chemical reaction
... – how many moles of products are produced with given a number of moles of reactants. ...
... – how many moles of products are produced with given a number of moles of reactants. ...
Nature of chemical reaction - Environmental-Chemistry
... from reactant-molecules and formation of new bonds in product-molecules. • Chemical reactions involve changes in energy. Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction. • Energy is released (exothermic) during formation of bonds and energy is required for breaking the bonds endothermic) • Energy is conse ...
... from reactant-molecules and formation of new bonds in product-molecules. • Chemical reactions involve changes in energy. Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction. • Energy is released (exothermic) during formation of bonds and energy is required for breaking the bonds endothermic) • Energy is conse ...
Chemistry 11 - Sardis Secondary
... - calculating the amount of excess reactant - calculating the amount of product formed in a reaction using the limiting reactant C. Percent Yield (text pgs. 365-373) - calculating the efficiency of a chemical reaction from percent yield ...
... - calculating the amount of excess reactant - calculating the amount of product formed in a reaction using the limiting reactant C. Percent Yield (text pgs. 365-373) - calculating the efficiency of a chemical reaction from percent yield ...
Reaction types and Stoichiometry
... Al + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 B 2Al + 3H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2 _ C 2Al + 3H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 D 2Al + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 20. Which of these is the general formula for a double-replacement reaction? A B C D ...
... Al + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 B 2Al + 3H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2 _ C 2Al + 3H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 D 2Al + H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + H2 20. Which of these is the general formula for a double-replacement reaction? A B C D ...
Enthalpy diagram relating the change for a reaction to enthalpies of
... 1. Physical state of the reactants: when reactants are in different phases for example when a solid reacts with a liquid the reaction is limited to the area of contact. Reactions involving solids will proceed faster if the surface area of the solid is increased. 2. Concentration of the reactants: as ...
... 1. Physical state of the reactants: when reactants are in different phases for example when a solid reacts with a liquid the reaction is limited to the area of contact. Reactions involving solids will proceed faster if the surface area of the solid is increased. 2. Concentration of the reactants: as ...
No Slide Title
... • One of the reactants is in limited supply and thus restricts the amount of product formed. • Think of it as: If you wanted to bake a batch of peanut butter cookies and the recipe calls for 1 cup of peanut butter and all you have is ½ a cup, even though you have all the other ingredients, you can a ...
... • One of the reactants is in limited supply and thus restricts the amount of product formed. • Think of it as: If you wanted to bake a batch of peanut butter cookies and the recipe calls for 1 cup of peanut butter and all you have is ½ a cup, even though you have all the other ingredients, you can a ...
C:\Users\mrh70950\Documents\My Files\WordPerfect
... i. anti-addition stereochemistry yields 1-alkenes from terminal alkynes and (E)-alkenes from internal alkynes 2. double hydrogenation: addition of 2 mol of H2 to yield alkanes a. noble metal catalyst + excess H2 3. electrophilic additions (all by very similar mechanisms) a. hydrohalogenation: addit ...
... i. anti-addition stereochemistry yields 1-alkenes from terminal alkynes and (E)-alkenes from internal alkynes 2. double hydrogenation: addition of 2 mol of H2 to yield alkanes a. noble metal catalyst + excess H2 3. electrophilic additions (all by very similar mechanisms) a. hydrohalogenation: addit ...
Aim # 8: How do we write and balance a chemical equation?
... Note: Oxygen is a diatomic molecule. 3. Balance the equation by supplying coefficients that will make the number of atoms of each element the same on both sides of the arrow. 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO (balanced) Begin by examining the first element on the left side and comparing it to itself on the right side ...
... Note: Oxygen is a diatomic molecule. 3. Balance the equation by supplying coefficients that will make the number of atoms of each element the same on both sides of the arrow. 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO (balanced) Begin by examining the first element on the left side and comparing it to itself on the right side ...
Chemistry Final Exam Test Yourself I
... Short Answer What are the 4 factors that affect the rate of a reaction? (Concentration, surface area, temperature, and adding a catalyst) As the number of ions increases in a solution, the ____________ goes down (Freezing point) ...
