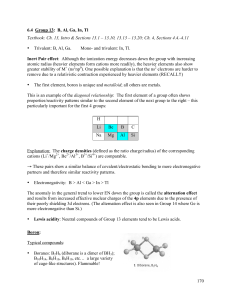
File
... b. cannot be broken down further. c. are all composed of carbon. d. have no mass. _____ 2. Using improved chemistry equipment in the late 1700s, chemists observed that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This scientific law is called the law of a. definite proportions. b. g ...
... b. cannot be broken down further. c. are all composed of carbon. d. have no mass. _____ 2. Using improved chemistry equipment in the late 1700s, chemists observed that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This scientific law is called the law of a. definite proportions. b. g ...
Chapter 10 - HCC Learning Web
... 52. Consider the species Cl2+, Cl2, and Cl2-. Which of these species will be paramagnetic? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 52. Consider the species Cl2+, Cl2, and Cl2-. Which of these species will be paramagnetic? A. B. C. D. E. ...
Document
... 15. How many protons and neutrons are there in an 13. This chart represents the melting points and boiling points of some substances. Which substance is a gas at 450C? ...
... 15. How many protons and neutrons are there in an 13. This chart represents the melting points and boiling points of some substances. Which substance is a gas at 450C? ...
SCSD Physical Science 9th - Shenandoah Community Schools
... o The number of valence electrons of an element is determined by its periodic table (I,D,M) o Responsible for the electrical conductivity of elements, may be divided into Metals (I,D,M) Nonmetals (I,D,M) Semiconductors (I,D,M) Metalloids (I,D,M) Understand chemical bonds (I,D,M) o An attraction betw ...
... o The number of valence electrons of an element is determined by its periodic table (I,D,M) o Responsible for the electrical conductivity of elements, may be divided into Metals (I,D,M) Nonmetals (I,D,M) Semiconductors (I,D,M) Metalloids (I,D,M) Understand chemical bonds (I,D,M) o An attraction betw ...
200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry
... form ions to obtain such a configuration of electrons. Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl It loses its 1 valence electron leaving 2 below it 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are fo ...
... form ions to obtain such a configuration of electrons. Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl It loses its 1 valence electron leaving 2 below it 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are fo ...
File - Get Involved!
... − Electronegative elements will have 0 or negative FC − Electropositive elements will have 0 or positive FC • Multiple Bonding − Higher bond order (double or triple bond) − Shorter bond length − Higher bond energy ...
... − Electronegative elements will have 0 or negative FC − Electropositive elements will have 0 or positive FC • Multiple Bonding − Higher bond order (double or triple bond) − Shorter bond length − Higher bond energy ...
The Periodic Table of Elements and Atoms…
... • Each atom has energy levels/orbitals that can only hold a certain amount of electrons. Electrons in orbitals farthest away from the nucleus have higher amounts of energy than those found in orbitals closer to the nucleus. ...
... • Each atom has energy levels/orbitals that can only hold a certain amount of electrons. Electrons in orbitals farthest away from the nucleus have higher amounts of energy than those found in orbitals closer to the nucleus. ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... pure sample of an element contains only atoms of the same kind. Atoms combine to make huge, 3-‐D arrangements called crystals or small discrete groups called molecules. Only the noble gases, such a ...
... pure sample of an element contains only atoms of the same kind. Atoms combine to make huge, 3-‐D arrangements called crystals or small discrete groups called molecules. Only the noble gases, such a ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... subscript written to the right of the element symbol. • If only one atom is present, do not include a subscript. • If polyatomic groups are present in the molecule, they are written inside parentheses if more than one group is present. • Examples: H2O, NaCl, KNO3, Mg(NO3)2 ...
... subscript written to the right of the element symbol. • If only one atom is present, do not include a subscript. • If polyatomic groups are present in the molecule, they are written inside parentheses if more than one group is present. • Examples: H2O, NaCl, KNO3, Mg(NO3)2 ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... 21. What is the difference between the Bohr model and the Quantum mechanical model? 22. a. What are flame tests? b. What area of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum allows us to observe flame tests? c. Is energy released or absorbed when an electron falls from a higher energy level to a lower ene ...
... 21. What is the difference between the Bohr model and the Quantum mechanical model? 22. a. What are flame tests? b. What area of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum allows us to observe flame tests? c. Is energy released or absorbed when an electron falls from a higher energy level to a lower ene ...
Key
... There is a σ bond between the N and each O, and one π bonding pair (in orbital A) distributed among all three N–O bonds. The bond order is 4/3, which is also what you get from resonance structures. iv. If you use the same MO diagram for the molecule SO3 , what S–O bond order do you get? How does thi ...
... There is a σ bond between the N and each O, and one π bonding pair (in orbital A) distributed among all three N–O bonds. The bond order is 4/3, which is also what you get from resonance structures. iv. If you use the same MO diagram for the molecule SO3 , what S–O bond order do you get? How does thi ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
... Chemical Formulas • For an ionic compound, there are no distinct molecules, so we use their empirical formula to identify them. • In the figure, each Na+ is associated with six Cl-, each Cl- is associated with six Na+, and the whole solid is electrically neutral. • Other ionic compounds may have di ...
