Final Exam Review Packet
... - The molecular mass is the mass of one mole of any substance. 6. The advantage of using moles is that the quantity will be much smaller and a number that is easier to deal with than if you use grams or pounds. Also, you can compare two quantities of moles to each other, but you cannot compare grams ...
... - The molecular mass is the mass of one mole of any substance. 6. The advantage of using moles is that the quantity will be much smaller and a number that is easier to deal with than if you use grams or pounds. Also, you can compare two quantities of moles to each other, but you cannot compare grams ...
Slide 1
... PT contains exactly 6.02x1023 atoms of that element. • And is equal to how much 1 mole of that sample would weigh in grams ...
... PT contains exactly 6.02x1023 atoms of that element. • And is equal to how much 1 mole of that sample would weigh in grams ...
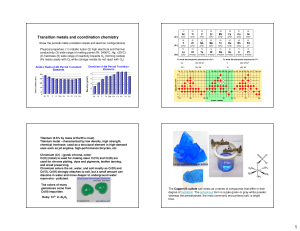
Transition metals and coordination chemistry
... metals. Detergents: complexation of Ca2+ and Mg2+ (reduction of water hardness). Photography: use of Fe(III)EDTA as oxidizing agent. Pulp and paper industry: complexation of heavy metals during chlorine-free bleaching, stabilization of hydrogen peroxide. Textile industry: complexation of heavy metal ...
... metals. Detergents: complexation of Ca2+ and Mg2+ (reduction of water hardness). Photography: use of Fe(III)EDTA as oxidizing agent. Pulp and paper industry: complexation of heavy metals during chlorine-free bleaching, stabilization of hydrogen peroxide. Textile industry: complexation of heavy metal ...
Chemistry
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The microscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been intr ...
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The microscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been intr ...
Energetics Past Paper Questions
... The lattice enthalpy of an ionic compound can be calculated using a Born-Haber cycle. Using lithium fluoride as the example, construct a Born-Haber cycle, labelling the cycle with the formulas and state symbols of the species present at each stage. (6) Two values of the lattice enthalpies for each o ...
... The lattice enthalpy of an ionic compound can be calculated using a Born-Haber cycle. Using lithium fluoride as the example, construct a Born-Haber cycle, labelling the cycle with the formulas and state symbols of the species present at each stage. (6) Two values of the lattice enthalpies for each o ...
Notes for Quarter I
... light passing through a prism can be separated into its component colors because of refraction also (Fig. 7, p. 648). Diffraction is the bending of waves around barriers or through openings. Light waves can’t diffract much around large obstacles such as buildings (which is why we can’t see around co ...
... light passing through a prism can be separated into its component colors because of refraction also (Fig. 7, p. 648). Diffraction is the bending of waves around barriers or through openings. Light waves can’t diffract much around large obstacles such as buildings (which is why we can’t see around co ...
AP Chemistry Review Preparing for the AP
... Know the 6 strong acids HCl, HI, HBr, H2SO4, HClO4, HNO3 and the one weak by formula acetic acid CH3COOH, everything else is weak. Remember that strong acids/bases don’t make buffers!!! You should be 100% confident what ionizes and what doesn’t Know the strong bases: Group 1 hydroxides, Ba(OH) 2, Sr ...
... Know the 6 strong acids HCl, HI, HBr, H2SO4, HClO4, HNO3 and the one weak by formula acetic acid CH3COOH, everything else is weak. Remember that strong acids/bases don’t make buffers!!! You should be 100% confident what ionizes and what doesn’t Know the strong bases: Group 1 hydroxides, Ba(OH) 2, Sr ...
Chapter 2 Elements and Compounds 2.1 The Structure of the Atom
... Every carbon atom has six protons, and the mass of electrons is negligible; this means we can conclude that the carbon atoms shown in Interactive Figure 2.1.2 have different mass numbers because each has a different number of neutrons. Atoms that have the same atomic number (Z) but different mass nu ...
... Every carbon atom has six protons, and the mass of electrons is negligible; this means we can conclude that the carbon atoms shown in Interactive Figure 2.1.2 have different mass numbers because each has a different number of neutrons. Atoms that have the same atomic number (Z) but different mass nu ...
lecture slides file
... Chemical properties describe the ability of the substance to form new substances, either by decomposition or reaction with other substances (corrosiveness, flammability, acidity, toxicity, etc.). No two substances have identical physical and chemical properties. Physical changes are reversible chang ...
