Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
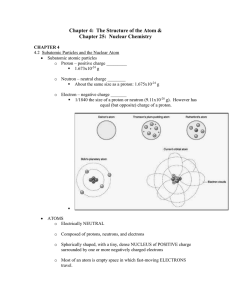
... o Proton – positive charge _________ 1.673x10-24 g o Neutron – neutral charge ________ About the same size as a proton: 1.675x10-24 g o Electron – negative charge _______ 1/1840 the size of a proton or neutron (9.11x10-28 g). However has equal (but opposite) charge of a proton. ...
... o Proton – positive charge _________ 1.673x10-24 g o Neutron – neutral charge ________ About the same size as a proton: 1.675x10-24 g o Electron – negative charge _______ 1/1840 the size of a proton or neutron (9.11x10-28 g). However has equal (but opposite) charge of a proton. ...
Unit 2 - Biochemistry Notes
... Molecule – when two or more atoms bond. CO2 , O2 , H2 and H2O are all molecules. Compound – when different elements combine. CO2 and H2O are molecules, but they are also compounds because they are molecules containing more than one element. ...
... Molecule – when two or more atoms bond. CO2 , O2 , H2 and H2O are all molecules. Compound – when different elements combine. CO2 and H2O are molecules, but they are also compounds because they are molecules containing more than one element. ...
Chapter 18
... Semiconductor do have a lower conductivity than metals but unique properties of semiconductors make them very useful materials. Electrical properties of semiconductors are very sensitive to the presence of impurities: • Intrinsic semiconductors - electrical conductivity is based on the electronic st ...
... Semiconductor do have a lower conductivity than metals but unique properties of semiconductors make them very useful materials. Electrical properties of semiconductors are very sensitive to the presence of impurities: • Intrinsic semiconductors - electrical conductivity is based on the electronic st ...
chapter-2 - HCC Learning Web
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons in electron shells • The periodic table of the elements shows the electron distribution for each element ...
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons in electron shells • The periodic table of the elements shows the electron distribution for each element ...
Test Objectives: Unit 1 – Measurement
... Covalent Bonding o know that when a bond is broken, energy is absorbed; when a bond is made, energy is released o define the term covalent bond and list the properties of covalent substances o know how to draw Lewis Dot structures for covalent compounds o distinguish between non-polar & polar coval ...
... Covalent Bonding o know that when a bond is broken, energy is absorbed; when a bond is made, energy is released o define the term covalent bond and list the properties of covalent substances o know how to draw Lewis Dot structures for covalent compounds o distinguish between non-polar & polar coval ...
Extrinsic Semiconductors
... This relationship is valid for both intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors. In an extrinsic semiconductor the increase in one type of carrier (n or p) reduces the concentration of the other through recombination so that the product of the two (n and p) is a constant at a any given temperature. The c ...
... This relationship is valid for both intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors. In an extrinsic semiconductor the increase in one type of carrier (n or p) reduces the concentration of the other through recombination so that the product of the two (n and p) is a constant at a any given temperature. The c ...
Compound Name
... how to recognize acids and bases from chemical formulae (H + for acids, OH- or CO32- for bases); Acids and bases combine in a neutralization reaction to form water and a salt; acids will react with metals and release hydrogen gas; ...
... how to recognize acids and bases from chemical formulae (H + for acids, OH- or CO32- for bases); Acids and bases combine in a neutralization reaction to form water and a salt; acids will react with metals and release hydrogen gas; ...
atomic number
... Elements are any single thing found in the periodic table (often called the periodic table of elements) Examples of elements: Au, Gold; S, Sulfur; Pb, Lead; Na, Sodium… In 1803, Dalton proposed an atomic theory that is still the basis for many of our theories about the atom. ...
... Elements are any single thing found in the periodic table (often called the periodic table of elements) Examples of elements: Au, Gold; S, Sulfur; Pb, Lead; Na, Sodium… In 1803, Dalton proposed an atomic theory that is still the basis for many of our theories about the atom. ...
Chapter 2
... • Transition elements (labeled with B) • Inner transition elements (shown below rest of table) ...
... • Transition elements (labeled with B) • Inner transition elements (shown below rest of table) ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... Average weight = % First isotope abundance x its mass + % Second isotope abundance x its mass What is the average atomic mass for thallium, Tl, if there are two isotopes with the following masses and abundances? (Tl-203 (203Tl) has a mass of 203.059 amu with ith an abundance ...
... Average weight = % First isotope abundance x its mass + % Second isotope abundance x its mass What is the average atomic mass for thallium, Tl, if there are two isotopes with the following masses and abundances? (Tl-203 (203Tl) has a mass of 203.059 amu with ith an abundance ...
Lecture 2
... In 1958 Ahrland classified metal cations as Type A and Type B, where: Type A metal cations included: • Alkali metal cations: Li+ to Cs+ • Alkaline earth metal cations: Be2+ to Ba2+ • Lighter transition metal cations in higher oxidation states: Ti4+, Cr3+, Fe3+, Co3+ • The proton, H+ Type B metal ca ...
... In 1958 Ahrland classified metal cations as Type A and Type B, where: Type A metal cations included: • Alkali metal cations: Li+ to Cs+ • Alkaline earth metal cations: Be2+ to Ba2+ • Lighter transition metal cations in higher oxidation states: Ti4+, Cr3+, Fe3+, Co3+ • The proton, H+ Type B metal ca ...
