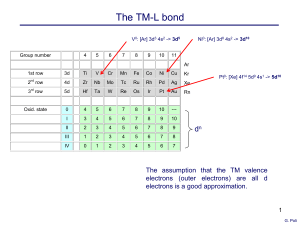
Unit B review - mvhs
... (A) A, B, and C will decrease. (B) A, B, and C will increase. (C) A will increase, B and C will decrease. (D) A and B will increase, C will decrease. (E) A will decrease, B and C will increase. 15. In any one period of the periodic table, the element in Group I, as compared to the element in Group V ...
... (A) A, B, and C will decrease. (B) A, B, and C will increase. (C) A will increase, B and C will decrease. (D) A and B will increase, C will decrease. (E) A will decrease, B and C will increase. 15. In any one period of the periodic table, the element in Group I, as compared to the element in Group V ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... A. These are forces or attractions between molecules of solids or liquids mainly, but can be gases too. B. They vary in strength; but are generally weaker than chemical bonds, as there is no real physical interaction like there are in bonds…hence the term forces. C. These forces usually affect the b ...
... A. These are forces or attractions between molecules of solids or liquids mainly, but can be gases too. B. They vary in strength; but are generally weaker than chemical bonds, as there is no real physical interaction like there are in bonds…hence the term forces. C. These forces usually affect the b ...
General Chemistry
... size of hydrogen relative to other atoms and molecules, the resulting charge, though only partial, nevertheless represents a large charge density. A hydrogen bond results when this strong positive charge density attracts a lone pair of electrons on another heteroatom, which becomes the hydrogen-bond ...
... size of hydrogen relative to other atoms and molecules, the resulting charge, though only partial, nevertheless represents a large charge density. A hydrogen bond results when this strong positive charge density attracts a lone pair of electrons on another heteroatom, which becomes the hydrogen-bond ...
Final Study Questions - Porterville College Home
... mass 60Ni atom = 59.930789 amu mass proton = 1.007276 amu mass neutron = 1.008665 amu 65. Which of the following compounds exhibit geometric isomers? I. Pt(NH3)2Cl2 (square planar) II. [Co(H2O)2]Cl3 III. Ni(NH3)4(NO2)2 IV. K2[CoCl4] 66. Explain why copper(I) complexes would be expected to be colorle ...
... mass 60Ni atom = 59.930789 amu mass proton = 1.007276 amu mass neutron = 1.008665 amu 65. Which of the following compounds exhibit geometric isomers? I. Pt(NH3)2Cl2 (square planar) II. [Co(H2O)2]Cl3 III. Ni(NH3)4(NO2)2 IV. K2[CoCl4] 66. Explain why copper(I) complexes would be expected to be colorle ...
lecture1 - Unaab.edu.ng
... • The second-(4d) and third-row (5d) transition metal ions prefer higher oxidation states (e.g. Mo(VI)), and require electronegative ligands for stability (hard ligands such as F-or O2-). (ii) Coordination numbers and preferred geometries Coordination preferences of the transition metals depend on t ...
... • The second-(4d) and third-row (5d) transition metal ions prefer higher oxidation states (e.g. Mo(VI)), and require electronegative ligands for stability (hard ligands such as F-or O2-). (ii) Coordination numbers and preferred geometries Coordination preferences of the transition metals depend on t ...
The Synthesis and Color of trans-Dichlorobis
... Isomers are substances that have the same chemical formula, but are different compounds; i.e., each has its own set of physical and chemical properties. Each of the above pictured isomers has the chemical formula CoCl2C4H16N4+ and yet the trans form is distinctly different than the cis form, as can ...
... Isomers are substances that have the same chemical formula, but are different compounds; i.e., each has its own set of physical and chemical properties. Each of the above pictured isomers has the chemical formula CoCl2C4H16N4+ and yet the trans form is distinctly different than the cis form, as can ...
Document
... one half as strong as the real cubic field. It should also be noted that the crystal field splitting in a tetrahedral symmetry is intrinsically smaller than in the octahedral symmetry as only four (instead of six) ligands interact with the metal ion. Approximately,: t = 4/9 o. This favors high spi ...
... one half as strong as the real cubic field. It should also be noted that the crystal field splitting in a tetrahedral symmetry is intrinsically smaller than in the octahedral symmetry as only four (instead of six) ligands interact with the metal ion. Approximately,: t = 4/9 o. This favors high spi ...
