fahad h. ahmad - Fahad`s Academy
... Where x = distance moved by the substance and; y = distance moved by the solvent Checking the Purity of Substances - Pure substances have FIXED MELTING AND BOILING POINTS. Pure water boils at 100oC and melts at 0oC. - Impure substances have NO FIXED MELTING AND BOILING POINTS. They melt and boil a ...
... Where x = distance moved by the substance and; y = distance moved by the solvent Checking the Purity of Substances - Pure substances have FIXED MELTING AND BOILING POINTS. Pure water boils at 100oC and melts at 0oC. - Impure substances have NO FIXED MELTING AND BOILING POINTS. They melt and boil a ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... The possession or use of any communications device is strictly prohibited when taking this examination. If you have or use any communications device, no matter how briefly, your examination will be invalidated and no score will be calculated for you. This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Us ...
... The possession or use of any communications device is strictly prohibited when taking this examination. If you have or use any communications device, no matter how briefly, your examination will be invalidated and no score will be calculated for you. This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Us ...
AP Chemistry Standards and Benchmarks
... • chemical reactivity and products of chemical reactions • relationships in the periodic table: horizontal, vertical and diagonal (with examples from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, the first series of transition elements) • introduction to organic chemistry: hydrocarbons and functio ...
... • chemical reactivity and products of chemical reactions • relationships in the periodic table: horizontal, vertical and diagonal (with examples from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, the first series of transition elements) • introduction to organic chemistry: hydrocarbons and functio ...
Here`s - Sonlight
... Compare this incredibly logical system of units to the chaotic English system. If we want to measure something short, we use the inch unit, which is equal to one-twelfth of a foot. On the other hand, if we want to measure something with small volume, we might use the quart unit, which is equal to on ...
... Compare this incredibly logical system of units to the chaotic English system. If we want to measure something short, we use the inch unit, which is equal to one-twelfth of a foot. On the other hand, if we want to measure something with small volume, we might use the quart unit, which is equal to on ...
chemistry
... may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. Base your answers to questions 66 through 68 on the information below. In the early 1800s, John Dalton proposed an atomic theory that was based on experimental observations made by several scientists. Three concepts of Dalto ...
... may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. Base your answers to questions 66 through 68 on the information below. In the early 1800s, John Dalton proposed an atomic theory that was based on experimental observations made by several scientists. Three concepts of Dalto ...
Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12
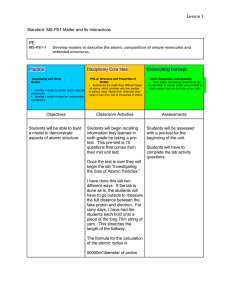
... At the same temperature gases have the highest potential and overall energy 33. The potential energy of the particles is the (highest/ lowest) in the gaseous state and (highest/ lowest) in the solid state. What happens when a liquid in a closed bottle evaporates 34. When some of the liquid in a clo ...
... At the same temperature gases have the highest potential and overall energy 33. The potential energy of the particles is the (highest/ lowest) in the gaseous state and (highest/ lowest) in the solid state. What happens when a liquid in a closed bottle evaporates 34. When some of the liquid in a clo ...
Energetics - chemistryatdulwich
... broken and new bonds of different strengths are being made. When we change the bonds within a system, we are changing the way atoms and electrons interact with each other, we change the way in which they are attracted and repelled to each other. This is why each bond has its own strength and energy ...
... broken and new bonds of different strengths are being made. When we change the bonds within a system, we are changing the way atoms and electrons interact with each other, we change the way in which they are attracted and repelled to each other. This is why each bond has its own strength and energy ...
program
... make a connection between bond types, lattice type, and the properties of a substance: • melting point and boiling point; • hardness and brittleness; • absence or presence of electrical conductivity in the solid, liquid, and/or dissolved ...
... make a connection between bond types, lattice type, and the properties of a substance: • melting point and boiling point; • hardness and brittleness; • absence or presence of electrical conductivity in the solid, liquid, and/or dissolved ...
www.fahadsacademy.com
... Hydrogen atom has one valency. To become stable with hydrogen atom, it needs one more electron, just like helium which has 2 valency. When 2 hydrogen atoms join, they share their electrons, on which, the share becomes 2 electrons, which is now a noble gas configuration, being shared between these 2 ...
... Hydrogen atom has one valency. To become stable with hydrogen atom, it needs one more electron, just like helium which has 2 valency. When 2 hydrogen atoms join, they share their electrons, on which, the share becomes 2 electrons, which is now a noble gas configuration, being shared between these 2 ...
Electron - CoolHub
... about a different atom. The periodic table shows all the atoms that everything in the known universe is made from. It’s kind of like the alphabet in which only 26 letters, in different combinations, make up many thousands of words. The 100 or so atoms of the periodic table, in different combinations ...
... about a different atom. The periodic table shows all the atoms that everything in the known universe is made from. It’s kind of like the alphabet in which only 26 letters, in different combinations, make up many thousands of words. The 100 or so atoms of the periodic table, in different combinations ...
Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12 Answer Key
... At the same temperature gases have the highest potential and overall energy 33. The potential energy of the particles is the (highest/ lowest) in the gaseous state and (highest/ lowest) in the solid state. What happens when a liquid in a closed bottle evaporates 34. When some of the liquid in a clo ...
... At the same temperature gases have the highest potential and overall energy 33. The potential energy of the particles is the (highest/ lowest) in the gaseous state and (highest/ lowest) in the solid state. What happens when a liquid in a closed bottle evaporates 34. When some of the liquid in a clo ...
File - jj-sct
... In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule ...
