Six slides per page
... A trivial example is water as a solid (ice), liquid (water) and gas (steam). If there were no attraction between individual water molecules then water would only exist as a gas. Interactions between water molecules (INTERmolecular interactions) are responsible for liquid and solid water. ...
... A trivial example is water as a solid (ice), liquid (water) and gas (steam). If there were no attraction between individual water molecules then water would only exist as a gas. Interactions between water molecules (INTERmolecular interactions) are responsible for liquid and solid water. ...
fo-Balancing Chemical Notes
... In general, you only want to change any coefficient one time. If you change a coefficient a second time, you will probably cause one of the 'earlier' elements to become 'unbalanced'. Example: Combustion of ethanol Question: Balance the following equation for the combustion of ethanol. CH3CH2OH + O2 ...
... In general, you only want to change any coefficient one time. If you change a coefficient a second time, you will probably cause one of the 'earlier' elements to become 'unbalanced'. Example: Combustion of ethanol Question: Balance the following equation for the combustion of ethanol. CH3CH2OH + O2 ...
(iii) Formation of Hydrogen chloride molecule
... The shape of benzene is a planar regular hexagon, with bond angles of 120°. ...
... The shape of benzene is a planar regular hexagon, with bond angles of 120°. ...
halogen compounds organic chemistry
... 3. Explain the polarity in Chlorobenzene. Polarity of carbon-halogen bond: The sp2 hybridized carbon atom in the C-X bond in haloarene molecule is more electronegative than the sp3 hybrid carbon atom in alkyl halide. This carbon has fewer tendencies to release electrons to the chlorine atom and so t ...
... 3. Explain the polarity in Chlorobenzene. Polarity of carbon-halogen bond: The sp2 hybridized carbon atom in the C-X bond in haloarene molecule is more electronegative than the sp3 hybrid carbon atom in alkyl halide. This carbon has fewer tendencies to release electrons to the chlorine atom and so t ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... Amount of energy that must be absorbed by reactants in 53. their ground states to reach the transition state so that a reaction can occur (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 54. Energy change associated with a mole of gas and ions reacting with water (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 55. The energy change whe ...
... Amount of energy that must be absorbed by reactants in 53. their ground states to reach the transition state so that a reaction can occur (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 54. Energy change associated with a mole of gas and ions reacting with water (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 55. The energy change whe ...
Elements and Atoms
... Atomic Number: Number of protons and it is also the number of electrons in an atom of an element. Element’s Symbol: An abbreviation for the element. Elements Name ...
... Atomic Number: Number of protons and it is also the number of electrons in an atom of an element. Element’s Symbol: An abbreviation for the element. Elements Name ...
Page | 1 MATS1101 Chemistry notes semester 2 2012 TOPIC 1
... Using this theory we can explain three fundamental laws of chemical behaviour: 1. Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy: Matter is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Energy is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but it may be transformed from one form to another. ...
... Using this theory we can explain three fundamental laws of chemical behaviour: 1. Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy: Matter is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Energy is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but it may be transformed from one form to another. ...
Chem MCQ for Class-9th
... 13. Triple covalent bond involves how many electrons? a. Eight b. six c. four d.only three ...
... 13. Triple covalent bond involves how many electrons? a. Eight b. six c. four d.only three ...
The Periodic Table - Mrs Molchany`s Webpage
... increasingly negative moving from left to right. (exception: the addition of an electron to a noble gas would require the electron to reside in a new, higher-energy subshell. Occupying a higher-energy subshell is energetically unfavorable, so the electron affinity is positive, meaning that the ion w ...
... increasingly negative moving from left to right. (exception: the addition of an electron to a noble gas would require the electron to reside in a new, higher-energy subshell. Occupying a higher-energy subshell is energetically unfavorable, so the electron affinity is positive, meaning that the ion w ...
CHM 103 Lecture 11 S07
... energy to break the bonds in the reactants. • bonds between atoms of the reactants (N2 and O2) are broken and new bonds (NO) can form. ...
... energy to break the bonds in the reactants. • bonds between atoms of the reactants (N2 and O2) are broken and new bonds (NO) can form. ...
HT-7上逃逸电子行为的研究进展
... make these interesting measurements, then since you have LHCD on HT-7, you might also consider measuring the runaway probability function by varying the rf phase velocity. To my knowledge, such a direct measurement has not yet been done, though much of the physics has been inferred from current (mag ...
... make these interesting measurements, then since you have LHCD on HT-7, you might also consider measuring the runaway probability function by varying the rf phase velocity. To my knowledge, such a direct measurement has not yet been done, though much of the physics has been inferred from current (mag ...
Elements
... Chemical formulas – atoms are indicated by the element symbols; number of each atom is indicated by a subscript – a number that appears to the right of and below the symbol for the element ...
... Chemical formulas – atoms are indicated by the element symbols; number of each atom is indicated by a subscript – a number that appears to the right of and below the symbol for the element ...
Midterm Review - Closter Public Schools
... liquids, they _____________________________. In gases they ________________________. Matter is said to be ______________ when it is has only one type of particle. Matter is said to be ______________when it has more than one type of particle. A ______________ is a pure substance that contains only a ...
