it was still not right. He gave us the idea of energy levels for electrons. BUT his idea only worked for one atom ...
... Bohr got closer than we had been so far, but it was still not right. He gave us the idea of energy levels for electrons. BUT his idea only worked for one atom ...
The Periodic Table
... Said properties of unknown elements could be predicted by the properties of elements around the missing element ...
... Said properties of unknown elements could be predicted by the properties of elements around the missing element ...
The study of chemistry involves the linking up of the phenomena in
... This time he saw a red fluorescence in the tube as well as a green fluorescence. The green fluorescence was caused by electrons. The red glow was caused by rays which were deflected by magnetic and electric fields in the direction opposite to electrons. Thomson called these rays positive rays. The m ...
... This time he saw a red fluorescence in the tube as well as a green fluorescence. The green fluorescence was caused by electrons. The red glow was caused by rays which were deflected by magnetic and electric fields in the direction opposite to electrons. Thomson called these rays positive rays. The m ...
1st Semester Practice Test
... 73. What type of ions have names ending in -ide? a. only cations c. only metal ions b. only anions d. only gaseous ions 74. When Group 2A elements form ions, they __. a. lose two protons c. lose two electrons b. gain two protons d. gain two electrons 75. When naming a transition metal ...
... 73. What type of ions have names ending in -ide? a. only cations c. only metal ions b. only anions d. only gaseous ions 74. When Group 2A elements form ions, they __. a. lose two protons c. lose two electrons b. gain two protons d. gain two electrons 75. When naming a transition metal ...
What are atoms like???
... For example, the resistance of mercury suddenly drops at 268.8°C. This is called superconductivity. The temprature where it drops is called the critical temperature. There are two types of superconductor: Type 1: which are metals Type 2: which are alloys ...
... For example, the resistance of mercury suddenly drops at 268.8°C. This is called superconductivity. The temprature where it drops is called the critical temperature. There are two types of superconductor: Type 1: which are metals Type 2: which are alloys ...
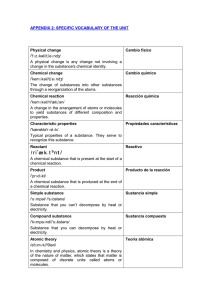
specific vocabulary of the unit
... infrared radiation from the surface and lower atmosphere from escaping into outer space. Climatic change Climate change is any long-term long change in the statistics of weather over durations ranging from decades to millions of years. It can be manifested manifest in changes to averages, extremes, ...
... infrared radiation from the surface and lower atmosphere from escaping into outer space. Climatic change Climate change is any long-term long change in the statistics of weather over durations ranging from decades to millions of years. It can be manifested manifest in changes to averages, extremes, ...
Parts of the Atom - centralscience10
... By the 1700s Chemists had gathered a lot of information about elements, however they still had many _____________________: o Why some elements gases and others are metals? o How many elements are there? o What relationships can be found between elements? ...
... By the 1700s Chemists had gathered a lot of information about elements, however they still had many _____________________: o Why some elements gases and others are metals? o How many elements are there? o What relationships can be found between elements? ...
ATOMIC MODEL
... · Democritus (about 470370 B.C.) thought that all forms of matter were finitely divisible into very small particles which cannot be divided further. He called these particles atoms.( atomos = indivisible in Greek) · Democritus idea was a speculative hypothesis which was not based on scientific ...
... · Democritus (about 470370 B.C.) thought that all forms of matter were finitely divisible into very small particles which cannot be divided further. He called these particles atoms.( atomos = indivisible in Greek) · Democritus idea was a speculative hypothesis which was not based on scientific ...
Chapter Twelve: Atoms and the Periodic Table
... • Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. • Mendeleev used the properties of existing elements to predict properties of undiscovered elements. • The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual prope ...
... • Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. • Mendeleev used the properties of existing elements to predict properties of undiscovered elements. • The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual prope ...