word-doc Practice for the final exam!
... 1. Matter in which physical state has no specific shape but does have a specific volume? a. gas b. solid c. liquid d. salts e. ice 2. A combination of sand, salt, and water is an example of a __________. a. homogeneous mixture b. heterogeneous mixture c. compound d. pure substance e. solid 3. If mat ...
... 1. Matter in which physical state has no specific shape but does have a specific volume? a. gas b. solid c. liquid d. salts e. ice 2. A combination of sand, salt, and water is an example of a __________. a. homogeneous mixture b. heterogeneous mixture c. compound d. pure substance e. solid 3. If mat ...
CHM 130 Final Exam Review Chapter 1 Scientific method Theory
... Chemical vs physical properties Chemical vs physical changes Conservation of mass and energy Chapter 5 Models of the atom Atomic notation Isotopes Radiant energy spectrum Wavelength, frequency, energy Levels, sublevels, orbitals Electron configuration Chapter 6 Group names Atomic size trend Metallic ...
... Chemical vs physical properties Chemical vs physical changes Conservation of mass and energy Chapter 5 Models of the atom Atomic notation Isotopes Radiant energy spectrum Wavelength, frequency, energy Levels, sublevels, orbitals Electron configuration Chapter 6 Group names Atomic size trend Metallic ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
... • Write the MO diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and sketch the bonding and antibonding MO’s. [note: H 1s energy = -13 eV, Cl 3s energy = -25 eV, Cl 3p energy = -14 ...
... • Write the MO diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and sketch the bonding and antibonding MO’s. [note: H 1s energy = -13 eV, Cl 3s energy = -25 eV, Cl 3p energy = -14 ...
File first semester final study guide key
... The periodic table organizes elements by putting them in __groups__________ or the elements in a vertical column on the periodic table and by _periods____ which are the elements in a horizontal row on the periodic table. Elements are placed in the periodic table in numerical order according to their ...
... The periodic table organizes elements by putting them in __groups__________ or the elements in a vertical column on the periodic table and by _periods____ which are the elements in a horizontal row on the periodic table. Elements are placed in the periodic table in numerical order according to their ...
Notes matter energy
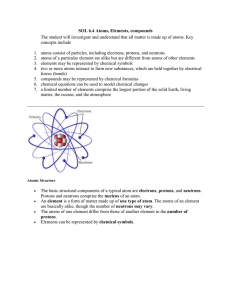
... Atoms are mostly empty space. Protons and neutrons are located in a dense nucleus. Electrons occupy the space around the nucleus. The number electrons is equal to number of protons for neutral elements. Protons have a +1 electrical charge. Neutrons have no electrical charge. Electrons have a -1 elec ...
... Atoms are mostly empty space. Protons and neutrons are located in a dense nucleus. Electrons occupy the space around the nucleus. The number electrons is equal to number of protons for neutral elements. Protons have a +1 electrical charge. Neutrons have no electrical charge. Electrons have a -1 elec ...
Reporting Category 3: Bonding and Chemical Reactions
... How can you apply metallic bonding theory to explain metallic properties? The nature of metallic bonding explains many physical properties of metals. For example, most metals are excellent conductors of thermal energy. When a difference in thermal energy is applied across a metal, it is quickly and ...
... How can you apply metallic bonding theory to explain metallic properties? The nature of metallic bonding explains many physical properties of metals. For example, most metals are excellent conductors of thermal energy. When a difference in thermal energy is applied across a metal, it is quickly and ...
CHEM_S1CourseReview_2011
... What rules must be obeyed to safely conduct an experiment? What are the components of a good scientific experiment? What rules must be obeyed to safely conduct an experiment? Why are significant figures important to chemists? What is the best method/graph to represent specific data? How ...
... What rules must be obeyed to safely conduct an experiment? What are the components of a good scientific experiment? What rules must be obeyed to safely conduct an experiment? Why are significant figures important to chemists? What is the best method/graph to represent specific data? How ...
Ch 4 Review
... a. in order of atomic charge c. in order of subatomic particles b. in order of atomic number d. in alphabetical order ____ 18. The attractive force between oppositely charged ions that result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another is known as a. a covalent bond. c. an atomic bond. b ...
... a. in order of atomic charge c. in order of subatomic particles b. in order of atomic number d. in alphabetical order ____ 18. The attractive force between oppositely charged ions that result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another is known as a. a covalent bond. c. an atomic bond. b ...
Ch 8 AP Practice
... (B) H2O (C) CH4 (D) C2H4 (E) PH3 3. The molecule with only one double bond 4. The molecule with the largest dipole moment 5. The molecule that has trigonal pyramidal geometry 53. According to the VSEPR model, the progressive decrease in the bond angles in the series of molecules CH4, NH3, and H2O is ...
... (B) H2O (C) CH4 (D) C2H4 (E) PH3 3. The molecule with only one double bond 4. The molecule with the largest dipole moment 5. The molecule that has trigonal pyramidal geometry 53. According to the VSEPR model, the progressive decrease in the bond angles in the series of molecules CH4, NH3, and H2O is ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 2 8thed
... electrons of nitrogen are distributed into three unshared orbitals and one shared orbital. When atoms interact to complete their valence shells, it is the unpaired electrons that are involved. Concept 2.3 The formation and function of molecules depend on chemical bonding between atoms. Atoms with ...
... electrons of nitrogen are distributed into three unshared orbitals and one shared orbital. When atoms interact to complete their valence shells, it is the unpaired electrons that are involved. Concept 2.3 The formation and function of molecules depend on chemical bonding between atoms. Atoms with ...