... liquids, they _____________________________. In gases they ________________________. Matter is said to be ______________ when it is has only one type of particle. Matter is said to be ______________when it has more than one type of particle. A ______________ is a pure substance that contains only a ...
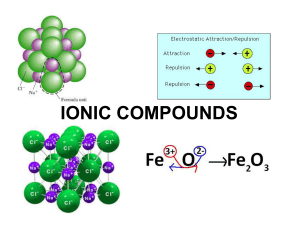
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... those 3A and 4A can form several different positive ions ...
... those 3A and 4A can form several different positive ions ...
Chapter 4.1 and 4.2 - science-b
... all elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Dalton was wrong about the “indivisible” part, but the rest of this tenet is still fundamental to chemistry. ...
... all elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Dalton was wrong about the “indivisible” part, but the rest of this tenet is still fundamental to chemistry. ...
Chapter 7
... • These are negatively charged ions resulting from a gain of electrons. • Nonmetals tend to add or share electrons into their highest occupied energy levels to become anions. This allows them to achieve an octet in their highest occupied energy level. • The charge for an anion is written with a numb ...
... • These are negatively charged ions resulting from a gain of electrons. • Nonmetals tend to add or share electrons into their highest occupied energy levels to become anions. This allows them to achieve an octet in their highest occupied energy level. • The charge for an anion is written with a numb ...
Period 6
... and arrangements of atoms in molecules. • In the formulas, dashes are made to represent bonds. ...
... and arrangements of atoms in molecules. • In the formulas, dashes are made to represent bonds. ...
Chemical Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... - There are 2 atoms H and 2 atoms O in the reactants. - There are 2 atoms H and 1 atom O in the product. To balance this equation, we take 2 water molecules containing 2 atoms O and 4 atoms H, and we take 2 hydrogen molecules and 1 oxygen molecule. H2 and H2 ...
... - There are 2 atoms H and 2 atoms O in the reactants. - There are 2 atoms H and 1 atom O in the product. To balance this equation, we take 2 water molecules containing 2 atoms O and 4 atoms H, and we take 2 hydrogen molecules and 1 oxygen molecule. H2 and H2 ...
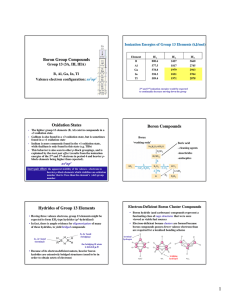
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... • Having three valence electrons, group 13 elements might be expected to form EH3-type hydrides (sp2-hybridized) • In fact, there is ample evidence for oligomerization of many of these hydrides, to yield bridged compounds ...
... • Having three valence electrons, group 13 elements might be expected to form EH3-type hydrides (sp2-hybridized) • In fact, there is ample evidence for oligomerization of many of these hydrides, to yield bridged compounds ...
Electron - HCC Learning Web
... • Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen make up 96% of living matter • Most of the remaining 4% consists of calcium, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur • Trace elements are those required by an organism in minute quantities ...
... • Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen make up 96% of living matter • Most of the remaining 4% consists of calcium, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur • Trace elements are those required by an organism in minute quantities ...
Honors-Final-Review-2014
... Describe what the valence electrons are doing. 4. Ionic compounds form when a _______________ bonds to a ______________. The resulting compound is called a _______________. Describe what the electrons are doing. 5. Review the properties of ionic and covalent compounds and list them below Ionic Prope ...
... Describe what the valence electrons are doing. 4. Ionic compounds form when a _______________ bonds to a ______________. The resulting compound is called a _______________. Describe what the electrons are doing. 5. Review the properties of ionic and covalent compounds and list them below Ionic Prope ...
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structure
... related to the fact that valence shells contain a single s orbital and three p orbitals that can accommodate up to eight electrons, and it is these orbitals that are most often involved in forming covalent bonds between nonmetals in covalent compounds. When determining whether elements have satisfie ...
... related to the fact that valence shells contain a single s orbital and three p orbitals that can accommodate up to eight electrons, and it is these orbitals that are most often involved in forming covalent bonds between nonmetals in covalent compounds. When determining whether elements have satisfie ...
Chemical Energetics
... • 3. a. The value of H depends on temp , pressure and concentrations of reactants. • b. H are measured under standard conditions : • Temperature = 298K ( 250 C ) • Pressure = 1 atm / 1.01 x 105 Pa • Concentrations = 1 mol dm-3 ...
... • 3. a. The value of H depends on temp , pressure and concentrations of reactants. • b. H are measured under standard conditions : • Temperature = 298K ( 250 C ) • Pressure = 1 atm / 1.01 x 105 Pa • Concentrations = 1 mol dm-3 ...
C. Adding acid shifts the equilibrium to the right
... Covalent compounds occur between two nonmetals or a nonmetal and hydrogen. In a covalent bond, atoms share electrons and neither atom has an ionic charge. The electronegativity difference of the bonding elements is less than 1.7. When hydrogen bonds with a nonmetal the bond is covalent. Characterist ...
... Covalent compounds occur between two nonmetals or a nonmetal and hydrogen. In a covalent bond, atoms share electrons and neither atom has an ionic charge. The electronegativity difference of the bonding elements is less than 1.7. When hydrogen bonds with a nonmetal the bond is covalent. Characterist ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.