File
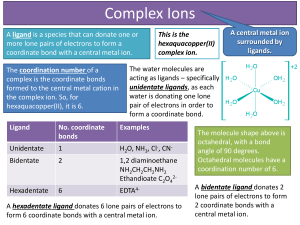
... Complex Ions A ligand is a species that can donate one or more lone pairs of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. The coordination number of a complex is the coordinate bonds formed to the central metal cation in the complex ion. So, for hexaquacopper(II), it is 6. ...
... Complex Ions A ligand is a species that can donate one or more lone pairs of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. The coordination number of a complex is the coordinate bonds formed to the central metal cation in the complex ion. So, for hexaquacopper(II), it is 6. ...
Chapter 8
... 1.6 and 2.0, their identities have to be considered. If a metal is involved, it will be deemed ionic. If 2 non-metals are bonded, it will be considered polar-covalent. ...
... 1.6 and 2.0, their identities have to be considered. If a metal is involved, it will be deemed ionic. If 2 non-metals are bonded, it will be considered polar-covalent. ...
Coordination Compounds: Chemistry and Application
... tetramminecopper(II), [Cu(NH3)4]2+, there are four nitrogen atoms from the NH3 molecules each bonded to Cu2+. Hexachloroplatinate(IV), [PtCl6]2-, is an example of an anion with a coordination number of six. Oxidation Numbers of Coordination Complexes The net charge on the coordination complex resul ...
... tetramminecopper(II), [Cu(NH3)4]2+, there are four nitrogen atoms from the NH3 molecules each bonded to Cu2+. Hexachloroplatinate(IV), [PtCl6]2-, is an example of an anion with a coordination number of six. Oxidation Numbers of Coordination Complexes The net charge on the coordination complex resul ...
Class 26: Calculating Electronic contribution to specific heat
... While it is indeed an improvement, the Drude-Sommerfeld model is still only a free electron model. There are no features in the model to enable it explain anisotropy in material properties. The parameter , the number of free electrons per unit volume, is the same regardless of direction, therefore d ...
... While it is indeed an improvement, the Drude-Sommerfeld model is still only a free electron model. There are no features in the model to enable it explain anisotropy in material properties. The parameter , the number of free electrons per unit volume, is the same regardless of direction, therefore d ...
chp 5 notes outline
... • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s _________ is concentrated in the ______________, and _______________ move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were __________ around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why ____________ charged electrons aren’t _____________ i ...
... • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s _________ is concentrated in the ______________, and _______________ move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were __________ around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why ____________ charged electrons aren’t _____________ i ...
Introduction to Magnetochemistry
... Magnetochemistry is the study of the magnetic properties of materials. By "magnetic properties" we mean not only whether a material will make a good bar magnet, but whether it will be attracted or repelled by a magnet. This includes synthesis, analysis and understanding. This short description is me ...
... Magnetochemistry is the study of the magnetic properties of materials. By "magnetic properties" we mean not only whether a material will make a good bar magnet, but whether it will be attracted or repelled by a magnet. This includes synthesis, analysis and understanding. This short description is me ...
Inorganic Chemistry (SCQF level 7)
... This Unit allows candidates to develop knowledge and understanding of Inorganic Chemistry within the contexts of electromagnetic radiation, atomic spectroscopy, shapes of atomic orbitals, electronic configurations, patterns in the Periodic Table, shapes of molecules and polyatomic ions and some chem ...
... This Unit allows candidates to develop knowledge and understanding of Inorganic Chemistry within the contexts of electromagnetic radiation, atomic spectroscopy, shapes of atomic orbitals, electronic configurations, patterns in the Periodic Table, shapes of molecules and polyatomic ions and some chem ...
Topic 6 Coordination Compounds Coordination Chemistry
... Charge on the metal (oxidation state) For first row transition elements DO varies from about 7,500 cm–1 to 12,500 cm–1 for divalent ions, and 14,000 cm–1 to 25,000 cm –1 for trivalent ions. Position in a group values for analogous complexes of metal ions in a group increases by 25% to 50% going from ...
... Charge on the metal (oxidation state) For first row transition elements DO varies from about 7,500 cm–1 to 12,500 cm–1 for divalent ions, and 14,000 cm–1 to 25,000 cm –1 for trivalent ions. Position in a group values for analogous complexes of metal ions in a group increases by 25% to 50% going from ...
in English
... mechanisms explaining the diversity of the reaction paths of alkylgallium complexes oxygenation were proposed. Moreover, the interesting results have been received for the oxygenation reactions of alkylaluminum derivatives with methyl ester of 2-pyrrolocarboxylic acid (metpyrrol-H) ligand. The final ...
... mechanisms explaining the diversity of the reaction paths of alkylgallium complexes oxygenation were proposed. Moreover, the interesting results have been received for the oxygenation reactions of alkylaluminum derivatives with methyl ester of 2-pyrrolocarboxylic acid (metpyrrol-H) ligand. The final ...
Introduction to Computational Chemistry
... from the province of a small nucleus of theoretical work to a large, significant component of scientific research. By virtue of the great flexibility and power of electronic computers, basic principles of classical and quantum mechanics are now implemented in a form which can handle the many-body pr ...
... from the province of a small nucleus of theoretical work to a large, significant component of scientific research. By virtue of the great flexibility and power of electronic computers, basic principles of classical and quantum mechanics are now implemented in a form which can handle the many-body pr ...
Crystalline Carbon and Silicon: Covalent or Ionic?
