Electrons
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bonds ...
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bonds ...
Reversed quantum-confined Stark effect and an asymmetric band
... the optical transitions and carrier dynamics related to the Ge dots in the development of Si-based optoelectronic devices. In spite of the fact that Si/ Ge interdiffusion will lead to some alloying of the dots we will refer to them as Ge dots. When an electric field is applied along a quantization d ...
... the optical transitions and carrier dynamics related to the Ge dots in the development of Si-based optoelectronic devices. In spite of the fact that Si/ Ge interdiffusion will lead to some alloying of the dots we will refer to them as Ge dots. When an electric field is applied along a quantization d ...
Chemistry basics powerpoint Chapter 2
... bonding partners An example is the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine After the transfer of an electron, both atoms have ...
... bonding partners An example is the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine After the transfer of an electron, both atoms have ...
Unit 3 Review Notes - Brinkmann chapter7_and_8_review1
... C3H5O2. The molecular mass of adipic acid is 146 g/mol. What is the molecular formula of adipic acid? 3. Multiply the empirical formula by this number to get the molecular formula. ...
... C3H5O2. The molecular mass of adipic acid is 146 g/mol. What is the molecular formula of adipic acid? 3. Multiply the empirical formula by this number to get the molecular formula. ...
HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY MINI-MOCK UNIT 2
... Which two sub-atomic particles are in the nucleus of an atom? ........................................................... and ............................................... ...
... Which two sub-atomic particles are in the nucleus of an atom? ........................................................... and ............................................... ...
ic199p5a
... to being the same size (as r+/r- -> 1) and the ZnS structure when the ions are most different in size. This rule, along with the fact that the sizes increase with incr. negative charge and decrease with incr. positive charge, along with the general dependance of atom sizes on their position in the p ...
... to being the same size (as r+/r- -> 1) and the ZnS structure when the ions are most different in size. This rule, along with the fact that the sizes increase with incr. negative charge and decrease with incr. positive charge, along with the general dependance of atom sizes on their position in the p ...
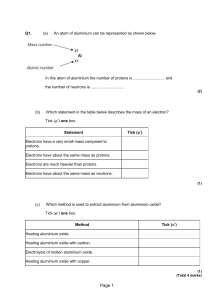
c2 atomic structure f pmh
... Which statement in the table below describes the mass of an electron? Tick ( ) one box. ...
... Which statement in the table below describes the mass of an electron? Tick ( ) one box. ...
CHEMISTRY: MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SPRING 2013 Multiple
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
Answer Key
... E) 42 g 9. The mass of 1.63 1021 silicon atoms is A) 1.04 104 g. B) 28.08 g. C) 2.71 10–23 g. D) 7.60 10–2 g. E) 4.58 1022 g. ...
... E) 42 g 9. The mass of 1.63 1021 silicon atoms is A) 1.04 104 g. B) 28.08 g. C) 2.71 10–23 g. D) 7.60 10–2 g. E) 4.58 1022 g. ...
Chapter 7-8-9
... a. linear c. trigonal planar b. bent d. tetrahedral 22. Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds? a. to become ions and attract each other b. to attain a noble-gas electron configuration c. to become more polar d. to increase their atomic numbers 23. Which molecule has a single covalent bond? ...
... a. linear c. trigonal planar b. bent d. tetrahedral 22. Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds? a. to become ions and attract each other b. to attain a noble-gas electron configuration c. to become more polar d. to increase their atomic numbers 23. Which molecule has a single covalent bond? ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 1. Democritus a. 400 BC, first suggested the existence of indivisible atoms b. No research, no experimental support 2. John Dalton a. late 1700’s conducted research and experiments b. result was Dalton’s atomic theory: 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms (we know ...
... 1. Democritus a. 400 BC, first suggested the existence of indivisible atoms b. No research, no experimental support 2. John Dalton a. late 1700’s conducted research and experiments b. result was Dalton’s atomic theory: 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms (we know ...
ď - Google Sites
... electronegativity is usually assigned on a developed scale – according to this scale, fluorine has been given the highest assigned electronegativity of 4.0 – cesium has the lowest assigned electronegativity of 0.8 metals tend to have low electronegativities non-metals tend to have high electro ...
