Name: Period:______ PHYSICAL SCIENCE 1st Semester Final
... The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual properties of new elements showed how useful his periodic table could be. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic number (number of protons). Each row on the table is a period. Each column on the ...
... The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual properties of new elements showed how useful his periodic table could be. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic number (number of protons). Each row on the table is a period. Each column on the ...
Slide 1
... and much more accurate quantum mechanics, and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. However, because of its simplicity, and its correct results for selected systems, the Bohr model is still commonly taught to introduce students to quantum mechanics, before moving on to the more ...
... and much more accurate quantum mechanics, and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. However, because of its simplicity, and its correct results for selected systems, the Bohr model is still commonly taught to introduce students to quantum mechanics, before moving on to the more ...
www.theallpapers.com
... the negative plate; electrons are attracted to the positive plate, through a much larger angle than protons, due to their much smaller mass. The relative sizes of the nucleus and the whole atom. Protons and neutrons reside within the nucleus, and electrons are in “orbitals” around the outside. The r ...
... the negative plate; electrons are attracted to the positive plate, through a much larger angle than protons, due to their much smaller mass. The relative sizes of the nucleus and the whole atom. Protons and neutrons reside within the nucleus, and electrons are in “orbitals” around the outside. The r ...
What`s in Chapter 9: Shapes of molecules affect: • reactivity
... Draw the lewis structure of the C2 anion. What is the MO orbital configuration and the bond order of this anion? Do VBT and MO theory agree? 4. The ionization energy of O2 is lower than the IE of atomic O. Explain this in terms of the where the electrons are in atomic and MO’s of O2. 5. Do you expec ...
... Draw the lewis structure of the C2 anion. What is the MO orbital configuration and the bond order of this anion? Do VBT and MO theory agree? 4. The ionization energy of O2 is lower than the IE of atomic O. Explain this in terms of the where the electrons are in atomic and MO’s of O2. 5. Do you expec ...
Quantum mechanical model for the study of pressure
... in astrophysics (for the understanding of stellar structure and evolution), and in the simulation of laser-driven experiments (for spectroscopic diagnostics for instance). It is worth mentioning that future big lasers will allow experiments at much higher densities § To whom correspondence should be ...
... in astrophysics (for the understanding of stellar structure and evolution), and in the simulation of laser-driven experiments (for spectroscopic diagnostics for instance). It is worth mentioning that future big lasers will allow experiments at much higher densities § To whom correspondence should be ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... d. The last group (18) are called the ___Noble Gasses____. They are non-reactive or ____inert____. e. Salt forming compounds come from group 17, the_halogens________. They are the most reactive nonmetals. f. Metalloids are found along the “___stair step line___”, and are often used as semiconductors ...
... d. The last group (18) are called the ___Noble Gasses____. They are non-reactive or ____inert____. e. Salt forming compounds come from group 17, the_halogens________. They are the most reactive nonmetals. f. Metalloids are found along the “___stair step line___”, and are often used as semiconductors ...
Atomic Structure. Chemical Bonds.
... Electrons with the same quantum number n are about the same distance from the nucleus, move in about the same electric field, and have similar energies. Such electrons occupy the same atomic shell. The energy of an electron depends also on the quantum number l. ...
... Electrons with the same quantum number n are about the same distance from the nucleus, move in about the same electric field, and have similar energies. Such electrons occupy the same atomic shell. The energy of an electron depends also on the quantum number l. ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 1. __Condensation___ occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. 2. All matter is made up of tiny particles called __atoms___. 3. When a solid becomes a liquid, _melting_____ occurs. 4. An _element_____ is made up of only one type of atom. 5. __freezing___ changes a liquid into a solid. 6. A mixture is made ...
... 1. __Condensation___ occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. 2. All matter is made up of tiny particles called __atoms___. 3. When a solid becomes a liquid, _melting_____ occurs. 4. An _element_____ is made up of only one type of atom. 5. __freezing___ changes a liquid into a solid. 6. A mixture is made ...
Slide 1
... NaCl (Symbol) • To write the symbol use the crisscross method to cancel the charges. • Ex: ...
... NaCl (Symbol) • To write the symbol use the crisscross method to cancel the charges. • Ex: ...
unit 5 hw packet - District 196 e
... Draw Lewis structures for each of the following covalent compounds. Your Hints for Drawing Lewis Structures will be helpful. H2O ...
... Draw Lewis structures for each of the following covalent compounds. Your Hints for Drawing Lewis Structures will be helpful. H2O ...
Preview Sample 1
... *(These are example results. Results will vary depending on solutions provided.) 1. Bromthymol blue changes color when mixed with an acid. What color does it become? ...