LFSE_ Studies_Cr_Complexes
... The d orbitals of a metal ion in an octahedral crystal field (surrounded by an octahedral array of ligands) are split into a higher energy eg set and a lower energy t2g. The energy difference between the upper and lower energy levels is designated as Δo or, in the older literature, as 10Dq. The degr ...
... The d orbitals of a metal ion in an octahedral crystal field (surrounded by an octahedral array of ligands) are split into a higher energy eg set and a lower energy t2g. The energy difference between the upper and lower energy levels is designated as Δo or, in the older literature, as 10Dq. The degr ...
Stability of Transition Metal Complexes
... but here NH3 and en (H2NCH2CH2NH2) are very similar to one another so ∆H is unlikely to vary much What about the other term in the equilibrium equation? Will ∆S change much in the reaction shown above? • Yes, we are going from a total of 3 particles to 5 as we displace two NH3 for every en. This is ...
... but here NH3 and en (H2NCH2CH2NH2) are very similar to one another so ∆H is unlikely to vary much What about the other term in the equilibrium equation? Will ∆S change much in the reaction shown above? • Yes, we are going from a total of 3 particles to 5 as we displace two NH3 for every en. This is ...
3 Principles of Structure and Symmetry
... The equations (3.12), (3.13) and (3.16) now allow us to construct a 3-dimensional depiction of the wave functions for n = 1, 2 and 3. Let’s begin with the spherical s-orbitals. 1s has no radial zero points, 2s has one, and 3s has two. We will depict a cross-section of the orbitals (for example z = 0 ...
... The equations (3.12), (3.13) and (3.16) now allow us to construct a 3-dimensional depiction of the wave functions for n = 1, 2 and 3. Let’s begin with the spherical s-orbitals. 1s has no radial zero points, 2s has one, and 3s has two. We will depict a cross-section of the orbitals (for example z = 0 ...
Transition Chemistry
... to form molecular orbitals, and hybrization (or hybrid orbitals) results. While important, this theory fails to give insight into the colors of coordination compounds and their magnetic properties. Instead, we turn to crystal field theory, which highlights the effects on the d-orbital energies of th ...
... to form molecular orbitals, and hybrization (or hybrid orbitals) results. While important, this theory fails to give insight into the colors of coordination compounds and their magnetic properties. Instead, we turn to crystal field theory, which highlights the effects on the d-orbital energies of th ...
4 Principles of Structure and Symmetry
... The equations (4.12), (4.13) and (4.16) now allow us to construct a 3-dimensional depiction of the wave functions for n = 1, 2 and 3. Let’s begin with the spherical s-orbitals. 1s has no radial zero points, 2s has one, and 3s has two. We will depict a cross-section of the orbitals (for example z = 0 ...
... The equations (4.12), (4.13) and (4.16) now allow us to construct a 3-dimensional depiction of the wave functions for n = 1, 2 and 3. Let’s begin with the spherical s-orbitals. 1s has no radial zero points, 2s has one, and 3s has two. We will depict a cross-section of the orbitals (for example z = 0 ...
2.4 Examples 2.4.1 Nuclei of Low Abundance: Satellite Spectra To
... paramagnetic shielding term is not only restricted to quadrupolar nuclei. Any species with low energy paramagnetic excited states can exhibit this effect. Thus 103Rh (I = ½ ) also has a very wide chemical shift range for the same reason. Finally, consider the table of data below. This illustrates on ...
... paramagnetic shielding term is not only restricted to quadrupolar nuclei. Any species with low energy paramagnetic excited states can exhibit this effect. Thus 103Rh (I = ½ ) also has a very wide chemical shift range for the same reason. Finally, consider the table of data below. This illustrates on ...
chemistry of transition elements
... though some of them are rather inert in this respect. Most of them show more than one oxidation state (variable valence). Because of partly filled d orbitals some transition metal ions containing odd number of electrons form paramagnetic compounds. They have unparallel tendency to form coordination ...
... though some of them are rather inert in this respect. Most of them show more than one oxidation state (variable valence). Because of partly filled d orbitals some transition metal ions containing odd number of electrons form paramagnetic compounds. They have unparallel tendency to form coordination ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... Chemistry Midterm Exam Review 2013 These are topics from a traditional 1st quarter. If you used the thematic approach with me this year, you will notice that the topics are not in order of their presentation throughout the year. The final exam is cumulative so this review will help you with reviewin ...
