doc - Dartmouth College
... (a) The molecular weight of aspirin is 180.16 g mol–1. Calculate the maximum mass of aspirin the student could synthesize. (b) The student collected and purified her aspirin product and wanted to calculate the yield of the reaction. Unfortunately her balance was broken, but her pH meter was in worki ...
... (a) The molecular weight of aspirin is 180.16 g mol–1. Calculate the maximum mass of aspirin the student could synthesize. (b) The student collected and purified her aspirin product and wanted to calculate the yield of the reaction. Unfortunately her balance was broken, but her pH meter was in worki ...
Chapter 16: Energy and Chemical Change
... about the caloric content of various foods. When your body breaks down sugars and fats to form carbon dioxide and water, these exothermic reactions generate heat that can be measured in Calories. Note that the nutritional Calorie is capitalized. That’s because one nutritional Calorie, also known as ...
... about the caloric content of various foods. When your body breaks down sugars and fats to form carbon dioxide and water, these exothermic reactions generate heat that can be measured in Calories. Note that the nutritional Calorie is capitalized. That’s because one nutritional Calorie, also known as ...
Structure and Properties of Polymers
... mass. Molecules of common low-molecular-weight substances, such as water - H2O, oxygen - O2, carbon dioxide - CO2, toluene - C6H5CH3, etc., have relative molecular masses of the order of magnitude of tens or hundreds. Macromolecules have masses hundred up to million times larger. High molecular mass ...
... mass. Molecules of common low-molecular-weight substances, such as water - H2O, oxygen - O2, carbon dioxide - CO2, toluene - C6H5CH3, etc., have relative molecular masses of the order of magnitude of tens or hundreds. Macromolecules have masses hundred up to million times larger. High molecular mass ...
Chapter 6 Table of Contents
... Answer One mole of elemental nitrogen reacts with three moles of elemental hydrogen to produce two moles of ammonia. ...
... Answer One mole of elemental nitrogen reacts with three moles of elemental hydrogen to produce two moles of ammonia. ...
Reactions of Plutonium Dioxide with Water and Oxygen
... adsorption and resorption of water changes the gmdient in oxygen concentration across the oxide layer. The proposed mechanism is described in detail and a possible explanation for throttled enhancement of the uranium corrosion rate in moist air is suggested. Results are applied in mnfkming that the ...
... adsorption and resorption of water changes the gmdient in oxygen concentration across the oxide layer. The proposed mechanism is described in detail and a possible explanation for throttled enhancement of the uranium corrosion rate in moist air is suggested. Results are applied in mnfkming that the ...
College Grossmont 115
... or numbers obtained by definition. For example, we can count the fingers on our hand and get an exact number (most people have 5). There is no uncertainty in this result, but we cannot count large groups of objects without some degree of uncertainty. For example, the number of stars in our galaxy is ...
... or numbers obtained by definition. For example, we can count the fingers on our hand and get an exact number (most people have 5). There is no uncertainty in this result, but we cannot count large groups of objects without some degree of uncertainty. For example, the number of stars in our galaxy is ...
MC_16_mac
... its elements in their standard states. • The thermochemical equation to accompany an enthalpy of formation shows the formation of one mole of the compound from its elements in their standard states. Chapter menu ...
... its elements in their standard states. • The thermochemical equation to accompany an enthalpy of formation shows the formation of one mole of the compound from its elements in their standard states. Chapter menu ...
Synthesis and Characterisation of N
... I hereby certify that I am the sole author of this thesis and that no part of this thesis has been published or submitted for publication. I certify that, to the best of my knowledge, my thesis does not infringe upon anyone’s copyright nor violate any proprietary rights and that any ideas, technique ...
... I hereby certify that I am the sole author of this thesis and that no part of this thesis has been published or submitted for publication. I certify that, to the best of my knowledge, my thesis does not infringe upon anyone’s copyright nor violate any proprietary rights and that any ideas, technique ...
spontaneous change: entropy and free energy
... evacuated bulb. After this expansion, the molecules are dispersed throughout the apparatus, with essentially equal numbers of molecules in both bulbs and a pressure of 0.50 atm. What causes this spontaneous expansion of the gas at a constant temperature? One of the characteristics of an ideal gas is ...
... evacuated bulb. After this expansion, the molecules are dispersed throughout the apparatus, with essentially equal numbers of molecules in both bulbs and a pressure of 0.50 atm. What causes this spontaneous expansion of the gas at a constant temperature? One of the characteristics of an ideal gas is ...
Chm 2
... b. 1.81 mol d. 11.0 mol For the reaction represented by the equation Cl2 + 2KBr 2KCl + Br2, how many moles of potassium chloride are produced from 119 g of potassium bromide? a. 0.119 mol c. 0.581 mol b. 0.236 mol d. 1.00 mol For the reaction represented by the equation 3Fe + 4H2O Fe3O4 + 4H2, h ...