... In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule ...
Lecture Presentation Book - Pottstown School District
... In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally ...
... In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally ...
lecture 3
... with two electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have eight electrons in their valence shell Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... with two electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have eight electrons in their valence shell Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Novel Class of Heterometallic Cubane and Boride Clusters
... tetrahedron. An alternative electron-counting method is also possible for this cluster. The 11-vertex polyhedron is a deltahedron with six degree 4 vertices for the four molybdenum atoms. The elemental polyhedral topology demands that among the remaining seven vertices two must be of degree 5 and th ...
... tetrahedron. An alternative electron-counting method is also possible for this cluster. The 11-vertex polyhedron is a deltahedron with six degree 4 vertices for the four molybdenum atoms. The elemental polyhedral topology demands that among the remaining seven vertices two must be of degree 5 and th ...
The Mole - Cloudfront.net
... the molecular mass/weight is the same numerical value as 1 mole of molecules. Only the units are different. (This is the beauty of Avogadro’s Number!) ...
... the molecular mass/weight is the same numerical value as 1 mole of molecules. Only the units are different. (This is the beauty of Avogadro’s Number!) ...
Periodic table Periodic Trends
... You can think of this displacement reaction as being a competition between the chlorine in the bromine for an extra electron. Remember that the atomic radius increases down a group. The atomic radius of chlorine (100pm) is smaller than that of bromine (117pm) so chlorine has a stronger attraction fo ...
... You can think of this displacement reaction as being a competition between the chlorine in the bromine for an extra electron. Remember that the atomic radius increases down a group. The atomic radius of chlorine (100pm) is smaller than that of bromine (117pm) so chlorine has a stronger attraction fo ...
Chemistry Notes for the Whole Year Powerpoint
... electrons so as to have eight electrons in their outer electron shell. This means that all atoms, in a Lewis structure, must have eight valence electrons around them (they can be either bonded or lone pair electrons). • Hydrogen and helium are exceptions to the octet rule. There is one more element ...
... electrons so as to have eight electrons in their outer electron shell. This means that all atoms, in a Lewis structure, must have eight valence electrons around them (they can be either bonded or lone pair electrons). • Hydrogen and helium are exceptions to the octet rule. There is one more element ...
Nickel(II) cis- and trans-Dimethyl Complexes of
... been prepared and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, and the complex [Ni(tBuCCmeth)Me2] (3) has been observed spectroscopically. Thermal decomposition studies show that 2 eliminates methane rapidly and quantitatively above 50 °C by a predominantly unimolecular dissociative pathway wi ...
... been prepared and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, and the complex [Ni(tBuCCmeth)Me2] (3) has been observed spectroscopically. Thermal decomposition studies show that 2 eliminates methane rapidly and quantitatively above 50 °C by a predominantly unimolecular dissociative pathway wi ...
George Facer`s A level Chemistry
... and trusted textbooks and revision guides, innovative, flexible and interactive digital resources, topical student magazines and specialist-led CPD events will ensure you are supported in all your teaching and assessment needs. We are working with Edexcel to get these resources endorsed: Edexcel A l ...
... and trusted textbooks and revision guides, innovative, flexible and interactive digital resources, topical student magazines and specialist-led CPD events will ensure you are supported in all your teaching and assessment needs. We are working with Edexcel to get these resources endorsed: Edexcel A l ...
Standard - Santee Education Complex
... place in NaCl is different than that in HCl. This gives NaCl and HCl very different structures, appearances, and properties.What other differences are noticeable among molecules that result from different types of chemical bonding? Think about what happens when a bunch of sodium and chlorine ions jo ...
... place in NaCl is different than that in HCl. This gives NaCl and HCl very different structures, appearances, and properties.What other differences are noticeable among molecules that result from different types of chemical bonding? Think about what happens when a bunch of sodium and chlorine ions jo ...
Chapter 1: Matter and Measurement
... Read atomic masses. Read the ions formed by main group elements. Read the electron configuration. Learn trends in physical and chemical properties. ...
... Read atomic masses. Read the ions formed by main group elements. Read the electron configuration. Learn trends in physical and chemical properties. ...
Monte Carlo Simulation of Water Radiolysis for
... + H2O2. In this work for the branching ratio we use 0.55 to H2 + H2O2 and 0.45 to H2O in order to reproduce consistent G-values for various radical species produced by electrons. Table 2 shows dissociation schemes and branching ratios for the physical products: e–sub, H2O+ and H2O*. For the spatial ...
... + H2O2. In this work for the branching ratio we use 0.55 to H2 + H2O2 and 0.45 to H2O in order to reproduce consistent G-values for various radical species produced by electrons. Table 2 shows dissociation schemes and branching ratios for the physical products: e–sub, H2O+ and H2O*. For the spatial ...
AP Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... 9.52 Draw a Lewis structure for (a) SiF4; (b) SeCL2; (c) COF2 (C central); (d) PH4 +; (e) C2F4. 9.54 Draw Lewis structure of all the important resonance forms of each of the following: (a) NO2; (b) NO2F (N central); (c) HNO3 (HONO2). 9.56 Draw a Lewis structure in the following g: (a) IF5; (b) AlH4- ...
... 9.52 Draw a Lewis structure for (a) SiF4; (b) SeCL2; (c) COF2 (C central); (d) PH4 +; (e) C2F4. 9.54 Draw Lewis structure of all the important resonance forms of each of the following: (a) NO2; (b) NO2F (N central); (c) HNO3 (HONO2). 9.56 Draw a Lewis structure in the following g: (a) IF5; (b) AlH4- ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.