![The atom: Isotopes (Grade 10) [NCS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016109524_1-1437871a54cd24e5ee13c27e98f0719d-300x300.png)
Nucleon number
... Define relative atomic mass and relative molecular mass based on the C-12 scale. Sketch and explain the function of the following main components of a simple mass spectrum: Analyze mass spectrum of an element. Name cations, anions and salt according to the ...
... Define relative atomic mass and relative molecular mass based on the C-12 scale. Sketch and explain the function of the following main components of a simple mass spectrum: Analyze mass spectrum of an element. Name cations, anions and salt according to the ...
Slide 1
... that a sixth quark existed. However, it took a team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton collisions performed shows a presence of a sixth q ...
... that a sixth quark existed. However, it took a team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton collisions performed shows a presence of a sixth q ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE - New York Science Teacher
... THE QUANTUM MODEL After viewing the video we see that Erwin Schrodinger allows us to describe the electrons in an atom with a set of 4 Quantum Numbers. • The quantum numbers help us to describe the relative energies and probable locations of the electrons. •The Principal Quantum Number (n) – corres ...
... THE QUANTUM MODEL After viewing the video we see that Erwin Schrodinger allows us to describe the electrons in an atom with a set of 4 Quantum Numbers. • The quantum numbers help us to describe the relative energies and probable locations of the electrons. •The Principal Quantum Number (n) – corres ...
Mileposts on the road to the atom (download)
... Experimentally mass could be measured Without knowledge of atomic mass, impossible to know how many atoms of one element combines with another Essential to know number of atoms to understand chemistry Atomic weight scale, enabled by Avogadro’s hypothesis, provides link between experimental observabl ...
... Experimentally mass could be measured Without knowledge of atomic mass, impossible to know how many atoms of one element combines with another Essential to know number of atoms to understand chemistry Atomic weight scale, enabled by Avogadro’s hypothesis, provides link between experimental observabl ...
The Atom
... – Changes in matter result from changes in groupings of atoms, and not changes in the atoms themselves ...
... – Changes in matter result from changes in groupings of atoms, and not changes in the atoms themselves ...
Homework Packet - Chemistry from AZ
... • The Periodic Law Periodic Law states that the properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. In other words, when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, the properties of the elements repeat regularly. ...
... • The Periodic Law Periodic Law states that the properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. In other words, when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, the properties of the elements repeat regularly. ...
3.1 The Atom: From Philosophical Idea to Theory
... Isotopes…Again (must be on the test) Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses due to varying numbers of neutrons. Isotope ...
... Isotopes…Again (must be on the test) Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses due to varying numbers of neutrons. Isotope ...
Chapter 3
... Isotopes…Again (must be on the test) Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses due to varying numbers of neutrons. Isotope ...
... Isotopes…Again (must be on the test) Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses due to varying numbers of neutrons. Isotope ...
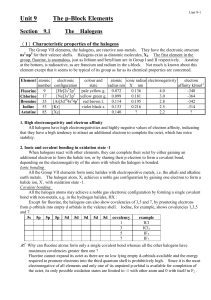
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
... (1)Characteristic properties of the halogens The Group VII elements, the halogens, are reactive non-metals. They have the electronic structure ns2 np5 for their valence shells. Halogens exist as diatomic molecules, X2. The first element in the group, fluorine, is anomalous, just as lithium and beryl ...
... (1)Characteristic properties of the halogens The Group VII elements, the halogens, are reactive non-metals. They have the electronic structure ns2 np5 for their valence shells. Halogens exist as diatomic molecules, X2. The first element in the group, fluorine, is anomalous, just as lithium and beryl ...
powerpoint - Charles Best Library
... The atomic theory of matter was first proposed by Leucippus, a Greek philosopher who lived at around 400BC. At this time the Greeks were trying to understand the way matter is made. According to Anassagora, it is possible to subdivide matter in smaller and smaller parts, and he proposed that this pr ...
... The atomic theory of matter was first proposed by Leucippus, a Greek philosopher who lived at around 400BC. At this time the Greeks were trying to understand the way matter is made. According to Anassagora, it is possible to subdivide matter in smaller and smaller parts, and he proposed that this pr ...
SCH 3U - othsmath
... 2) Going down a group, a new energy level is added with each subsequent atom, ensuring the valence electrons are moved further and further from the nucleus. This increases the shielding provided by non-valence electrons, decreases the ENC (even though the number of protons in the nucleus is increasi ...
... 2) Going down a group, a new energy level is added with each subsequent atom, ensuring the valence electrons are moved further and further from the nucleus. This increases the shielding provided by non-valence electrons, decreases the ENC (even though the number of protons in the nucleus is increasi ...
atoms
... One atom says to the other, “Hey! I think I lost an electron!” The other says, “Are you sure??” “Yes, I’m positive!” ...
... One atom says to the other, “Hey! I think I lost an electron!” The other says, “Are you sure??” “Yes, I’m positive!” ...
Chapter 16 Physical Science The Periodic Table Parts of an Atom
... The number of Neutrons in an atom will sometimes vary, that’s why the atomic mass of the elements is not an even number. For Hydrogen, the mass is 1.008. Most atoms of Hydrogen have 0 neutrons, but some have 1 neutron and a very very few will have 2 neutrons. When you “weigh” trillions of Hydrogen a ...
