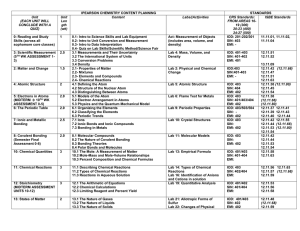
Organic Chemistry - University of California, Riverside
... The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity difference for a C-H bond suggests that C is (δ-) while H is (δ+), however the magnitude of the electronegativity difference is so small tha ...
... The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity difference for a C-H bond suggests that C is (δ-) while H is (δ+), however the magnitude of the electronegativity difference is so small tha ...
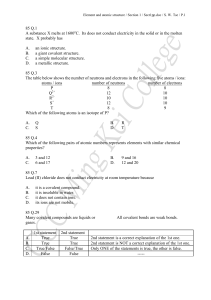
85 Q.1 A substance X melts at 1600oC. Its does
... M is an element in the third period of the Periodic Table. M forms a sulphate which has the formula M2(SO4)3. The formula of the nitrate of M is A. C. ...
... M is an element in the third period of the Periodic Table. M forms a sulphate which has the formula M2(SO4)3. The formula of the nitrate of M is A. C. ...
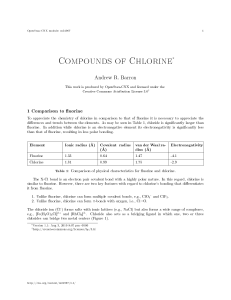
Compounds of Chlorine
... more than one bond, means that higher uorides of chlorine are also known, i.e., ClF3 and ClF5 . Chlorine tri uoride (CF3 , Bp = 11.75 ◦ C) is a useful uorinating agent, that is prepared by the high temperature reaction of elemental chlorine and uorine, is a useful uorinating age. The gaseous pen ...
... more than one bond, means that higher uorides of chlorine are also known, i.e., ClF3 and ClF5 . Chlorine tri uoride (CF3 , Bp = 11.75 ◦ C) is a useful uorinating agent, that is prepared by the high temperature reaction of elemental chlorine and uorine, is a useful uorinating age. The gaseous pen ...
Cleaning Up With Atom Economy
... materials or reagents into the final product. It is essentially pollution prevention at the molecular level. For example, a chemist practicing atom economy would choose to synthesize a needed product by putting together basic building blocks, rather than by breaking down a much larger starting mater ...
... materials or reagents into the final product. It is essentially pollution prevention at the molecular level. For example, a chemist practicing atom economy would choose to synthesize a needed product by putting together basic building blocks, rather than by breaking down a much larger starting mater ...
CHEMISTRY
... know, what they need to know, and any formulas that may help. Sometimes a problem may have numbers or other information that is not important for a calculation. Help the students discern what is and what is not relevant to solve a problem. 2. A math review would probably be advisable. Review basic a ...
... know, what they need to know, and any formulas that may help. Sometimes a problem may have numbers or other information that is not important for a calculation. Help the students discern what is and what is not relevant to solve a problem. 2. A math review would probably be advisable. Review basic a ...
chemistry
... (1) They have identical molecular and identical properties. (2) They have identical molecular and different properties. (3) They have different molecular and identical properties. (4) They have different molecular and different properties. ...
... (1) They have identical molecular and identical properties. (2) They have identical molecular and different properties. (3) They have different molecular and identical properties. (4) They have different molecular and different properties. ...
PDF on arxiv.org - at www.arxiv.org.
... predicting chemical properties. While many twentieth century bonding models provide useful information for a variety of chemical systems, these models are sometimes less insightful for more lofty goals such as designing metalloenzymes. The design process of novel catalysts could be improved if more ...
... predicting chemical properties. While many twentieth century bonding models provide useful information for a variety of chemical systems, these models are sometimes less insightful for more lofty goals such as designing metalloenzymes. The design process of novel catalysts could be improved if more ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Element “X” is actually the real element ________________________________. Regions in space occupied by electrons are called ___________________________ Write the ground state electron configurations (eg. 1s2 2s2 2p6) for the following atoms or ions. You may use the core notation. a) ...
... Element “X” is actually the real element ________________________________. Regions in space occupied by electrons are called ___________________________ Write the ground state electron configurations (eg. 1s2 2s2 2p6) for the following atoms or ions. You may use the core notation. a) ...
CP Chemistry - Final Exam Review KEY
... An excited atom moves up to a higher energy level. On the way down, it releases the extra energy as light. Each element has its own electron configuration and its own color released from the electrons. ...
... An excited atom moves up to a higher energy level. On the way down, it releases the extra energy as light. Each element has its own electron configuration and its own color released from the electrons. ...
The Mole
... an amount equal to the atomic mass of the element expressed in grams. • Example: for Neon, Atomic Mass = 20.18 amu Molar Mass = 20.18 g ...
... an amount equal to the atomic mass of the element expressed in grams. • Example: for Neon, Atomic Mass = 20.18 amu Molar Mass = 20.18 g ...
C H
... Configuration of a molecule – three-dimentional arrangement of atoms in the molecule. The ability to form two or more molecules with different configuration is called stereoisomerism. Stereocenter is defined as an atom bearing groups such that an interchanging of any two groups leads to a stereoisom ...
... Configuration of a molecule – three-dimentional arrangement of atoms in the molecule. The ability to form two or more molecules with different configuration is called stereoisomerism. Stereocenter is defined as an atom bearing groups such that an interchanging of any two groups leads to a stereoisom ...
answers to part a of the national high school
... the symbol, or they could have calculated the molar mass from the formula (but in the latter case they would have lost precious time). The formula given in the question is MnSiO3 3Mn2O3, and the question focuses on understanding what this type of formula means. The dot in the middle of the formula ...