HOMEWORK : CHAPTER 20
... 20.36 The second ionization energy of magnesium is only about twice as great as the first, but the third ionization energy is 10 times as great. Why does it take so much more energy to remove the third electron? 20.38 Helium contains the same number of electrons in its outer shell as do the alkaline ...
... 20.36 The second ionization energy of magnesium is only about twice as great as the first, but the third ionization energy is 10 times as great. Why does it take so much more energy to remove the third electron? 20.38 Helium contains the same number of electrons in its outer shell as do the alkaline ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
Standards Practice
... B. hydrogen bond. C. ionic bond. D. metallic bond. 2. When atoms combine to form a molecule by sharing electrons, what type of bonds are formed? A. covalent B. hydrogen C. ionic D. polar ionic 3. Which is the best way to express the relationship between hydrogen and fluorine when they combine? ...
... B. hydrogen bond. C. ionic bond. D. metallic bond. 2. When atoms combine to form a molecule by sharing electrons, what type of bonds are formed? A. covalent B. hydrogen C. ionic D. polar ionic 3. Which is the best way to express the relationship between hydrogen and fluorine when they combine? ...
Chemistry I - Net Start Class
... b. Atoms of the same element are identical. c. Atoms are made of protons and electrons. d. Atoms unite in definite ratios to form compounds. 74. Which of these statements is NOT true? a. atoms of the same element can have different masses b. atoms of isotopes of an element have different numbers of ...
... b. Atoms of the same element are identical. c. Atoms are made of protons and electrons. d. Atoms unite in definite ratios to form compounds. 74. Which of these statements is NOT true? a. atoms of the same element can have different masses b. atoms of isotopes of an element have different numbers of ...
Writing formulas and naming ionic bonds
... What type of nuclear reaction produces electricity? Fission When a chemical reaction occurs, the mass of the reactants ___ the mass of the products. Equals If the mass of the reactants is 10 g, then the mass of the products is ___ g. ...
... What type of nuclear reaction produces electricity? Fission When a chemical reaction occurs, the mass of the reactants ___ the mass of the products. Equals If the mass of the reactants is 10 g, then the mass of the products is ___ g. ...
First of all, do you know any methods to check
... Electron-Surface Interaction Auger electrons can be generated by any energetic particles, which are able to and excite electrons and leave holes, such as X-Ray irradiation, ion-beam bombardment and electron beam irradiation. In the sense of AES, it is excited by electrons. Electrons interaction wit ...
... Electron-Surface Interaction Auger electrons can be generated by any energetic particles, which are able to and excite electrons and leave holes, such as X-Ray irradiation, ion-beam bombardment and electron beam irradiation. In the sense of AES, it is excited by electrons. Electrons interaction wit ...
C1a - Mr Corfe
... Most reactive least reactive caesium Cs rubidium Rb potassium K sodium Na lithium Li calcium Ca magnesium Mg aluminium Al zinc Zn iron Fe Gold Au silver Ag RULE: An metal is more reactive if it is further to the left of the periodic table or further down in the group (not inclu ...
... Most reactive least reactive caesium Cs rubidium Rb potassium K sodium Na lithium Li calcium Ca magnesium Mg aluminium Al zinc Zn iron Fe Gold Au silver Ag RULE: An metal is more reactive if it is further to the left of the periodic table or further down in the group (not inclu ...
Introduction to Oxidation Reduction
... b. Identify two characteristics common to these equations. The first three reactions show an element, in this case oxygen, converted to the combined form of oxygen in a compound. An element was converted to a compound in the reactions. In the fourth reaction, a compound decomposed into its elements. ...
... b. Identify two characteristics common to these equations. The first three reactions show an element, in this case oxygen, converted to the combined form of oxygen in a compound. An element was converted to a compound in the reactions. In the fourth reaction, a compound decomposed into its elements. ...
IntroRedoxDCIAns
... b. Identify two characteristics common to these equations. The first three reactions show an element, in this case oxygen, converted to the combined form of oxygen in a compound. An element was converted to a compound in the reactions. In the fourth reaction, a compound decomposed into its elements. ...
... b. Identify two characteristics common to these equations. The first three reactions show an element, in this case oxygen, converted to the combined form of oxygen in a compound. An element was converted to a compound in the reactions. In the fourth reaction, a compound decomposed into its elements. ...
What You Need to Know to Pass the Chemistry
... Substances in a mixture retain their original properties. Substances in a mixture may be separated by their size, polarity, density, boiling and freezing points, and solubility (among others). Filtration and distillation are examples of processes used to separate mixtures. 2. An element is a s ...
... Substances in a mixture retain their original properties. Substances in a mixture may be separated by their size, polarity, density, boiling and freezing points, and solubility (among others). Filtration and distillation are examples of processes used to separate mixtures. 2. An element is a s ...
Covalent Bonding - whitburnscience
... All discrete covalent molecules have low melting and boiling points and tend to be liquids and gases at room temperature. Between all molecules in the liquid or solid state weak forces called van der waals’ forces exist these forces become larger as the size of the molecule increases, it is these fo ...
... All discrete covalent molecules have low melting and boiling points and tend to be liquids and gases at room temperature. Between all molecules in the liquid or solid state weak forces called van der waals’ forces exist these forces become larger as the size of the molecule increases, it is these fo ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
8.P.1.1Homework for Website
... B. It cannot combine with other substances, liquid at room temperature, and cannot be changed into simpler substances. C. It is solid at room temperature, can be broken down from compounds by chemical changes, and composed of one kind of atom. 7. Which is a homogeneous mixture? A. woven fabric B. co ...
... B. It cannot combine with other substances, liquid at room temperature, and cannot be changed into simpler substances. C. It is solid at room temperature, can be broken down from compounds by chemical changes, and composed of one kind of atom. 7. Which is a homogeneous mixture? A. woven fabric B. co ...