ACS Practice Test 1
... (C)The inter-ionic attraction effect is increased by adding the H2SO4. (D)An electric lamp placed in a circuit in series with the solution becomes dim as the H2SO4 is added ...
... (C)The inter-ionic attraction effect is increased by adding the H2SO4. (D)An electric lamp placed in a circuit in series with the solution becomes dim as the H2SO4 is added ...
File
... Metals are elements that have luster, conduct heat and electricity, usually bend without breaking (malleable) and are ductile. Most have extremely high melting points. Reactivity increases as you go down within a group for metals. With metals the greater the tendency to lose electrons, the more reac ...
... Metals are elements that have luster, conduct heat and electricity, usually bend without breaking (malleable) and are ductile. Most have extremely high melting points. Reactivity increases as you go down within a group for metals. With metals the greater the tendency to lose electrons, the more reac ...
SUPERNOVAE A. Supernovae.-Several years ago, Baade andI
... a point where it is not any more able to support these space charges. At that stage the mean free paths of the individual corpuscles will also have become very large because of the exceedingly rapidly decreasing density of the expanding gas clouds. Breakdown of the enormous electric potentials will ...
... a point where it is not any more able to support these space charges. At that stage the mean free paths of the individual corpuscles will also have become very large because of the exceedingly rapidly decreasing density of the expanding gas clouds. Breakdown of the enormous electric potentials will ...
Complex Atoms I L-S Coupling - Astrophysik Uni
... consists of orbitals with l+1 different m value, each with two possible values s. Thus the nl orbital can hold a maximum 2(2l+1) electrons. An atomic configuration is given by distributing electrons among orbitals. First fill the atomic orbitals in energy order from the lowest energy orbitals upward ...
... consists of orbitals with l+1 different m value, each with two possible values s. Thus the nl orbital can hold a maximum 2(2l+1) electrons. An atomic configuration is given by distributing electrons among orbitals. First fill the atomic orbitals in energy order from the lowest energy orbitals upward ...
Chemistry I Exam
... A. They are negatively charged, their mass/charge ratio, and that they are part of all matter. B. They are negatively charged, their mass, and that they are part of all matter C. They are negatively charged, their mass/charge ratio. D. They are negatively charged. E. Thomson did not perform the “cat ...
... A. They are negatively charged, their mass/charge ratio, and that they are part of all matter. B. They are negatively charged, their mass, and that they are part of all matter C. They are negatively charged, their mass/charge ratio. D. They are negatively charged. E. Thomson did not perform the “cat ...
Characterization of Products from Oxalato Complexes
... (Delgado et al., 2002) such as the work by Youssef (1986) that reported thermal decomposition on of some oxalates, being precursor of oxide. Especially, the tris-chelated [M(C2O4)3]3- complex (M=trivalent first row transition) is well known ligand in the preparation of heterometallic complexes when ...
... (Delgado et al., 2002) such as the work by Youssef (1986) that reported thermal decomposition on of some oxalates, being precursor of oxide. Especially, the tris-chelated [M(C2O4)3]3- complex (M=trivalent first row transition) is well known ligand in the preparation of heterometallic complexes when ...
A2 Chemistry key word list
... A special type of E/Z isomerism in which each carbon of the C=C double bond carries the same atom or group: the cis isomer (Z isomer) has that group on each carbon on the same side; the trans isomer (E isomer) has that group on each carbon on different ...
... A special type of E/Z isomerism in which each carbon of the C=C double bond carries the same atom or group: the cis isomer (Z isomer) has that group on each carbon on the same side; the trans isomer (E isomer) has that group on each carbon on different ...
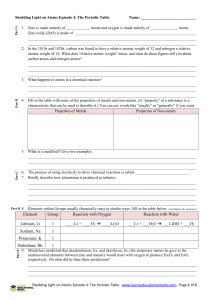
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... This task involves you putting yourself in Mendeleev’s shoes and making predictions! The trends actually work better if you use atomic number instead of atomic weight. The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons inside the atom’s nucleus. More about this in Episode 5. ...
... This task involves you putting yourself in Mendeleev’s shoes and making predictions! The trends actually work better if you use atomic number instead of atomic weight. The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons inside the atom’s nucleus. More about this in Episode 5. ...
ElectronicStructureSurfaces.pdf
... The electronic structure of solids is usually described by a theory called Band Theory, a derivative of Molecular Orbital Theory. However, the best way to describe band theory is to go back and go through the process of forming molecular orbitals from the atomic orbitals for a simple diatomic like ...
... The electronic structure of solids is usually described by a theory called Band Theory, a derivative of Molecular Orbital Theory. However, the best way to describe band theory is to go back and go through the process of forming molecular orbitals from the atomic orbitals for a simple diatomic like ...