... *(These are example results. Results will vary depending on solutions provided.) 1. Bromthymol blue changes color when mixed with an acid. What color does it become? ...
General Chemistry
... The absolute value of the difference in electronegativity of two bonded atoms gives a rough measure of the polarity of the bond as follows: 1- When this difference is small (less than 0.5), the bond is nonpolar. 2- When this difference is large (greater than 0.5), the bond is considered polar. 3- Wh ...
... The absolute value of the difference in electronegativity of two bonded atoms gives a rough measure of the polarity of the bond as follows: 1- When this difference is small (less than 0.5), the bond is nonpolar. 2- When this difference is large (greater than 0.5), the bond is considered polar. 3- Wh ...
Chapter 2 - Molecules of Life (Biochemistry) Periodic Table of
... • Electrons not shared equally! • One atom “hogs” the electrons! • This leads to the formation of hydrogen bonds.! ...
... • Electrons not shared equally! • One atom “hogs” the electrons! • This leads to the formation of hydrogen bonds.! ...
Two valence electrons.
... atoms. When elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements with similar properties. ...
... atoms. When elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements with similar properties. ...
Glossary - WordPress.com
... element E the ratio in which they do so may be the same or some simple multiple of the ratio in which these two elements (A and B) combine with each other. ...
... element E the ratio in which they do so may be the same or some simple multiple of the ratio in which these two elements (A and B) combine with each other. ...
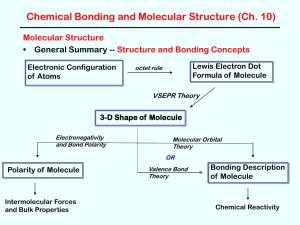
Chapter 9
... Three (or more) atom molecules cannot be explained by simple overlap of orbitals. Fact: a bond generally forms between two half-filled orbitals. Fact: an s-type orbital is spherical, so it could form a bond in any direction. Fact: the three p-type orbitals are at 90 degree angles to each other. ...
... Three (or more) atom molecules cannot be explained by simple overlap of orbitals. Fact: a bond generally forms between two half-filled orbitals. Fact: an s-type orbital is spherical, so it could form a bond in any direction. Fact: the three p-type orbitals are at 90 degree angles to each other. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Study Guide
... Atomic Number: Number of protons; defines the atom Beta Particle: -1 proton, mass number =0; medium ionizing ability, medium energy Boiling: Phase change from a liquid to a gas Bronsted-Lowry Acid: Donates a proton, H+ Bronsted-Lowry Base: Accepts a proton, H+ Calorimetry: Means of measuring the hea ...
... Atomic Number: Number of protons; defines the atom Beta Particle: -1 proton, mass number =0; medium ionizing ability, medium energy Boiling: Phase change from a liquid to a gas Bronsted-Lowry Acid: Donates a proton, H+ Bronsted-Lowry Base: Accepts a proton, H+ Calorimetry: Means of measuring the hea ...
Metastable inner-shell molecular state

Metastable Innershell Molecular State (MIMS) is a class of ultra-high-energy short-lived molecules have the binding energy up to 1,000 times larger and bond length up to 100 times smaller than typical molecules. MIMS is formed by inner-shell electrons that are normally resistant to molecular formation. However, in stellar conditions, the inner-shell electrons become reactive to form molecular structures (MIMS) from combinations of all elements in the periodic table. MIMS upon dissociation can emit x-ray photons with energies up to 100 keV at extremely high conversion efficiencies from compression energy to photon energy. MIMS is predicted to exist and dominate radiation processes in extreme astrophysical environments, such as large planet cores, star interiors, and black hole and neutron star surroundings. There, MIMS is predicted to enable highly energy-efficient transformation of the stellar compression energy into the radiation energy.The right schematic illustration shows the proposed four stages of the K-shell MIMS (K-MIMS) formation and x-ray generation process. Stage I: Individual atoms are subjected to the stellar compression and ready for absorbing the compression energy. Stage II: The outer electron shells fuse together under increasing ""stellar"" pressure. Stage III: At the peak pressure, via pressure ionization K-shell orbits form the K-MIMS, which is vibrationally hot and encapsulated by a Rydberg-like pseudo-L-Shell structure. Stage IV: The K-MIMS cools down by ionizing (""boiling-off"") a number of pseudo-L-shell electrons and subsequent optical decay by emitting an x-ray photon. The dissociated atoms return their original atoms states and are ready for absorbing the compression energy.MIMS also can be readily produced in laboratory and industrial environments, such as hypervelocity particle impact, laser fusion and z-machine. MIMS can be exploited for highly energy-efficient production of high intensity x-ray beams for a wide range of innovative applications, such as photolithography, x-ray lasers, and inertial fusion.