... electronegativity is usually assigned on a developed scale – according to this scale, fluorine has been given the highest assigned electronegativity of 4.0 – cesium has the lowest assigned electronegativity of 0.8 metals tend to have low electronegativities non-metals tend to have high electro ...
M.Sc. 2015
... Consider the statements in the mechanism of halogenations of benzene: (i) chloronium ion can attack the π-electron cloud of benzene to form π-complex. (ii) the π-complex is then converted into σ-complex. (iii) the σ-complex thus formed is a carbonium ion which is stabilized by resonance. (i), (ii) a ...
... Consider the statements in the mechanism of halogenations of benzene: (i) chloronium ion can attack the π-electron cloud of benzene to form π-complex. (ii) the π-complex is then converted into σ-complex. (iii) the σ-complex thus formed is a carbonium ion which is stabilized by resonance. (i), (ii) a ...
Organic Structure Determination Analytical Chemistry
... DIRECTION OF THE BOND DIPOLE MOMENT the field can "pull" the atoms apart (if the frequency is matched) and thus increase the amplitude of the vibration (the atoms separate more), in this way the IR energy is absorbed into the molecule, the energy is "used" to make the bind vibrate with a larger ampl ...
... DIRECTION OF THE BOND DIPOLE MOMENT the field can "pull" the atoms apart (if the frequency is matched) and thus increase the amplitude of the vibration (the atoms separate more), in this way the IR energy is absorbed into the molecule, the energy is "used" to make the bind vibrate with a larger ampl ...
Dalton`s Laws worksheet
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory of Matter 1. Which of the following statements is part of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter? a. All atoms are identical b. All atoms of a given element are identical c. All atoms differ from one another d. Atoms of the same element can have a different shape 2. Dalton suggested ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory of Matter 1. Which of the following statements is part of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter? a. All atoms are identical b. All atoms of a given element are identical c. All atoms differ from one another d. Atoms of the same element can have a different shape 2. Dalton suggested ...
Problem
... • The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers n, l, ml and ms. – For a given orbital the values of n, l, and ml ...
... • The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers n, l, ml and ms. – For a given orbital the values of n, l, and ml ...
Year End Chemistry Review
... 4. Density as measured by water displacement: Find the density of a metal if its mass = 5.0 grams, the initial volume of water without metal = 10.0 mL and the final volume of water with metal = 12.5 mL. 5. Significant figures: How many significant figures are in each of the following: a) 0.003 g b) ...
... 4. Density as measured by water displacement: Find the density of a metal if its mass = 5.0 grams, the initial volume of water without metal = 10.0 mL and the final volume of water with metal = 12.5 mL. 5. Significant figures: How many significant figures are in each of the following: a) 0.003 g b) ...
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures
... ion that differ in the positions of lone pairs and multiple bonds but not in the positions of the atoms in the structure. It is as if the molecule or ion were able to shift from one of these structures to another by shifting pairs of electrons from one position to another. Resonance The hypothetical ...
... ion that differ in the positions of lone pairs and multiple bonds but not in the positions of the atoms in the structure. It is as if the molecule or ion were able to shift from one of these structures to another by shifting pairs of electrons from one position to another. Resonance The hypothetical ...
Test Objectives: Unit 1 – Measurement
... Define orbital (a region of space in the modern model that holds two electrons); know the difference between orbit and orbital ...
... Define orbital (a region of space in the modern model that holds two electrons); know the difference between orbit and orbital ...
Inorganic Chemistry Lesson 3
... formed by silver and oxygen has a formula Ag2 O. Using this information, can you predict a formula of a compound containing silver and chlorine? It is intuitively clear that, since oxygen binds to two atoms of hydrogen, valence of oxygen is as twice as big as valence of hydrogen. H2 O and Ag2 O form ...
... formed by silver and oxygen has a formula Ag2 O. Using this information, can you predict a formula of a compound containing silver and chlorine? It is intuitively clear that, since oxygen binds to two atoms of hydrogen, valence of oxygen is as twice as big as valence of hydrogen. H2 O and Ag2 O form ...
AP Biology
... the organelle or part of the organelle. The important concept is to note how the specific structure allows for the specific function to be accomplished. a. Nucleus ...
... the organelle or part of the organelle. The important concept is to note how the specific structure allows for the specific function to be accomplished. a. Nucleus ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.