Name - Madison County Schools
... A. Name the three subatomic particles: proton, neutron, electron B. Give the location where each can be found: nucleus – proton & neutron; electrons in electron cloud C. Give their electric charges: proton is +; electron is - ; neutron is neutral D. Give their relative masses: proton ~ neutron are a ...
... A. Name the three subatomic particles: proton, neutron, electron B. Give the location where each can be found: nucleus – proton & neutron; electrons in electron cloud C. Give their electric charges: proton is +; electron is - ; neutron is neutral D. Give their relative masses: proton ~ neutron are a ...
bonding and geometry
... conduction electrons, and the metallic ions within the metals, because it involves the sharing of free electrons among a lattice of positively-charged metal ions Occurs between 2 or more metals Result of the attraction of free floating valence electrons for the ...
... conduction electrons, and the metallic ions within the metals, because it involves the sharing of free electrons among a lattice of positively-charged metal ions Occurs between 2 or more metals Result of the attraction of free floating valence electrons for the ...
Chapter 10_Handouts_6
... substance whose properties are different from those of the individual substances that participate in the reaction. ...
... substance whose properties are different from those of the individual substances that participate in the reaction. ...
Chapter 1
... B) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of single electrons between atoms. C) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction between atoms. D) Covalent bonds involve the s ...
... B) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of single electrons between atoms. C) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction between atoms. D) Covalent bonds involve the s ...
Investigating Chemistry - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... There are 32 columns, called “groups” or “families”, 18 obvious ones plus the lanthanides and actinides. Group 1 is the Alkali Metals. Groups 2 is the Alkaline Earth Metals. Groups 3-12 are the Transition Metals. Groups 13-16 are referred to by the first element or simply the group number. Group 17 ...
... There are 32 columns, called “groups” or “families”, 18 obvious ones plus the lanthanides and actinides. Group 1 is the Alkali Metals. Groups 2 is the Alkaline Earth Metals. Groups 3-12 are the Transition Metals. Groups 13-16 are referred to by the first element or simply the group number. Group 17 ...
Grades 9-12 Chemistry California Content Standards
... c. how to use the Periodic Table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, and trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms. d. how to use the Periodic Table to determine the number of electrons available for bonding. e. the n ...
... c. how to use the Periodic Table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, and trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms. d. how to use the Periodic Table to determine the number of electrons available for bonding. e. the n ...
Chemistry - Gorman Learning Center
... c. how to use the Periodic Table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, and trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms. d. how to use the Periodic Table to determine the number of electrons available for bonding. e. the n ...
... c. how to use the Periodic Table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, and trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms. d. how to use the Periodic Table to determine the number of electrons available for bonding. e. the n ...
Polarizability
... is usually quite small. Only larger positively charged ions can be easily polarizable. Negative ions are easily polarizable because they have a larger electron cloud that tends to be more polarizable. Small, positively charged ions can easily distort theses negative ions. ...
... is usually quite small. Only larger positively charged ions can be easily polarizable. Negative ions are easily polarizable because they have a larger electron cloud that tends to be more polarizable. Small, positively charged ions can easily distort theses negative ions. ...
Metastable inner-shell molecular state

Metastable Innershell Molecular State (MIMS) is a class of ultra-high-energy short-lived molecules have the binding energy up to 1,000 times larger and bond length up to 100 times smaller than typical molecules. MIMS is formed by inner-shell electrons that are normally resistant to molecular formation. However, in stellar conditions, the inner-shell electrons become reactive to form molecular structures (MIMS) from combinations of all elements in the periodic table. MIMS upon dissociation can emit x-ray photons with energies up to 100 keV at extremely high conversion efficiencies from compression energy to photon energy. MIMS is predicted to exist and dominate radiation processes in extreme astrophysical environments, such as large planet cores, star interiors, and black hole and neutron star surroundings. There, MIMS is predicted to enable highly energy-efficient transformation of the stellar compression energy into the radiation energy.The right schematic illustration shows the proposed four stages of the K-shell MIMS (K-MIMS) formation and x-ray generation process. Stage I: Individual atoms are subjected to the stellar compression and ready for absorbing the compression energy. Stage II: The outer electron shells fuse together under increasing ""stellar"" pressure. Stage III: At the peak pressure, via pressure ionization K-shell orbits form the K-MIMS, which is vibrationally hot and encapsulated by a Rydberg-like pseudo-L-Shell structure. Stage IV: The K-MIMS cools down by ionizing (""boiling-off"") a number of pseudo-L-shell electrons and subsequent optical decay by emitting an x-ray photon. The dissociated atoms return their original atoms states and are ready for absorbing the compression energy.MIMS also can be readily produced in laboratory and industrial environments, such as hypervelocity particle impact, laser fusion and z-machine. MIMS can be exploited for highly energy-efficient production of high intensity x-ray beams for a wide range of innovative applications, such as photolithography, x-ray lasers, and inertial fusion.