... Chemistry Midterm Exam Review 2013 These are topics from a traditional 1st quarter. If you used the thematic approach with me this year, you will notice that the topics are not in order of their presentation throughout the year. The final exam is cumulative so this review will help you with reviewin ...
2H + CO3 H2CO3 H2O + CO2(g) H3N Co H3N NH3 OH2 Cl Cl H3N
... However in the "trigonal prism" structure all the Me groups are equivalent, so this is consistent with the NMR data. In both cases it is useful to consider a C2 axis that includes Zr and bisects the dppe CH2CH2 backbone. 2. (a) [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl cis and trans isomers for the cation; 6-coordinate, octa ...
... However in the "trigonal prism" structure all the Me groups are equivalent, so this is consistent with the NMR data. In both cases it is useful to consider a C2 axis that includes Zr and bisects the dppe CH2CH2 backbone. 2. (a) [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl cis and trans isomers for the cation; 6-coordinate, octa ...
Coordination Chemistry and Organo Metallics
... The constituent is not retained in solutions. For example NiCl 2 4NH3 is stable in solid state as well as in aqueous solution. Its aqueous solution does not give test for Ni ++ or Cl- and NH4. It is also defined as a compound which contains a complex ion. (i) Complex ion d-block elements or their i ...
... The constituent is not retained in solutions. For example NiCl 2 4NH3 is stable in solid state as well as in aqueous solution. Its aqueous solution does not give test for Ni ++ or Cl- and NH4. It is also defined as a compound which contains a complex ion. (i) Complex ion d-block elements or their i ...
Investigation of Nickel and Copper Coordination Complexes
... Typically, as ligand is added to the solution of metal ion, ML is formed first. As the addition of ligand is continued, the ML2 concentration rises, while the ML concentration drops. Then ML3 becomes dominant with ML and ML2 becoming unimportant. This process continues until the highest complex, ML6 ...
... Typically, as ligand is added to the solution of metal ion, ML is formed first. As the addition of ligand is continued, the ML2 concentration rises, while the ML concentration drops. Then ML3 becomes dominant with ML and ML2 becoming unimportant. This process continues until the highest complex, ML6 ...
C - Upton-by-Chester High School
... Ionic compounds are held together by many strong electrostatic attractions or attractions between oppositely charged ions(1) Lots energy is needed to overcome them (1) (no mention of molecules!) c) Metals have quite high melting and boiling points. Metals are held together by many strong electrostat ...
... Ionic compounds are held together by many strong electrostatic attractions or attractions between oppositely charged ions(1) Lots energy is needed to overcome them (1) (no mention of molecules!) c) Metals have quite high melting and boiling points. Metals are held together by many strong electrostat ...
Reaction mechanism of Coordination Complexes
... Reaction mechanism of Coordination Complexes Complexes are classified as Inert and Labile ( kinetic stability) depending on their reactivity. According to Henry Taube, a Nobel Laureate, the definition is ...
... Reaction mechanism of Coordination Complexes Complexes are classified as Inert and Labile ( kinetic stability) depending on their reactivity. According to Henry Taube, a Nobel Laureate, the definition is ...
To do List - kurtniedenzu
... 1. He configuration - 1st five elements - often show tendency to form dative bonds. 2. Odd number of valence electrons (often form free radicals) First two cases are rare; third case is more common. 3. Central atom holds more than 8 electrons. Not found in second series elements because they don't h ...
... 1. He configuration - 1st five elements - often show tendency to form dative bonds. 2. Odd number of valence electrons (often form free radicals) First two cases are rare; third case is more common. 3. Central atom holds more than 8 electrons. Not found in second series elements because they don't h ...
Jahn–Teller effect
-3D-balls.png?width=300)
The Jahn–Teller effect, sometimes also known as Jahn–Teller distortion, describes the geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that is associated with certain electron configurations. This electronic effect is named after Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, who proved, using group theory, that orbital nonlinear spatially degenerate molecules cannot be stable. The Jahn–Teller theorem essentially states that any nonlinear molecule with a spatially degenerate electronic ground state will undergo a geometrical distortion that removes that degeneracy, because the distortion lowers the overall energy of the species. For a description of another type of geometrical distortion that occurs in crystals with substitutional impurities see article off-center ions.