ALKALI EARTH METALS Introduction Properties Beryllium
... Alkaline earth metals, after the alkali metals, are secondary metals with strong metallic properties. The group 2A elements are less active than those of 1A, but more active than those of group 3A. Except Be, all form ionic compounds. Be forms mostly covalent compounds. The atomic radius increases f ...
... Alkaline earth metals, after the alkali metals, are secondary metals with strong metallic properties. The group 2A elements are less active than those of 1A, but more active than those of group 3A. Except Be, all form ionic compounds. Be forms mostly covalent compounds. The atomic radius increases f ...
topic 3: periodicity
... As you go down: reactivity decreases; fluorine is the most reactive halogen and best oxidising agent (why does the oxidising ability decrease as you go down?) (fluorine has the highest electronegativity because of its smallest radius and little shielding); F2 oxidises Cl-, Br- and I- to Cl2, Br2 a ...
... As you go down: reactivity decreases; fluorine is the most reactive halogen and best oxidising agent (why does the oxidising ability decrease as you go down?) (fluorine has the highest electronegativity because of its smallest radius and little shielding); F2 oxidises Cl-, Br- and I- to Cl2, Br2 a ...
Cl Cl and
... many electrons does each nucleus of chlorine “feel” going around it? How does this number compare to the number of electrons around the nucleus of the next noble gas? 18, the same. 12. Give, in your own words, an explanation for the fact that the element chlorine at room temperature exists as diatom ...
... many electrons does each nucleus of chlorine “feel” going around it? How does this number compare to the number of electrons around the nucleus of the next noble gas? 18, the same. 12. Give, in your own words, an explanation for the fact that the element chlorine at room temperature exists as diatom ...
Atoms - Red Hook Central Schools
... 400 b.c. Greeks • Greeks philosophers ponder the nature of matter: what is it made of? • Democritus: basic particle of matter = “atom” which means “indivisble”. Envisions these to be “hard spheres” • Aristotle: does not believe in atoms ...
... 400 b.c. Greeks • Greeks philosophers ponder the nature of matter: what is it made of? • Democritus: basic particle of matter = “atom” which means “indivisble”. Envisions these to be “hard spheres” • Aristotle: does not believe in atoms ...
Chemistry 199 - Oregon State chemistry
... sides of the reaction arrow is 60 and the atomic number on both sides of the reaction arrow is 27. This corresponds to 6027Co. 60m27Co is in the excited state and will emit a gamma ray to become 6027Co. A student isolates a sample of tritium containing 1,000 atoms. What will be the number of tritium ...
... sides of the reaction arrow is 60 and the atomic number on both sides of the reaction arrow is 27. This corresponds to 6027Co. 60m27Co is in the excited state and will emit a gamma ray to become 6027Co. A student isolates a sample of tritium containing 1,000 atoms. What will be the number of tritium ...
Physical Science Week 1
... • Matter: Anything that takes up space and has mass. • Atom: The smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. ...
... • Matter: Anything that takes up space and has mass. • Atom: The smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. ...
Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest
... Element – A substance that cannot be broken down into another substance by physical or chemical means. Compound – A substance made of 2 or elements chemically combined in a specific ratio. Chemical bond – the force that holds 2 atoms together. Mixture – Two or more substances that are mixed together ...
... Element – A substance that cannot be broken down into another substance by physical or chemical means. Compound – A substance made of 2 or elements chemically combined in a specific ratio. Chemical bond – the force that holds 2 atoms together. Mixture – Two or more substances that are mixed together ...
Dr Davids Essential Chemistry Definitions Bk1
... The number of particles present in 1 mole of a substance. It has a numerical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Oxidation number: The difference between the number of electrons associated with an element in a compound and the element itself. Just for the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers all compounds ...
... The number of particles present in 1 mole of a substance. It has a numerical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Oxidation number: The difference between the number of electrons associated with an element in a compound and the element itself. Just for the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers all compounds ...
Honors Chemistry Exam Review Questions
... 23. What is the specific heat of a 35.0 gram sample of a metal that gives off 825 J of energy when the cools from 95oC to 25oC. A 0.589 J/goC B 0.403 J/goC ...
... 23. What is the specific heat of a 35.0 gram sample of a metal that gives off 825 J of energy when the cools from 95oC to 25oC. A 0.589 J/goC B 0.403 J/goC ...
Nuclear - Orangefield ISD
... ◦ Sir William Crooks discovered the cathode ray Led to invention of TV Cathode ray particles carry negative charge ...
... ◦ Sir William Crooks discovered the cathode ray Led to invention of TV Cathode ray particles carry negative charge ...
CHEMISTRY FALL FINAL PRACTICE 2016
... How many significant digits does each of the following have: 45000 ____ 0.00320 ______ ...
... How many significant digits does each of the following have: 45000 ____ 0.00320 ______ ...
AQA C2 revision book
... Other elements have a tendency to change their electronic structures to become more like noble gases and therefore more stable. They can do this by losing, gaining or sharing electrons. ...
... Other elements have a tendency to change their electronic structures to become more like noble gases and therefore more stable. They can do this by losing, gaining or sharing electrons. ...