... The number of Neutrons in an atom will sometimes vary, that’s why the atomic mass of the elements is not an even number. For Hydrogen, the mass is 1.008. Most atoms of Hydrogen have 0 neutrons, but some have 1 neutron and a very very few will have 2 neutrons. When you “weigh” trillions of Hydrogen a ...
Nature of Atoms Atomic Structure Atomic number Atomic mass
... together in a stable association Compounds are molecules containing yp of element more than one type Atoms are held together in molecules or compounds by chemical bonds ...
... together in a stable association Compounds are molecules containing yp of element more than one type Atoms are held together in molecules or compounds by chemical bonds ...
File
... Mendeleev was born in Siberia, Russia in the year 1834. He died in 1907 He was a professor of Chemistry at the St. Petersburg University. Trying to explain to his students how elements had similar properties, he started organizing the elements into rows and columns He observed that some elements hav ...
... Mendeleev was born in Siberia, Russia in the year 1834. He died in 1907 He was a professor of Chemistry at the St. Petersburg University. Trying to explain to his students how elements had similar properties, he started organizing the elements into rows and columns He observed that some elements hav ...
Unit 1 – Physical Science and Chemical Reactions
... This work led one of Rutherford’s students (H. G. Mosely) to discover that the positive charge inside the nucleus increased by one from element to element in Mendeleev’s periodic table. From this he coined the phrase atomic number (the number of protons inside the nucleus of an atom). This disco ...
... This work led one of Rutherford’s students (H. G. Mosely) to discover that the positive charge inside the nucleus increased by one from element to element in Mendeleev’s periodic table. From this he coined the phrase atomic number (the number of protons inside the nucleus of an atom). This disco ...
Atomic theory.notebook
... • Neils Bohr – proposed quantum model of the atom • Electrons move about the atom in circular paths of specific energies • Termed these paths energy levels • Later determined to be fundamentally incorrect ...
... • Neils Bohr – proposed quantum model of the atom • Electrons move about the atom in circular paths of specific energies • Termed these paths energy levels • Later determined to be fundamentally incorrect ...
1 Notes Ch. 4 and 25: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry
... • In 1919 Rutherford was the first to induce (_____________________) transmutation. • He proved that nuclear reactions can be produced __________________________. • Induced transmutation can occur by ______________________an atom with alpha particles, protons or neutrons. III. Transuranium Elements ...
... • In 1919 Rutherford was the first to induce (_____________________) transmutation. • He proved that nuclear reactions can be produced __________________________. • Induced transmutation can occur by ______________________an atom with alpha particles, protons or neutrons. III. Transuranium Elements ...
File - Rogers` Honors Chemistry
... 1906 received Nobel Prize for physics for his research into the electrical conductivity of gases. Thomson was a great teacher and an outstanding scientist. Seven of his students and assistants also received Nobel Prizes ...
... 1906 received Nobel Prize for physics for his research into the electrical conductivity of gases. Thomson was a great teacher and an outstanding scientist. Seven of his students and assistants also received Nobel Prizes ...
Catalyst
... • 1.6 – I can explain the development of atomic theory incorporating the contributions of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr. • 1.7 – I can define electronegativity and explain how it relates to the charge of the nucleus and the electron. Furthermore, I can explain how this trend changes as you m ...
... • 1.6 – I can explain the development of atomic theory incorporating the contributions of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr. • 1.7 – I can define electronegativity and explain how it relates to the charge of the nucleus and the electron. Furthermore, I can explain how this trend changes as you m ...
Bohr Models - Athena Chemistry
... 1. What is the advantage to using the Bohr model as opposed to the Lewis model? a. The Bohr model provides more information than the Lewis model. b. The Bohr model is less bulky than the Lewis model. c. The Bohr model shows the valence electrons. d. The Bohr model shows how many bonds atoms of an el ...
... 1. What is the advantage to using the Bohr model as opposed to the Lewis model? a. The Bohr model provides more information than the Lewis model. b. The Bohr model is less bulky than the Lewis model. c. The Bohr model shows the valence electrons. d. The Bohr model shows how many bonds atoms of an el ...
history of atomic theory (ending with Dalton)
... • Atoms of different elements have different masses and properties. • Atoms only combine in small, whole number ratios such as 1:1, 1:2, 2:3, etc. • Chemical reactions are the rearrangements of atoms. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
... • Atoms of different elements have different masses and properties. • Atoms only combine in small, whole number ratios such as 1:1, 1:2, 2:3, etc. • Chemical reactions are the rearrangements of atoms. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
No Slide Title
... An element is a substance whose atoms all have the same atomic number. The neutron is a nuclear particle having a mass almost identical to that of a proton, but no electric charge. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus. A nuclide is an atom characterized by a defi ...
... An element is a substance whose atoms all have the same atomic number. The neutron is a nuclear particle having a mass almost identical to that of a proton, but no electric charge. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus. A nuclide is an atom characterized by a defi ...
Part a
... Electrical energy—results from movement of charged particles Mechanical energy—directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic energy—exhibits wavelike properties (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
... Electrical energy—results from movement of charged particles Mechanical energy—directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic energy—exhibits wavelike properties (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...