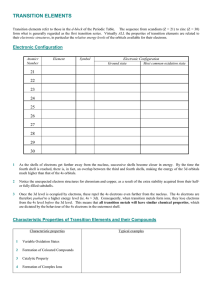
TRANSITION ELEMENTS
... As the shells of electrons get further away from the nucleus, successive shells become closer in energy. By the time the fourth shell is reached, there is, in fact, an overlap between the third and fourth shells, making the energy of the 3d orbitals much higher than that of the 4s orbitals. ...
... As the shells of electrons get further away from the nucleus, successive shells become closer in energy. By the time the fourth shell is reached, there is, in fact, an overlap between the third and fourth shells, making the energy of the 3d orbitals much higher than that of the 4s orbitals. ...
Demonstrating the style for the Journal of Physics - HAL
... sections of the order of the kbarn per target electron for highly charged ions in the present energy range. As noted previously, a thin crystal is a very dense electron target and, thus, these processes can be studied with very good statistics and used to characterize the electron gas sampled by cha ...
... sections of the order of the kbarn per target electron for highly charged ions in the present energy range. As noted previously, a thin crystal is a very dense electron target and, thus, these processes can be studied with very good statistics and used to characterize the electron gas sampled by cha ...
Review topics-blog
... (e.g. you might recall the ground state electron configuration of carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p2). ...
... (e.g. you might recall the ground state electron configuration of carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p2). ...
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
... How are nuclear reactions different from chemical reactions? ...
... How are nuclear reactions different from chemical reactions? ...
Chemistry 1 Revision: Metals and their uses
... on the l................. and c..................., non-metals are found on the r................ of the P...................... T.................... Elements in the same g.................... have similar p......................... because they have the same number of e............................ ...
... on the l................. and c..................., non-metals are found on the r................ of the P...................... T.................... Elements in the same g.................... have similar p......................... because they have the same number of e............................ ...
Chapter 2 BIO 100 Chemistry
... • Covalent bond between two atoms of the same element is always nonpolar. •A covalent bond between atoms that have similar electronegativities is also nonpolar. •Because carbon and hydrogen do not differ greatly in electronegativities, the bonds of CH4 are nonpolar. ...
... • Covalent bond between two atoms of the same element is always nonpolar. •A covalent bond between atoms that have similar electronegativities is also nonpolar. •Because carbon and hydrogen do not differ greatly in electronegativities, the bonds of CH4 are nonpolar. ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... from 1 mol of gaseous atoms/ions. Factors include proton number; shielding by inner shells (hence the effective nuclear charge is less than the proton number); distance of outermost electron from the nucleus. Hence I.E. increases across a period and decreases down a group. Slight decreases: from Gp ...
... from 1 mol of gaseous atoms/ions. Factors include proton number; shielding by inner shells (hence the effective nuclear charge is less than the proton number); distance of outermost electron from the nucleus. Hence I.E. increases across a period and decreases down a group. Slight decreases: from Gp ...
Microsymposia - IUCr Journals
... This presentation intends to point out some recent achievements in the field of photoswitchable high spin molecules. These compounds might be viewed as Photo-Magnetic Molecular Devices (PMMDs) devoted to molecular spintronics. Results have been firstly obtained on a polynuclear complex, Mo(IV)Cu(II) ...
... This presentation intends to point out some recent achievements in the field of photoswitchable high spin molecules. These compounds might be viewed as Photo-Magnetic Molecular Devices (PMMDs) devoted to molecular spintronics. Results have been firstly obtained on a polynuclear complex, Mo(IV)Cu(II) ...
Chemistry 215 Quiz 1 (20 points)
... is considered "ideal" if it is not compressible one mole of it occupies exactly 1 liter at standard temperature and pressure it can be shown to occupy zero volume at 0C. its behavior is described by the ideal-gas equation one mole of it in a one-liter container exerts a pressure of exactly 1 atm at ...
... is considered "ideal" if it is not compressible one mole of it occupies exactly 1 liter at standard temperature and pressure it can be shown to occupy zero volume at 0C. its behavior is described by the ideal-gas equation one mole of it in a one-liter container exerts a pressure of exactly 1 atm at ...
PHYS 1400 Sample Exam Questions: Properties of Matter (Atoms) 1
... even though Lothar Meyer came up with almost exactly the same table at almost exactly the same time? D) Mendeleyev used his periodic table to predict the existence of previously undiscovered elements. For example, the element gallium was discovered after Mendeleyev's table indicated that an element ...
... even though Lothar Meyer came up with almost exactly the same table at almost exactly the same time? D) Mendeleyev used his periodic table to predict the existence of previously undiscovered elements. For example, the element gallium was discovered after Mendeleyev's table indicated that an element ...
Week 8 – Intermolecular Forces
... (B) C atoms are smaller than Mn atoms, therefore they interfere more with the displacement of atoms in the alloy. (C) Mn atoms are less polarizable than the C atoms, therefore Mn has weaker intermolecular forces. (D) C atoms have a higher melting point than Mn atoms. (E) Mn atoms have similar metall ...
... (B) C atoms are smaller than Mn atoms, therefore they interfere more with the displacement of atoms in the alloy. (C) Mn atoms are less polarizable than the C atoms, therefore Mn has weaker intermolecular forces. (D) C atoms have a higher melting point than Mn atoms. (E) Mn atoms have similar metall ...
FREE Sample Here
... *(These are example results. Results will vary depending on solutions provided.) 1. Bromthymol blue changes color when mixed with an acid. What color does it become? ...
... *(These are example results. Results will vary depending on solutions provided.) 1. Bromthymol blue changes color when mixed with an acid. What color does it become? ...
