Chapter 30 - The Chemical Basis of Animal Life
... How Electrons Are Arranged in Atoms. (a) Sodium (Na) atom, showing its three energy-level shells. (b) In reality, electrons are not found in a definite location but travel rapidly in a three-dimensional space (X, Y, and Z planes) around the nucleus. ...
... How Electrons Are Arranged in Atoms. (a) Sodium (Na) atom, showing its three energy-level shells. (b) In reality, electrons are not found in a definite location but travel rapidly in a three-dimensional space (X, Y, and Z planes) around the nucleus. ...
CHEM 1211K Test IV MULTIPLE CHOICE. (3 points each) 1) The
... C) Non-reacting gas mixtures are homogeneous. D) Gases expand spontaneously to fill the container they are placed in. E) Bases are highly compressible. 11) Of the following, __________ is a correct statement of Boyle's law. A) n/P = constant B) V/P = constant C) V/T = constant D) P/V = constant E) P ...
... C) Non-reacting gas mixtures are homogeneous. D) Gases expand spontaneously to fill the container they are placed in. E) Bases are highly compressible. 11) Of the following, __________ is a correct statement of Boyle's law. A) n/P = constant B) V/P = constant C) V/T = constant D) P/V = constant E) P ...
Physical Science Semester 2 Final Exam 2013 –STUDY GUIDE
... 17. Increasing the speed of an object ____ its potential energy. 18. The SI (metric) unit for energy is the ____. 19. You can calculate kinetic energy by using the equation ____. 20. You can calculate gravitational potential energy by using the equation ____. 21. According to the law of conservatio ...
... 17. Increasing the speed of an object ____ its potential energy. 18. The SI (metric) unit for energy is the ____. 19. You can calculate kinetic energy by using the equation ____. 20. You can calculate gravitational potential energy by using the equation ____. 21. According to the law of conservatio ...
AP Semester I Review: Free Response Questions
... water to produce 100. mL of solution. A 20.0 mL portion of the solution was titrated with KMnO4 (aq). The balanced equation for the reaction that occurred is as follows: 16 H+ (aq) + 2 MnO4- (aq) + 5 C2O42- (aq) 2 Mn2+ (aq) + 10 CO2 (g) + 8 H2O (l) The volume of 0.0150 M KMnO4 (aq) required to rea ...
... water to produce 100. mL of solution. A 20.0 mL portion of the solution was titrated with KMnO4 (aq). The balanced equation for the reaction that occurred is as follows: 16 H+ (aq) + 2 MnO4- (aq) + 5 C2O42- (aq) 2 Mn2+ (aq) + 10 CO2 (g) + 8 H2O (l) The volume of 0.0150 M KMnO4 (aq) required to rea ...
Using mass to calculate molecular formula
... (common salt). 1 mole of HCl (36.5 g) reacts with 1 mole of NaOH (23+16+1=40 g) to form 1 mole of water (18 g) and 1 mole of NaCl (23+35.5=58.5 g) CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O methane + oxygen carbon dioxide + water Check that the number of atoms of each type is correct and that the masses are conserved ...
... (common salt). 1 mole of HCl (36.5 g) reacts with 1 mole of NaOH (23+16+1=40 g) to form 1 mole of water (18 g) and 1 mole of NaCl (23+35.5=58.5 g) CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O methane + oxygen carbon dioxide + water Check that the number of atoms of each type is correct and that the masses are conserved ...
New substances are formed by chemical reactions. When elements
... Covalent bonds Compounds formed from non-metals consist of molecules. The atoms in a molecule are joined together by covalent bonds. These bonds form when atoms share pairs of electrons. Chemical formulas The chemical formula of a compound shows how many of each type of atom join together to make th ...
... Covalent bonds Compounds formed from non-metals consist of molecules. The atoms in a molecule are joined together by covalent bonds. These bonds form when atoms share pairs of electrons. Chemical formulas The chemical formula of a compound shows how many of each type of atom join together to make th ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... ____ 37) What characteristic of metals makes them good electrical conductors? a. They have mobile valence electrons. c. They have mobile cations. b. They have mobile protons. d. Their crystal structures can be rearranged easily. ____ 38) Which of these elements does not exist as a diatomic molecule ...
