A Model For the Calculation of Solvent ... Reaction Rates for Process Design Purposes
... models for the assessment of solvents as reaction media that are fast, and therefore able to screen large numbers of molecules in a reasonable time, as well as applicable to a wide range of solvents and reactions and able to provide results that are accurate for process design needs. Solvent effects ...
... models for the assessment of solvents as reaction media that are fast, and therefore able to screen large numbers of molecules in a reasonable time, as well as applicable to a wide range of solvents and reactions and able to provide results that are accurate for process design needs. Solvent effects ...
E:\My Documents\sch4u\SCH4U review McKay answers.wpd
... CH3F, has a higher boiling point because it is polar and has greater London forces. 3) The element iodine exists as solid crystals composed of I2 molecules. A chemist wishing to dissolve iodine has a choice of two solvents; water and tetrachloromethane. Which of these two solvents would be the best ...
... CH3F, has a higher boiling point because it is polar and has greater London forces. 3) The element iodine exists as solid crystals composed of I2 molecules. A chemist wishing to dissolve iodine has a choice of two solvents; water and tetrachloromethane. Which of these two solvents would be the best ...
Solubility Solubility is defined as the amount of solute that will
... Rates and rate laws We are interested in the experimental results but what is of greater interest is how does the rate vary as a function of concentration. We can graph our experimental data as instantaneous rate vs concentration and come up with the following sort of graph. I have not used numbers ...
... Rates and rate laws We are interested in the experimental results but what is of greater interest is how does the rate vary as a function of concentration. We can graph our experimental data as instantaneous rate vs concentration and come up with the following sort of graph. I have not used numbers ...
PDF of this page
... will select courses to satisfy entry requirements in the particular program of interest. The chemistry major is designed for students to develop the critical thinking skills needed for problem solving. Students will be able to state a problem succinctly, outline methods of solving the problem, and p ...
... will select courses to satisfy entry requirements in the particular program of interest. The chemistry major is designed for students to develop the critical thinking skills needed for problem solving. Students will be able to state a problem succinctly, outline methods of solving the problem, and p ...
PDF of this page
... CHE 211 Organic Chemistry I 4 Credits TThe structure, chemical properties, and methods of preparation of the more important classes of carbon compounds are studied, with an emphasis on the relationship of structure, stereochemistry, and conformation to chemical reactivity. The preparation and reacti ...
... CHE 211 Organic Chemistry I 4 Credits TThe structure, chemical properties, and methods of preparation of the more important classes of carbon compounds are studied, with an emphasis on the relationship of structure, stereochemistry, and conformation to chemical reactivity. The preparation and reacti ...
CYPRUS
... Course lectures are in Greek and the students must take a final exam for each course. The final grade results from a combination of homework grades, intermediate (mid-term) exams, literature projects or laboratory reports. There are no prerequisite courses, but in a series of related courses (e.g., ...
... Course lectures are in Greek and the students must take a final exam for each course. The final grade results from a combination of homework grades, intermediate (mid-term) exams, literature projects or laboratory reports. There are no prerequisite courses, but in a series of related courses (e.g., ...
Chapter 19
... atoms are covalently bonded to other atoms. For example, the following equation represents the redox reaction used to manufacture ammonia (NH 3). N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) → 2NH 3(g) This process involves neither ions nor any obvious transfer of electrons. The reactants and products are all molecular compoun ...
... atoms are covalently bonded to other atoms. For example, the following equation represents the redox reaction used to manufacture ammonia (NH 3). N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) → 2NH 3(g) This process involves neither ions nor any obvious transfer of electrons. The reactants and products are all molecular compoun ...
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
... Available: 0.5 mol Al , 2.5 mol Cl2 Fritz does the reaction with the available reagents he only ends up with 34g. What is the % yield of the reaction? ...
... Available: 0.5 mol Al , 2.5 mol Cl2 Fritz does the reaction with the available reagents he only ends up with 34g. What is the % yield of the reaction? ...
tro2_ppt_lecture_04 - Louisiana Tech University
... Limiting Reactant • For reactions with multiple reactants, it is likely that one of the reactants will be completely used before the others. • When this reactant is used up, the reaction stops and no more product is made. • The reactant that limits the amount of product is called the limiting react ...