... protect themselves first; thus, there are no electrons on the axis between any two atoms in the perfect crystal. The “bonding” in the MCAS model would be described as “ionic”. Electrostatics of such bonds have been present elsewhere.15 In the sp3-QM model, each sp3 orbital is independent of the othe ...
... protect themselves first; thus, there are no electrons on the axis between any two atoms in the perfect crystal. The “bonding” in the MCAS model would be described as “ionic”. Electrostatics of such bonds have been present elsewhere.15 In the sp3-QM model, each sp3 orbital is independent of the othe ...
Chem 241 Sample Questions Exam #3 Transition Metal Bonding 1
... 3. Determine the bond order for Ni(NH3)62+ and for Cr(NH3)62+. They have the same MO diagram but differ in their number of electrons. ...
... 3. Determine the bond order for Ni(NH3)62+ and for Cr(NH3)62+. They have the same MO diagram but differ in their number of electrons. ...
CHM 411 PART C PHYSICAL TECHNIQUES IN INORGANIC
... of structures in terms of features such as bond lengths and angles relative positions of ions and molecules in a unit cell. Structural data obtained are useful in interpretation of ionic and atomic radii useful in prediction of structures and trends in many properties. X-RAY DIFFRACTION:Diffraction ...
... of structures in terms of features such as bond lengths and angles relative positions of ions and molecules in a unit cell. Structural data obtained are useful in interpretation of ionic and atomic radii useful in prediction of structures and trends in many properties. X-RAY DIFFRACTION:Diffraction ...
chapter 24
... !Fe is used to make steel and stainless steel !Ti is used to make lightweight alloys !Transition metal compounds are used as pigments ...
... !Fe is used to make steel and stainless steel !Ti is used to make lightweight alloys !Transition metal compounds are used as pigments ...
No Slide Title
... Group 8A Elements (ns2np6, n 2) Completely filled ns and np subshells. Highest ionization energy of all elements. No tendency to accept extra electrons. ...
... Group 8A Elements (ns2np6, n 2) Completely filled ns and np subshells. Highest ionization energy of all elements. No tendency to accept extra electrons. ...
1st Semester Practice Test
... 61. Each period in the periodic table corresponds to __. a. a principal energy level c. an orbital b. an energy sublevel d. a suborbital 62. The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic __. a. mass c. number b. charge d. radius 63. To what category of elements do ...
... 61. Each period in the periodic table corresponds to __. a. a principal energy level c. an orbital b. an energy sublevel d. a suborbital 62. The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic __. a. mass c. number b. charge d. radius 63. To what category of elements do ...
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Linear M--X
... primarily in the region of the zone center but that of the z band in the region of the zone edge. The xz orbital of ML3 interacts with the x orbital of X leading to 7~ bands and likewise for yz and y. Since the two sets of T bands are equivalent, we will only consider the T bands obtained from yz an ...
... primarily in the region of the zone center but that of the z band in the region of the zone edge. The xz orbital of ML3 interacts with the x orbital of X leading to 7~ bands and likewise for yz and y. Since the two sets of T bands are equivalent, we will only consider the T bands obtained from yz an ...
2011 Midterm 1 KEY
... NH3 is a stronger field ligand than water so replacement of the z axis waters with NH3 will cause greater repulsion in the z direction than in the (still equivalent) x and y. This splits the eg set with dx2-y2 lower than dz2 and it also splits the t2g set with dxy lower than either dxz or dyz: ...
... NH3 is a stronger field ligand than water so replacement of the z axis waters with NH3 will cause greater repulsion in the z direction than in the (still equivalent) x and y. This splits the eg set with dx2-y2 lower than dz2 and it also splits the t2g set with dxy lower than either dxz or dyz: ...
Lecture 9
... Transition elements: the theories I PHYSICAL PROPERTIES The physical properties are dominated by the fact that the electrons with the highest energies go into an inner 3d orbital rather than the outer 4s orbital. These electrons in an underlying d orbital increase the electron repulsion on the outer ...
... Transition elements: the theories I PHYSICAL PROPERTIES The physical properties are dominated by the fact that the electrons with the highest energies go into an inner 3d orbital rather than the outer 4s orbital. These electrons in an underlying d orbital increase the electron repulsion on the outer ...
5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II
... As with the σ interaction, the (M-Lπ)* interaction for the d-orbitals is de-stabilizing and the metal-based orbital is destablized by eπ, whereas the Lπ ligands are stabilized by eπ. The same case occurs for a ligand possessing a δ orbital, with the only difference being an energy of stabilization ...
... As with the σ interaction, the (M-Lπ)* interaction for the d-orbitals is de-stabilizing and the metal-based orbital is destablized by eπ, whereas the Lπ ligands are stabilized by eπ. The same case occurs for a ligand possessing a δ orbital, with the only difference being an energy of stabilization ...
Jahn–Teller effect
-3D-balls.png?width=300)
The Jahn–Teller effect, sometimes also known as Jahn–Teller distortion, describes the geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that is associated with certain electron configurations. This electronic effect is named after Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, who proved, using group theory, that orbital nonlinear spatially degenerate molecules cannot be stable. The Jahn–Teller theorem essentially states that any nonlinear molecule with a spatially degenerate electronic ground state will undergo a geometrical distortion that removes that degeneracy, because the distortion lowers the overall energy of the species. For a description of another type of geometrical distortion that occurs in crystals with substitutional impurities see article off-center ions.