Periodic Trends
... occurs is related to the number of valence electrons. First ionization energy increases from left to right across a period. First ionization energy decreases down a group because atomic size increases and less energy is required to remove an electron farther from the nucleus. ...
... occurs is related to the number of valence electrons. First ionization energy increases from left to right across a period. First ionization energy decreases down a group because atomic size increases and less energy is required to remove an electron farther from the nucleus. ...
QUIZ
... a. The Principle Quantum Number is the electrons distance from the nucleus b. The Orbital Quantum Number is the shape of the electrons orbital c. The Magnetic Quantum Number is the electrons three dimensional position in space d. The Spin Quantum Number is the direction of the electrons spin 43. I l ...
... a. The Principle Quantum Number is the electrons distance from the nucleus b. The Orbital Quantum Number is the shape of the electrons orbital c. The Magnetic Quantum Number is the electrons three dimensional position in space d. The Spin Quantum Number is the direction of the electrons spin 43. I l ...
Additional Chemistry
... 2. Increase the pressure and it will make less molecules in order to decrease the pressure again and visa versa. 3. If you add more of anything in the equilibrium it will move the other way to get rid of it and visa versa. ...
... 2. Increase the pressure and it will make less molecules in order to decrease the pressure again and visa versa. 3. If you add more of anything in the equilibrium it will move the other way to get rid of it and visa versa. ...
Elements, mixtures and compounds lecture
... I. Element (ie: oxygen, hydrogen, lead, gold, krypton): A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken do ...
... I. Element (ie: oxygen, hydrogen, lead, gold, krypton): A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken do ...
An element`s properties depend on the structure of its atoms
... Ants of the species Myrmelachista schumanni kill nonhost trees by injecting the leaves with formic acid, thus creating hospitable habitats (Devi's gardens) for the ant colony. ...
... Ants of the species Myrmelachista schumanni kill nonhost trees by injecting the leaves with formic acid, thus creating hospitable habitats (Devi's gardens) for the ant colony. ...
File - Mr. Holz`s Website
... Ionic Bond – Transfer of electrons to create a bond between two ions that are attracted by opposite charges Covalent Bond – Bond that forms when electrons are shared between atoms Ion – Charged atoms that form from ionic bonds; atoms in which the number of electrons does not equal the number of prot ...
... Ionic Bond – Transfer of electrons to create a bond between two ions that are attracted by opposite charges Covalent Bond – Bond that forms when electrons are shared between atoms Ion – Charged atoms that form from ionic bonds; atoms in which the number of electrons does not equal the number of prot ...
AP Chemistry 2013 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Problems
... b. What is the molecular formula of this substance? c. Draw the Lewis structure of the molecule using the fact that the Cl atoms bond to a single C atom, there is a C-C bond, and two C-O bonds in the compound. 17. Draw the Lewis structures for BH3 and NH3. a. What is the bond angle around the centra ...
... b. What is the molecular formula of this substance? c. Draw the Lewis structure of the molecule using the fact that the Cl atoms bond to a single C atom, there is a C-C bond, and two C-O bonds in the compound. 17. Draw the Lewis structures for BH3 and NH3. a. What is the bond angle around the centra ...
Atom (A) or Ion
... 17. This substance is nitrogen. 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny ind ...
... 17. This substance is nitrogen. 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny ind ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 17. This substance is nitrogen. 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny ind ...
... 17. This substance is nitrogen. 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny ind ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 17. This substance is nitrogen. 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny ind ...
... 17. This substance is nitrogen. 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny ind ...
Ch. 2 note packet
... In a given compound, the relative numbers of atoms of each kind are definite and constant. In general, these relative numbers can be expressed as integers or simple fractions. IN GENERAL Elements consist of tiny particles called _________, which retain their identity in ____________________. In a co ...
... In a given compound, the relative numbers of atoms of each kind are definite and constant. In general, these relative numbers can be expressed as integers or simple fractions. IN GENERAL Elements consist of tiny particles called _________, which retain their identity in ____________________. In a co ...
Chemistry Notes with Blanks
... with the coal? The elements (carbon in coal; hydrogen and oxygen in water) only combine as sugar when _________bonds form Sugar cannot be easily separated into its components. So…Can you break gold down into a simpler substance??? NO…because it is an element Atoms are the basic building blocks of al ...
... with the coal? The elements (carbon in coal; hydrogen and oxygen in water) only combine as sugar when _________bonds form Sugar cannot be easily separated into its components. So…Can you break gold down into a simpler substance??? NO…because it is an element Atoms are the basic building blocks of al ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... An atom that has gained or lost an electron is called a(n) _________________________ What is a cation? ____________________________________ What is an anion? ____________________________________ The charge becomes positive when what has happened? _____________________________________________________ ...
... An atom that has gained or lost an electron is called a(n) _________________________ What is a cation? ____________________________________ What is an anion? ____________________________________ The charge becomes positive when what has happened? _____________________________________________________ ...
Intermolecular Forces, Bonding and Atomic Theory
... 7. Talk about EN differences when you are talking about bonds (within a molecule). You need to talk about IMF’s when talking about attractions between molecules. This is most important for explaining physical properties and states of substances. 8. Students often talk about atoms “wanting to gain/lo ...
... 7. Talk about EN differences when you are talking about bonds (within a molecule). You need to talk about IMF’s when talking about attractions between molecules. This is most important for explaining physical properties and states of substances. 8. Students often talk about atoms “wanting to gain/lo ...
SUMMER WORK AP Chemistry
... experiment requires 15.0 g of cyclohexane, whose density at 25 °C is 0.7781 g/mL. What volume of cyclohexane should be used? (c) A spherical ball of lead has a diameter of 5.0 cm. What is the mass of the sphere if lead has a density of 11.34 g.cm3? (The volume of a sphere is (4/3)πr3where r is the r ...
... experiment requires 15.0 g of cyclohexane, whose density at 25 °C is 0.7781 g/mL. What volume of cyclohexane should be used? (c) A spherical ball of lead has a diameter of 5.0 cm. What is the mass of the sphere if lead has a density of 11.34 g.cm3? (The volume of a sphere is (4/3)πr3where r is the r ...
Chapter 8
... Explain how the conductivity of electricity and high melting points of metals are explained by metallic bonding. What is an alloy? How does a substitutional alloy differ from an interstitial alloy? In the lab, how could you determine if a solid has an ionic bond or a metallic bond? ...
... Explain how the conductivity of electricity and high melting points of metals are explained by metallic bonding. What is an alloy? How does a substitutional alloy differ from an interstitial alloy? In the lab, how could you determine if a solid has an ionic bond or a metallic bond? ...
Lewis
... For n > 2 one can have more than 4 bonds, because there are empty low-level d orbitals avaiable. For elements of 3. period, the maximum number of bonds is 7. * Number of electrons in bonds ...
... For n > 2 one can have more than 4 bonds, because there are empty low-level d orbitals avaiable. For elements of 3. period, the maximum number of bonds is 7. * Number of electrons in bonds ...
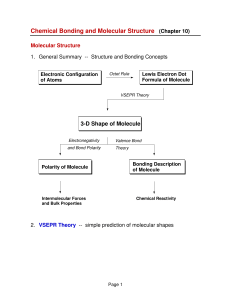
3-D Shape of Molecule
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
The Atom - Williamstown Independent Schools
... of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.