... ____ 37) What characteristic of metals makes them good electrical conductors? a. They have mobile valence electrons. c. They have mobile cations. b. They have mobile protons. d. Their crystal structures can be rearranged easily. ____ 38) Which of these elements does not exist as a diatomic molecule ...
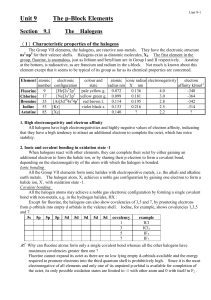
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
... In diamond, every carbon atom can be imagined to be at the center of a regular tetrahedron surrounded by four carbon atoms whose centers are at the corners of the tetrahedron. Within the structure, every carbon atom forms four covalent bonds by sharing electrons with each of its four nearest neighbo ...
... In diamond, every carbon atom can be imagined to be at the center of a regular tetrahedron surrounded by four carbon atoms whose centers are at the corners of the tetrahedron. Within the structure, every carbon atom forms four covalent bonds by sharing electrons with each of its four nearest neighbo ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... a Noble gas element. B. Energy is released in bond formation between atoms. C. Energy is required in the breaking of a bond between atoms. 1. The energy to make or break a bond is referred to as bond energy. 2. It is reported as kiloJoules/mole (kJ/mol) 3. The octet rule applied to the number of bon ...
... a Noble gas element. B. Energy is released in bond formation between atoms. C. Energy is required in the breaking of a bond between atoms. 1. The energy to make or break a bond is referred to as bond energy. 2. It is reported as kiloJoules/mole (kJ/mol) 3. The octet rule applied to the number of bon ...
Chapter 6.2 Notes
... have covalent bonds – bonds formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons - electrons are shared so that both atoms have full outer energy levels - also called molecules - low melting and boiling points - do no conduct electricity - formed between nonmetals ...
... have covalent bonds – bonds formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons - electrons are shared so that both atoms have full outer energy levels - also called molecules - low melting and boiling points - do no conduct electricity - formed between nonmetals ...
Chemistry - Delhi Public School, Faridabad
... How is the formal charge on an atom in a molecule/ion calculated? Explain taking the example of ozone molecule. ...
... How is the formal charge on an atom in a molecule/ion calculated? Explain taking the example of ozone molecule. ...
Chemistry I Review - BarbaraElam-Rice
... 31) An intermolecular force that holds ionic compounds together is called electrostatic attraction. 32) Describe the 3 intermolecular forces? Which of these forces is the strongest? weakest? 33) How are intermolecular forces different from chemical bonds? Which is stronger? 34) If the electronegativ ...
... 31) An intermolecular force that holds ionic compounds together is called electrostatic attraction. 32) Describe the 3 intermolecular forces? Which of these forces is the strongest? weakest? 33) How are intermolecular forces different from chemical bonds? Which is stronger? 34) If the electronegativ ...
Document
... subscript means that each water molecule has two hydrogen atoms. Since each water molecule has 2 hydrogen atoms and there are two water molecules, there must be 4 (2 × 2) hydrogen atoms. ...
... subscript means that each water molecule has two hydrogen atoms. Since each water molecule has 2 hydrogen atoms and there are two water molecules, there must be 4 (2 × 2) hydrogen atoms. ...
Endothermic And Exothermic Reactions
... A chemical reaction that absorbs energy from its surroundings. More energy is required to break the bonds in the reactants than is released by the formation of bonds in the products. In these reactions, heat is shown as one This is a typical graph of an of the reactants endothermic reaction with the ...
... A chemical reaction that absorbs energy from its surroundings. More energy is required to break the bonds in the reactants than is released by the formation of bonds in the products. In these reactions, heat is shown as one This is a typical graph of an of the reactants endothermic reaction with the ...
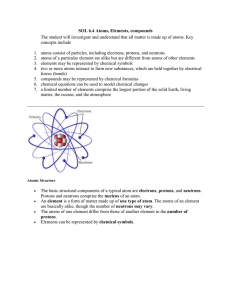
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
Atoms Matter Energy Notes
... o Recognized patterns based on physical and chemical properties of the elements that have been discovered o Also included: atomic mass: average mass of an atom o The periodic table is organized by physical properties. Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into smaller substances by ordin ...