Topic 7.1-Discrete energy and radioactivity
... • In 1897, he physicist J. J. Thomson, through his work on cathode rays, discovered the electron and its subatomic nature, which destroyed the concept of atoms as being indivisible units. • Thomson believed that the electrons were distributed throughout the atom, with their charge balanced by the ...
... • In 1897, he physicist J. J. Thomson, through his work on cathode rays, discovered the electron and its subatomic nature, which destroyed the concept of atoms as being indivisible units. • Thomson believed that the electrons were distributed throughout the atom, with their charge balanced by the ...
Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements
... i. In the Bohr Atom (one electron systems) there is a one-to-one correspondence between an orbit and its energy level (En = -B/n2). Example: the 3s, 3p, 3d orbitals in Hydrogen all have the same energy. ii. In the Quantum Mechanical version of the atom, the energy level of multielectron atoms depend ...
... i. In the Bohr Atom (one electron systems) there is a one-to-one correspondence between an orbit and its energy level (En = -B/n2). Example: the 3s, 3p, 3d orbitals in Hydrogen all have the same energy. ii. In the Quantum Mechanical version of the atom, the energy level of multielectron atoms depend ...
Definitions - Loreto Science
... • is a substance that is made up of two or more different elements combined together chemically. ...
... • is a substance that is made up of two or more different elements combined together chemically. ...
SCSD Physical Science 9th - Shenandoah Community Schools
... Complete shell tend to be chemically inert (I,D,M) Closed shell with one or two valance electrons highly reactive (I,D,M) Less than a closed shell with one or two valance electrons highly reactive (I,D,M) o The number of valence electrons of an element is determined by its periodic table (I,D,M) o R ...
... Complete shell tend to be chemically inert (I,D,M) Closed shell with one or two valance electrons highly reactive (I,D,M) Less than a closed shell with one or two valance electrons highly reactive (I,D,M) o The number of valence electrons of an element is determined by its periodic table (I,D,M) o R ...
Atomic Theory (2
... 1.) Who were the early contributors to the atomic theory, and what was their view of the atom? 2.) Who discovered the electron? 3.) Who discovered the charge of an electron? 4.) Who discovered the nucleus? 5.) Who discovered the proton? 6.) Describe the composition of the atom and the experiments th ...
... 1.) Who were the early contributors to the atomic theory, and what was their view of the atom? 2.) Who discovered the electron? 3.) Who discovered the charge of an electron? 4.) Who discovered the nucleus? 5.) Who discovered the proton? 6.) Describe the composition of the atom and the experiments th ...
Notes Atoms
... The number of protons is the atomic number (3 in this case) Note: In atoms the number of protons & electrons are the same Neutrons: no charge, also found in the nucleus of atoms Electrons: negative charge, found in electron shells in the electron cloud ...
... The number of protons is the atomic number (3 in this case) Note: In atoms the number of protons & electrons are the same Neutrons: no charge, also found in the nucleus of atoms Electrons: negative charge, found in electron shells in the electron cloud ...
Name: Period: _____ Date: 8th Grade Fall Semester Exam Review
... A. take away an electron B. take away the nucleus C. add an extra proton D. add an extra neutron 5. The Bohr model of an atom is not an exact model of a real atom because A. the protons are negatively charged. B. the nucleus of a real atom is much smaller than a Bohr model nucleus. C. the electrons ...
... A. take away an electron B. take away the nucleus C. add an extra proton D. add an extra neutron 5. The Bohr model of an atom is not an exact model of a real atom because A. the protons are negatively charged. B. the nucleus of a real atom is much smaller than a Bohr model nucleus. C. the electrons ...
Chapter 4: Introduction to Earth Chemistry Section 1 Notes
... Elements rarely occur ____________ in Earth’s crust. They generally occur ____________ with other elements. compound a __________________________________________________________________________ The properties of a compound differ from the properties of the __________ that make up the compound. _____ ...
... Elements rarely occur ____________ in Earth’s crust. They generally occur ____________ with other elements. compound a __________________________________________________________________________ The properties of a compound differ from the properties of the __________ that make up the compound. _____ ...
Metastable inner-shell molecular state

Metastable Innershell Molecular State (MIMS) is a class of ultra-high-energy short-lived molecules have the binding energy up to 1,000 times larger and bond length up to 100 times smaller than typical molecules. MIMS is formed by inner-shell electrons that are normally resistant to molecular formation. However, in stellar conditions, the inner-shell electrons become reactive to form molecular structures (MIMS) from combinations of all elements in the periodic table. MIMS upon dissociation can emit x-ray photons with energies up to 100 keV at extremely high conversion efficiencies from compression energy to photon energy. MIMS is predicted to exist and dominate radiation processes in extreme astrophysical environments, such as large planet cores, star interiors, and black hole and neutron star surroundings. There, MIMS is predicted to enable highly energy-efficient transformation of the stellar compression energy into the radiation energy.The right schematic illustration shows the proposed four stages of the K-shell MIMS (K-MIMS) formation and x-ray generation process. Stage I: Individual atoms are subjected to the stellar compression and ready for absorbing the compression energy. Stage II: The outer electron shells fuse together under increasing ""stellar"" pressure. Stage III: At the peak pressure, via pressure ionization K-shell orbits form the K-MIMS, which is vibrationally hot and encapsulated by a Rydberg-like pseudo-L-Shell structure. Stage IV: The K-MIMS cools down by ionizing (""boiling-off"") a number of pseudo-L-shell electrons and subsequent optical decay by emitting an x-ray photon. The dissociated atoms return their original atoms states and are ready for absorbing the compression energy.MIMS also can be readily produced in laboratory and industrial environments, such as hypervelocity particle impact, laser fusion and z-machine. MIMS can be exploited for highly energy-efficient production of high intensity x-ray beams for a wide range of innovative applications, such as photolithography, x-ray lasers, and inertial fusion.