... Limiting Reactant • For reactions with multiple reactants, it is likely that one of the reactants will be completely used before the others. • When this reactant is used up, the reaction stops and no more product is made. • The reactant that limits the amount of product is called the limiting react ...
Lectures on Chapter 4, Part 2 Powerpoint 97 Document
... SO32-(aq) SO42-(aq) + 2 e Add water to the reactant side to supply an oxygen and add two protons to the product side that will remain plus the two electrons. SO32-(aq) + H2O(l) SO42-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 e Reduction: MnO4-(aq) + 3 eMnO2 (s) Add water to the product side to take up the extra oxygen fro ...
... SO32-(aq) SO42-(aq) + 2 e Add water to the reactant side to supply an oxygen and add two protons to the product side that will remain plus the two electrons. SO32-(aq) + H2O(l) SO42-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 e Reduction: MnO4-(aq) + 3 eMnO2 (s) Add water to the product side to take up the extra oxygen fro ...
corrected Amino acids and Protein
... There are mainly three groups of biological polymers: 1) Polysaccharides: Functions primarily as energy reserves and in plants as structural materials. 2) Nucleic acids: Serve two major purposes; storage and transmission of information. 3) Proteins: They are substances of life. Of all chemical compo ...
... There are mainly three groups of biological polymers: 1) Polysaccharides: Functions primarily as energy reserves and in plants as structural materials. 2) Nucleic acids: Serve two major purposes; storage and transmission of information. 3) Proteins: They are substances of life. Of all chemical compo ...
2014 Syllabus - Cambridge International Examinations
... A Cambridge International A Level counts as a double-credit qualification and a Cambridge International AS Level as a single-credit qualification within the Cambridge AICE Diploma award framework. To be considered for an AICE Diploma, a candidate must earn the equivalent of six credits by passing a ...
... A Cambridge International A Level counts as a double-credit qualification and a Cambridge International AS Level as a single-credit qualification within the Cambridge AICE Diploma award framework. To be considered for an AICE Diploma, a candidate must earn the equivalent of six credits by passing a ...
Syllabus and Regulations for 2-year, 4
... by the College authority and will be duly notified. Total duration of the course is two years [hereafter, “Course” refers to M. Sc. Course in Chemistry and “Paper” refers to the individual papers of 75/80/85/90/100 marks divided into two halves: Group-A: Theoretical (50-marks) and Group-B: Practical ...
... by the College authority and will be duly notified. Total duration of the course is two years [hereafter, “Course” refers to M. Sc. Course in Chemistry and “Paper” refers to the individual papers of 75/80/85/90/100 marks divided into two halves: Group-A: Theoretical (50-marks) and Group-B: Practical ...
CHEMISTRY
... Covers several advanced topics of Organic Chemistry including: named organic reactions, other advanced reactions including stereoselective and stereospecific reactions, cycloaddition reactions, sigmatropic rearrangements, and organometallic reactions; mechanisms, synthetic applications. A detailed s ...
... Covers several advanced topics of Organic Chemistry including: named organic reactions, other advanced reactions including stereoselective and stereospecific reactions, cycloaddition reactions, sigmatropic rearrangements, and organometallic reactions; mechanisms, synthetic applications. A detailed s ...
Groups 2 and 7
... Electronegativity of the halogens decreases down the group due to an increase in atomic radius. Increased nuclear charge has no significant effect because there are more electron shells and more shielding. Iodine atoms therefore attract electron density in a covalent bond less strongly than fluorine ...
... Electronegativity of the halogens decreases down the group due to an increase in atomic radius. Increased nuclear charge has no significant effect because there are more electron shells and more shielding. Iodine atoms therefore attract electron density in a covalent bond less strongly than fluorine ...
Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Chemistry Syllabus code 9701
... 1.3 Cambridge Advanced International Certificate of Education (AICE) Cambridge AICE is the group award of Cambridge International Advanced Supplementary Level and Advanced Level (AS Level and A Level). Cambridge AICE involves the selection of subjects from three curriculum areas – Mathematics and Sc ...