... Short Answer What are the 4 factors that affect the rate of a reaction? (Concentration, surface area, temperature, and adding a catalyst) As the number of ions increases in a solution, the ____________ goes down (Freezing point) ...
Thermochemistry: The Heat of Neutralization
... Some reactions are too violent and dangerous to perform in a closed calorimeter system. Other reactions generate so much heat that simple calorimeters cannot be used. In such cases, it is practical to examine a series of reactions whose net effect is the desired reaction, but whose heats of reaction ...
... Some reactions are too violent and dangerous to perform in a closed calorimeter system. Other reactions generate so much heat that simple calorimeters cannot be used. In such cases, it is practical to examine a series of reactions whose net effect is the desired reaction, but whose heats of reaction ...
Chapter 7
... temperature will increase the reaction rate. • Ex: You store milk in a refrigerator to slow down the reactions that cause the milk to spoil • Increasing the temperature of a substance causes its particles to move faster, on average. • Particles that move faster are both more likely to collide and mo ...
... temperature will increase the reaction rate. • Ex: You store milk in a refrigerator to slow down the reactions that cause the milk to spoil • Increasing the temperature of a substance causes its particles to move faster, on average. • Particles that move faster are both more likely to collide and mo ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... consolidate this knowledge by extending it beyond the limits usually set at Secondary Education Certificate (SEC) level to cover more advanced concepts in chemistry which are dealt with in a broad manner. Most of the concepts studied at intermediate level will not be developed to the same depth and ...
... consolidate this knowledge by extending it beyond the limits usually set at Secondary Education Certificate (SEC) level to cover more advanced concepts in chemistry which are dealt with in a broad manner. Most of the concepts studied at intermediate level will not be developed to the same depth and ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... consolidate this knowledge by extending it beyond the limits usually set at Secondary Education Certificate (SEC) level to cover more advanced concepts in chemistry which are dealt with in a broad manner. Most of the concepts studied at intermediate level will not be developed to the same depth and ...
... consolidate this knowledge by extending it beyond the limits usually set at Secondary Education Certificate (SEC) level to cover more advanced concepts in chemistry which are dealt with in a broad manner. Most of the concepts studied at intermediate level will not be developed to the same depth and ...
Name: Date: AP Chemistry/Chemistry 145 Summer Assignment
... Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction, including states for each reactant and product. ...
... Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction, including states for each reactant and product. ...
Advanced Placement (AP) Chemistry 2012 – 2013 Ramsay High
... Students will also attend three six hour Saturday sessions to address specific content topics in more depth. Lab sessions will be scheduled approximately every two weeks and are listed in the course outline. Throughout the year, before school, after school or nighttime review sessions will be regula ...
... Students will also attend three six hour Saturday sessions to address specific content topics in more depth. Lab sessions will be scheduled approximately every two weeks and are listed in the course outline. Throughout the year, before school, after school or nighttime review sessions will be regula ...
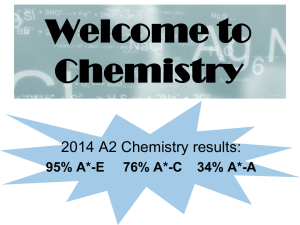
Welcome to Chemistry
... A level is the full 2 year qualification with all the exams at the end of Y13. ...
... A level is the full 2 year qualification with all the exams at the end of Y13. ...
experiment 10 - Faculty Web Pages
... where A, B, C, and D all exist as ions in solution. Will a reaction happen, and if so, what will be the products? Each of the positive ions could combine with the negative ion of the other compound, i.e. A+ and D¯ and C+ and B¯. The formation of a precipitate, the evolution of a gas, and a temperatu ...
... where A, B, C, and D all exist as ions in solution. Will a reaction happen, and if so, what will be the products? Each of the positive ions could combine with the negative ion of the other compound, i.e. A+ and D¯ and C+ and B¯. The formation of a precipitate, the evolution of a gas, and a temperatu ...