... Chemical properties describe the ability of the substance to form new substances, either by decomposition or reaction with other substances (corrosiveness, flammability, acidity, toxicity, etc.). No two substances have identical physical and chemical properties. Physical changes are reversible chang ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical
... (c). the sum of atomic weights of each atom in its chemical formula (d). the weight of a sample of the substance. 33. The mass % of C in methane (CH4) is _________. (a). 25.13 (b). 13.36 (c). 92.26 (d).74.87 Explanation: Calculate the formula mass of methane first (= 16.042 g/mol) and then divide th ...
... (c). the sum of atomic weights of each atom in its chemical formula (d). the weight of a sample of the substance. 33. The mass % of C in methane (CH4) is _________. (a). 25.13 (b). 13.36 (c). 92.26 (d).74.87 Explanation: Calculate the formula mass of methane first (= 16.042 g/mol) and then divide th ...
3: Haloalkanes, Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity difference for a C-H bond suggests that C is (δ-) while H is (δ+), however the magnitude of the electronegativity difference is so small tha ...
... The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity difference for a C-H bond suggests that C is (δ-) while H is (δ+), however the magnitude of the electronegativity difference is so small tha ...
chapter 23 the transition elements and their
... Name nickel as nickel(II) to indicate oxidation state. Ligands are six (hexa-) waters (aqua). Put together with chloride anions to give hexaaquanickel(II) chloride. b) The cation is [Cr(en)3]n+ and the anion is ClO4–, the perchlorate ion. The charge on the cation is +3 to make a neutral salt in comb ...
... Name nickel as nickel(II) to indicate oxidation state. Ligands are six (hexa-) waters (aqua). Put together with chloride anions to give hexaaquanickel(II) chloride. b) The cation is [Cr(en)3]n+ and the anion is ClO4–, the perchlorate ion. The charge on the cation is +3 to make a neutral salt in comb ...
2.6 M - Thierry Karsenti
... atoms in the cyclic structure is other than carbon. Heterocyclic componds may be aliphatic or aromatic 15. Isomers: These are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Isomers are further subdivided into: (a) structural isomers, (b) geometrical isomers and (c) stereoisomers(optical i ...
... atoms in the cyclic structure is other than carbon. Heterocyclic componds may be aliphatic or aromatic 15. Isomers: These are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Isomers are further subdivided into: (a) structural isomers, (b) geometrical isomers and (c) stereoisomers(optical i ...
3: Haloalkanes, Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity difference for a C-H bond suggests that C is (δ-) while H is (δ+), however the magnitude of the electronegativity difference is so small tha ...
... The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity difference for a C-H bond suggests that C is (δ-) while H is (δ+), however the magnitude of the electronegativity difference is so small tha ...
CHAPTER 23 THE TRANSITION ELEMENTS AND THEIR
... As manganese is bonded to more oxygen atoms in its different oxides, its oxidation number becomes more positive. In solution a water molecule is attracted to the increasingly positive manganese and one of its protons becomes easier to lose. ...
... As manganese is bonded to more oxygen atoms in its different oxides, its oxidation number becomes more positive. In solution a water molecule is attracted to the increasingly positive manganese and one of its protons becomes easier to lose. ...
Chapter 2 - San Joaquin Memorial High School
... 1691), who carefully measured the relationship between the pressure and volume of air. When Boyle published his book The Skeptical Chymist in 1661, the quantitative sciences of physics and chemistry were born. In addition to his results on the quantitative behavior of gases, Boyle’s other major cont ...
... 1691), who carefully measured the relationship between the pressure and volume of air. When Boyle published his book The Skeptical Chymist in 1661, the quantitative sciences of physics and chemistry were born. In addition to his results on the quantitative behavior of gases, Boyle’s other major cont ...
Chapter 4: Oxidation and Reduction MH5 4
... balancing of redox equations. They simplify the electron bookkeeping. Each atom in a compound can be assigned an oxidation number. Rules for assigning Oxidation Numbers : 1. Any allotrope of any element in the free state has an oxidation number of zero. (i.e. C(Diamond) , C(Graphite) , C(Gas) for C ...