... o Recognized patterns based on physical and chemical properties of the elements that have been discovered o Also included: atomic mass: average mass of an atom o The periodic table is organized by physical properties. Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into smaller substances by ordin ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... us to observe flame tests? Is energy released or absorbed when an electron falls from a higher energy level to a lower energy level? 8. What is the difference between a ground state and an excited state? 9. What is the lowest energy level? The lowest sublevel? 10. What is the maximum number of elect ...
... us to observe flame tests? Is energy released or absorbed when an electron falls from a higher energy level to a lower energy level? 8. What is the difference between a ground state and an excited state? 9. What is the lowest energy level? The lowest sublevel? 10. What is the maximum number of elect ...
Chem 1411 Chapt2
... Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species that have a net charge. Monatomic- cations: K+, Na+, Mg+2, Al+3 Anions: Cl-, O2-, BrThe monatomic ions like to take charge ...
... Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species that have a net charge. Monatomic- cations: K+, Na+, Mg+2, Al+3 Anions: Cl-, O2-, BrThe monatomic ions like to take charge ...
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
... 9.4 Covalent Bonding and Orbital Overlap • Lewis structures and VSEPR theory give us the shape and location of electrons in a molecule. • They do not explain why a chemical bond forms. • How can quantum mechanics be used to account for molecular shape? What are the orbitals that are involved in bond ...
... 9.4 Covalent Bonding and Orbital Overlap • Lewis structures and VSEPR theory give us the shape and location of electrons in a molecule. • They do not explain why a chemical bond forms. • How can quantum mechanics be used to account for molecular shape? What are the orbitals that are involved in bond ...
Chem 150 - Fall 2015 Exam I
... aluminum and cesium are normal while in the UK and elsewhere the usual spelling is sulphur. Atomic weights (mean relative masses): Apart from the heaviest elements, these are IUPAC 2007 values (Pure & Appl. Chem., 2007, in press). Elements with values given in brackets have no stable nuclides and ar ...
... aluminum and cesium are normal while in the UK and elsewhere the usual spelling is sulphur. Atomic weights (mean relative masses): Apart from the heaviest elements, these are IUPAC 2007 values (Pure & Appl. Chem., 2007, in press). Elements with values given in brackets have no stable nuclides and ar ...
Exam 2 Form N - TAMU Chemistry
... b) The number of electrons ejected from a metal surface irradiated with visible light does not depend on the color of the light as long as the light is above a certain, minimum energy . c) Electrons in atoms are found in s, p, d, or f orbitals. d) After an electron (in an atom) is excited to a highe ...
... b) The number of electrons ejected from a metal surface irradiated with visible light does not depend on the color of the light as long as the light is above a certain, minimum energy . c) Electrons in atoms are found in s, p, d, or f orbitals. d) After an electron (in an atom) is excited to a highe ...
Objective 4
... series of Chemical Reactions in which Sugars are broken down to Carbon Dioxide and Water In this process, energy is released for use by the body. (Breaking Chemical Bonds Releases ...
... series of Chemical Reactions in which Sugars are broken down to Carbon Dioxide and Water In this process, energy is released for use by the body. (Breaking Chemical Bonds Releases ...
ppt - Yale University
... signal shifts upfield). This handy picture of diamagnetic The H nucleianisotropy of benzene due to ring lie outside the current orbital path may there well be nonsense! when is ring current. (B0 augmented; (Prof. Wiberg showed it to signal shifts downfield). be nonsense for 13C.) ...
... signal shifts upfield). This handy picture of diamagnetic The H nucleianisotropy of benzene due to ring lie outside the current orbital path may there well be nonsense! when is ring current. (B0 augmented; (Prof. Wiberg showed it to signal shifts downfield). be nonsense for 13C.) ...
Chemistry (B) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 50. How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? a. It decreases. c. It stays the same. b. It increases. d. It doubles. ____ 51. What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital? a. sphere c. bar b. dumbbell d. two perpendicular dumbbells ____ 52. What is ...
... ____ 50. How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? a. It decreases. c. It stays the same. b. It increases. d. It doubles. ____ 51. What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital? a. sphere c. bar b. dumbbell d. two perpendicular dumbbells ____ 52. What is ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.