... b. 1.81 mol d. 11.0 mol For the reaction represented by the equation Cl2 + 2KBr 2KCl + Br2, how many moles of potassium chloride are produced from 119 g of potassium bromide? a. 0.119 mol c. 0.581 mol b. 0.236 mol d. 1.00 mol For the reaction represented by the equation 3Fe + 4H2O Fe3O4 + 4H2, h ...
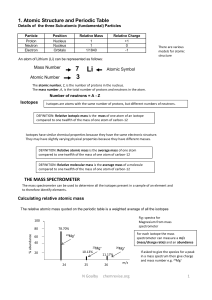
1. Atomic Structure and Periodic Table THE MASS SPECTROMETER
... A. As one goes down a group, the outer electrons are found in shells further from the nucleus and are more shielded so the attraction of the nucleus becomes smaller Q. Why is there a general increase in first ionisation energy across a period? A. As one goes across a period , the number of protons i ...
... A. As one goes down a group, the outer electrons are found in shells further from the nucleus and are more shielded so the attraction of the nucleus becomes smaller Q. Why is there a general increase in first ionisation energy across a period? A. As one goes across a period , the number of protons i ...
Mechanochemistry: the varied applications of mechanical bond
... Mechanochemistry means mechanical breakage of intramolecular bonds by external force and must be differentiated from molecular solid-state chemistry, where contacts between micronized molecular solids are created by the mechanical action for mutual approach of the reacting centers. After an outline ...
... Mechanochemistry means mechanical breakage of intramolecular bonds by external force and must be differentiated from molecular solid-state chemistry, where contacts between micronized molecular solids are created by the mechanical action for mutual approach of the reacting centers. After an outline ...
Acidic Environment by Ahmad Shah Idil
... of the equation; this opposes the change, as it reduces the concentration of the species by producing more products on the opposite side. DECREASED, the equilibrium point will shift towards the same side of the equation the species is on; this opposes the change, as it increases the concentration ...
... of the equation; this opposes the change, as it reduces the concentration of the species by producing more products on the opposite side. DECREASED, the equilibrium point will shift towards the same side of the equation the species is on; this opposes the change, as it increases the concentration ...
PAGE PROOFS
... What can send a shiver down your spine, bring tears to your eyes and make your mouth pucker? Simply the taste of a freshly cut lemon or unripe pineapple. The vinegar in salad dressing, though less stringent, has the same effect. Even a cola or a glass of sparkling wine may leave a slightly sour tast ...
... What can send a shiver down your spine, bring tears to your eyes and make your mouth pucker? Simply the taste of a freshly cut lemon or unripe pineapple. The vinegar in salad dressing, though less stringent, has the same effect. Even a cola or a glass of sparkling wine may leave a slightly sour tast ...
Sustainable Oxidation Catalysis for Synthesis
... problematic on a larger scale. There is a need to develop efficient catalysts that use sustainable terminal oxidants such as molecular oxygen or hydrogen peroxide. Although such methods are employed in the preparation of commodity chemicals, they are rarely used for the synthesis of fine chemicals, ...
... problematic on a larger scale. There is a need to develop efficient catalysts that use sustainable terminal oxidants such as molecular oxygen or hydrogen peroxide. Although such methods are employed in the preparation of commodity chemicals, they are rarely used for the synthesis of fine chemicals, ...
GCE Chemistry SAMs 2009 onwards pdf
... Reliable resources of energy need to be available in the future. A UK report anticipates the differing quantities of fuels needed in 50 years time. In this report three predictions are made based on different assumptions about future energy supply and demand. Among the assumptions the following were ...
... Reliable resources of energy need to be available in the future. A UK report anticipates the differing quantities of fuels needed in 50 years time. In this report three predictions are made based on different assumptions about future energy supply and demand. Among the assumptions the following were ...
2010 Released SOL
... exothermic reactions release heat and will feel warm/hot to the observer. As a result, a temperature probe can be used to determine if the reaction is increasing in temperature. POINTS: 1 / 1 ...
... exothermic reactions release heat and will feel warm/hot to the observer. As a result, a temperature probe can be used to determine if the reaction is increasing in temperature. POINTS: 1 / 1 ...
Chapter 16: Energy and Chemical Change
... of any substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of that substance by one degree Celsius. Because different substances have different compositions, each substance has its own specific heat. The specific heats of several common substances are listed in Table 16-2. ...
... of any substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of that substance by one degree Celsius. Because different substances have different compositions, each substance has its own specific heat. The specific heats of several common substances are listed in Table 16-2. ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2: Organic
... The energy required to promote the electron would be more than offset by the formation of two extra covalent bonds. However, whereas the others would involve 2p orbitals. Spectroscopic measurements show that all four bonds in methane are identical. Let's look at an alkane, ethane for example. Each c ...
... The energy required to promote the electron would be more than offset by the formation of two extra covalent bonds. However, whereas the others would involve 2p orbitals. Spectroscopic measurements show that all four bonds in methane are identical. Let's look at an alkane, ethane for example. Each c ...