... Chemical Formulas • For an ionic compound, there are no distinct molecules, so we use their empirical formula to identify them. • In the figure, each Na+ is associated with six Cl-, each Cl- is associated with six Na+, and the whole solid is electrically neutral. • Other ionic compounds may have di ...
Prerequisite Knowledge for Chemistry
... Compounds are represented by chemical formulas consisting of element symbols and subscripts. For instance, water’s chemical formula is H2O. The “H” stands for hydrogen and the “O” stands for oxygen. The subscripts come after the element to which they refer. Subscripts state the number of atoms of th ...
... Compounds are represented by chemical formulas consisting of element symbols and subscripts. For instance, water’s chemical formula is H2O. The “H” stands for hydrogen and the “O” stands for oxygen. The subscripts come after the element to which they refer. Subscripts state the number of atoms of th ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... 9. State 3-4 properties of each of the families above. 10. Which family is the most stable? 11. Which family reacts vigorously with water? 12. Which family is extracted from mineral ores? 13. Which family are the most reactive metals? 14. Which family of nonmetals combines with 1A and 2Ametals to ma ...
... 9. State 3-4 properties of each of the families above. 10. Which family is the most stable? 11. Which family reacts vigorously with water? 12. Which family is extracted from mineral ores? 13. Which family are the most reactive metals? 14. Which family of nonmetals combines with 1A and 2Ametals to ma ...
Document
... Atoms gain electrons (negatives) and become more negative. Atoms with 2-3 valence electrons will LOSE electrons and become more positive. Who will lose and who will gain an electron? ...
... Atoms gain electrons (negatives) and become more negative. Atoms with 2-3 valence electrons will LOSE electrons and become more positive. Who will lose and who will gain an electron? ...
Elements Elements (cont.) Elements (cont.)
... n mber of each type t pe of atom is indicated by b a subscript written to the right of the element symbol. • If only one atom is present, do not include a subscript. • If p polyatomic y ggroups p are present p in the molecule,, they are written inside parentheses if more than one group is present. • ...
... n mber of each type t pe of atom is indicated by b a subscript written to the right of the element symbol. • If only one atom is present, do not include a subscript. • If p polyatomic y ggroups p are present p in the molecule,, they are written inside parentheses if more than one group is present. • ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same ...
... 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same ...
Periodic Table, Bonding, Reactions, and Moles
... 6. Explain, in terms of electrons, why the ionic radius of a Group 2 element is smaller than its atomic radius. 7. What is the total number of electron pairs shared between the carbon atom and one of the oxygen atoms in a carbon dioxide molecule? 8. Explain, in terms of valence electrons, why the bo ...
... 6. Explain, in terms of electrons, why the ionic radius of a Group 2 element is smaller than its atomic radius. 7. What is the total number of electron pairs shared between the carbon atom and one of the oxygen atoms in a carbon dioxide molecule? 8. Explain, in terms of valence electrons, why the bo ...
Terminology 1
... (The chemical identity of an atom can be determined solely by it’s atomic number) When the atom is neutral, i.e. not electrically charged, the atomic number equals the number of electrons in its shells ...
... (The chemical identity of an atom can be determined solely by it’s atomic number) When the atom is neutral, i.e. not electrically charged, the atomic number equals the number of electrons in its shells ...
Chapter 2: Matter
... Ex. Hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen occur naturally as colorless gases but when combined they form Nylon which is a flexible solid. ...
... Ex. Hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen occur naturally as colorless gases but when combined they form Nylon which is a flexible solid. ...
Unit 3 - Chemistry
... pudding model for the atom could not be correct. • The large deflections of the α particles could be caused only by a center of concentrated positive charge that would repel the _______________ charged α particles. • Most of the α particles passed directly through the foil because the atom is mostly ...
... pudding model for the atom could not be correct. • The large deflections of the α particles could be caused only by a center of concentrated positive charge that would repel the _______________ charged α particles. • Most of the α particles passed directly through the foil because the atom is mostly ...
File - docstover.org
... Using the periodic table, answer the following questions: 1. Which element stands alone in its family? ______________ 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius A or C? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius C or D? _____________ 4. Which element has a higher electronegativity? A ...
... Using the periodic table, answer the following questions: 1. Which element stands alone in its family? ______________ 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius A or C? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius C or D? _____________ 4. Which element has a higher electronegativity? A ...
High School Curriculum Standards: Chemistry
... In the late 1700s solid evidence about the nature of matter, gained through quantitative scientific experiments, accumulated. Such evidence included the finding that during a chemical reaction matter was conserved. In the early 1800s a theory was proposed to explain these experimental facts. In this ...
... In the late 1700s solid evidence about the nature of matter, gained through quantitative scientific experiments, accumulated. Such evidence included the finding that during a chemical reaction matter was conserved. In the early 1800s a theory was proposed to explain these experimental facts. In this ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.