... balancing of redox equations. They simplify the electron bookkeeping. Each atom in a compound can be assigned an oxidation number. Rules for assigning Oxidation Numbers : 1. Any allotrope of any element in the free state has an oxidation number of zero. (i.e. C(Diamond) , C(Graphite) , C(Gas) for C ...
chapter 3
... This is a balanced equation - same number of H and O atoms on both sides. To balance an equation, we adjust the coefficients - these are numbers in front of reactant and product molecules. BALANCING SUGGESTIONS: 1) Change coefficients NOT subscripts. 2) Balance elements in the most complex formula f ...
... This is a balanced equation - same number of H and O atoms on both sides. To balance an equation, we adjust the coefficients - these are numbers in front of reactant and product molecules. BALANCING SUGGESTIONS: 1) Change coefficients NOT subscripts. 2) Balance elements in the most complex formula f ...
regents chemistry midterm - irondequoit 2014_entire exam w key
... 3) The forming of the H–Cl bond absorbs energy. 4) The forming of the H–Cl bond releases energy. 26. Which is an empirical formula? 1) C2H2 3) H2O2 2) H2O 4) C6Hl2O6 27. Which symbol represents an atom in the ground state with the most stable valence electron configuration? 1) B 3) Li 2) O 4) Ne 28. ...
... 3) The forming of the H–Cl bond absorbs energy. 4) The forming of the H–Cl bond releases energy. 26. Which is an empirical formula? 1) C2H2 3) H2O2 2) H2O 4) C6Hl2O6 27. Which symbol represents an atom in the ground state with the most stable valence electron configuration? 1) B 3) Li 2) O 4) Ne 28. ...
1 What is the angular momentum quantum number (l) value for the
... Which of the following covalent single bonds is the shortest based on the atomic radius trends in the periodic table? A C–F CORRECT: The smaller the atomic radii of the bonding atoms the shorter the bond. Atomic radius generally decreases left to right across a period and increases down a group in ...
... Which of the following covalent single bonds is the shortest based on the atomic radius trends in the periodic table? A C–F CORRECT: The smaller the atomic radii of the bonding atoms the shorter the bond. Atomic radius generally decreases left to right across a period and increases down a group in ...
Chem 150 Unit 2 - Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups
... • Esters, on the other hand, produce the sweet, often pleasant order associated with flowers, perfumes and various natural and artificial flavorings. The next slide shows Figure 4.24 from Raymond, which gives some specific examples. ...
... • Esters, on the other hand, produce the sweet, often pleasant order associated with flowers, perfumes and various natural and artificial flavorings. The next slide shows Figure 4.24 from Raymond, which gives some specific examples. ...
X PS EM - deo kadapa
... Ans:- (a) Heat:- Heat is form of energy that is flows from a hotter to a cooler body. (b) Temperature :- Temperature is the measure of the degree of hotness or coldness. (c) Thermal equilibrium:- Thermal equilibrium denotes a state of a body where it neither receives nor gives out heat energy. (d) C ...
... Ans:- (a) Heat:- Heat is form of energy that is flows from a hotter to a cooler body. (b) Temperature :- Temperature is the measure of the degree of hotness or coldness. (c) Thermal equilibrium:- Thermal equilibrium denotes a state of a body where it neither receives nor gives out heat energy. (d) C ...
Document
... The first time we did an experiment with copper sulphate pentahydrate(CuSO4.5H2O) I was fascinated with it’s blue color. The colour of copper in metal form is brownish, and it’s colour in solution is blue. Although we know that reactants lose their properties when forming a product, I wondered why i ...
... The first time we did an experiment with copper sulphate pentahydrate(CuSO4.5H2O) I was fascinated with it’s blue color. The colour of copper in metal form is brownish, and it’s colour in solution is blue. Although we know that reactants lose their properties when forming a product, I wondered why i ...
AP Chemistry
... In the procedure described above, 46.00 mL of 0.03109 M K2Cr2O7 was added to the ore sample after it was dissolved in acid. When the chemical reaction had progressed as completely as possible, the amount of unreacted (excess) Cr2O72- was determined by titrating the solution with 0.110 M Fe(NO3)2. Th ...
... In the procedure described above, 46.00 mL of 0.03109 M K2Cr2O7 was added to the ore sample after it was dissolved in acid. When the chemical reaction had progressed as completely as possible, the amount of unreacted (excess) Cr2O72- was determined by titrating the solution with 0.110 M Fe(NO3)2. Th ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.