... 1.3 Cambridge Advanced International Certificate of Education (AICE) Cambridge AICE is the group award of Cambridge International Advanced Supplementary Level and Advanced Level (AS Level and A Level). Cambridge AICE involves the selection of subjects from three curriculum areas – Mathematics and Sc ...
Homework Solutions Week 6
... 40.0 mL x 0.0400 mmol Hg22+/mL x 2 mmol I-/1 mmol Hg22+ x 1 mL/0.100 mmol I- = 32.0 mL 7-8. For reaction 7-1, how many milliliters of 0.1650 M KMnO4 are needed to react with 108.0 mL of 0.1650 oxalic acid? How many milliliters of 0.1650 M oxalic acid are required to reaction with 108.0 mL of 0.1650 ...
... 40.0 mL x 0.0400 mmol Hg22+/mL x 2 mmol I-/1 mmol Hg22+ x 1 mL/0.100 mmol I- = 32.0 mL 7-8. For reaction 7-1, how many milliliters of 0.1650 M KMnO4 are needed to react with 108.0 mL of 0.1650 oxalic acid? How many milliliters of 0.1650 M oxalic acid are required to reaction with 108.0 mL of 0.1650 ...
thermodynamics
... gas or coal burns in air. The chemical energy may also be used to do mechanical work when a fuel burns in an engine or to provide electrical energy through a galvanic cell like dry cell. Thus, various forms of energy are interrelated and under certain conditions, these may be transformed from one fo ...
... gas or coal burns in air. The chemical energy may also be used to do mechanical work when a fuel burns in an engine or to provide electrical energy through a galvanic cell like dry cell. Thus, various forms of energy are interrelated and under certain conditions, these may be transformed from one fo ...
- sartep.com
... 48. __________ Which ionic compound has the lowest melting point? (The other test asked HIGHEST melting point.) (A) KCl (B) K2O (C) CaCl2 (D) CaO (E) CaF2 49. __________ Which of following is true for ionic compounds but false for metals? (A) They are malleable. (B) Their solid form can conduct elec ...
... 48. __________ Which ionic compound has the lowest melting point? (The other test asked HIGHEST melting point.) (A) KCl (B) K2O (C) CaCl2 (D) CaO (E) CaF2 49. __________ Which of following is true for ionic compounds but false for metals? (A) They are malleable. (B) Their solid form can conduct elec ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY, CFS, IIUM
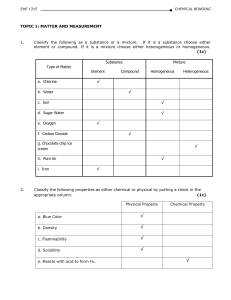
... producing new kinds of matter is called a physical property. A characteristic that depends on how a kind of matter changes suring interactions with other kinds of matter is called chemical property. Matter can also be classified according to the basic types of matter it contains. A simple substance ...
... producing new kinds of matter is called a physical property. A characteristic that depends on how a kind of matter changes suring interactions with other kinds of matter is called chemical property. Matter can also be classified according to the basic types of matter it contains. A simple substance ...
Topic 9 Oxidation and Reduction Answers - slider-dpchemistry-11
... Rule/s: Three rules are used here. Firstly, hydrogen always has an oxidation of +1 (except in combination with reactive metals such as Na when it is -1). Secondly, oxygen always has an oxidation state of –2 (except in H2O2 where it is -1). These known values are used first. Finally, as all these mol ...
... Rule/s: Three rules are used here. Firstly, hydrogen always has an oxidation of +1 (except in combination with reactive metals such as Na when it is -1). Secondly, oxygen always has an oxidation state of –2 (except in H2O2 where it is -1). These known values are used first. Finally, as all these mol ...
Conformational studies of aliphatic secondary ozonides
... apart from each other as possible with a dihedral CCCC angle of 180 degrees. It is well established that different staggered conformers can be formed only as result of rotations around the two closest to the ring CC bonds of aliphatic chains. In the case of an aliphatic group attached to the COCOO ri ...
... apart from each other as possible with a dihedral CCCC angle of 180 degrees. It is well established that different staggered conformers can be formed only as result of rotations around the two closest to the ring CC bonds of aliphatic chains. In the case of an aliphatic group attached to the COCOO ri ...