... the symbol, or they could have calculated the molar mass from the formula (but in the latter case they would have lost precious time). The formula given in the question is MnSiO3 3Mn2O3, and the question focuses on understanding what this type of formula means. The dot in the middle of the formula ...
Chemical Equations
... Suggestions to Balance Equations Work with elements that appear in the fewest formulas first (in one formula on “each side” of the reaction arrow. Proceed to elements appearing in greater and greater numbers of formulas. Always check to see that elements are in same numbers on both sides. ...
... Suggestions to Balance Equations Work with elements that appear in the fewest formulas first (in one formula on “each side” of the reaction arrow. Proceed to elements appearing in greater and greater numbers of formulas. Always check to see that elements are in same numbers on both sides. ...
Q - PIMS
... The substance whose analysis is required for the separation of isotopes is converted into vapours. The pressure of vapours is reduced to 106—107 torr. These vapours at low pressure are allowed to enter the ionization chamber. ...
... The substance whose analysis is required for the separation of isotopes is converted into vapours. The pressure of vapours is reduced to 106—107 torr. These vapours at low pressure are allowed to enter the ionization chamber. ...
SELECTED ANSWERS
... The Lewis structure shows the two O–H covalent bonds and the two lone pairs on the oxygen atom. The space-filling model provides the most accurate representation of the electron charge clouds for the atoms and the bonding electrons. The ball-and-stick model emphasizes the molecule’s correct molecula ...
... The Lewis structure shows the two O–H covalent bonds and the two lone pairs on the oxygen atom. The space-filling model provides the most accurate representation of the electron charge clouds for the atoms and the bonding electrons. The ball-and-stick model emphasizes the molecule’s correct molecula ...
Beginning Chemistry
... its structure, the changes which it undergoes, and the laws governing those changes. Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Any material object, no matter how large or small, is composed of matter. In contrast, light, heat, and sound are forms of energy. Energy is the ability to produc ...
... its structure, the changes which it undergoes, and the laws governing those changes. Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Any material object, no matter how large or small, is composed of matter. In contrast, light, heat, and sound are forms of energy. Energy is the ability to produc ...
Teaching with CAChe - Photochemical Dynamics Group
... began when we found unpredicted results; the results often pointed out our own misconceptions about the underlying chemistry. Presently, we site license CAChe software. The site license has made CAChe accessible to faculty and students; CAChe is available on all department and campus computer lab ma ...
... began when we found unpredicted results; the results often pointed out our own misconceptions about the underlying chemistry. Presently, we site license CAChe software. The site license has made CAChe accessible to faculty and students; CAChe is available on all department and campus computer lab ma ...
CHAPTER I
... Electron spin. Three quantum numbers (n, ℓ , and mℓ ) allow us to define the orbital for an electron. To describe completely an electron in an atom with many electrons, however, we still need one more quantum number, the electron spin quantum number, ms. In approximately 1920, theoretical chemists r ...
... Electron spin. Three quantum numbers (n, ℓ , and mℓ ) allow us to define the orbital for an electron. To describe completely an electron in an atom with many electrons, however, we still need one more quantum number, the electron spin quantum number, ms. In approximately 1920, theoretical chemists r ...
Exam No. 1
... Born-Haber cycle relates the lattice energy of an ionic compound to other theoretical data. (b) The amount of energy released when one mole of ionic crystal is formed from its constituent ions in the gaseous phase is known as lattice energy. **(c) Lowering the energy of a system is associated to a d ...
... Born-Haber cycle relates the lattice energy of an ionic compound to other theoretical data. (b) The amount of energy released when one mole of ionic crystal is formed from its constituent ions in the gaseous phase is known as lattice energy. **(c) Lowering the energy of a system is associated to a d ...
Acids and Bases
... The tendency of soft acids to bond to soft bases and of hard acids to bond to hard bases explains certain aspects of the Goldschmidt classification of the elements into 4 types. (2 of the classes are the lithophile elements and the chalcophile elements.) ...
... The tendency of soft acids to bond to soft bases and of hard acids to bond to hard bases explains certain aspects of the Goldschmidt classification of the elements into 4 types. (2 of the classes are the lithophile elements and the chalcophile elements.) ...
Photoactivation mechanism of PAmCherry based on crystal
... 4° (Fig. 1 A). As none of the torsion angles is 0° or 180°, the C atom in Tyr-67 has sp3 hybridization, not sp2 hybridization as observed in mCherry (15). This suggests that PAmCherry1 in the OFF state has a single bond, not a double bond, between the C atom in Tyr-67 and the imidazol-5-ol ring. T ...
... 4° (Fig. 1 A). As none of the torsion angles is 0° or 180°, the C atom in Tyr-67 has sp3 hybridization, not sp2 hybridization as observed in mCherry (15). This suggests that PAmCherry1 in the OFF state has a single bond, not a double bond, between the C atom in Tyr-67 and the imidazol-5-ol ring. T ...
Course Map_2011-2012 - Kenwood Academy High School
... 12.11.51 Understand the values of standard temperature and pressure (STP): 0° Celsius and 1 atm. 12.11.52 Understand how to convert between Celsius and Kelvin temperature scales. Understand that there is no temperature lower than 0 Kelvin, or absolute zero. ...
... 12.11.51 Understand the values of standard temperature and pressure (STP): 0° Celsius and 1 atm. 12.11.52 Understand how to convert between Celsius and Kelvin temperature scales. Understand that there is no temperature lower than 0 Kelvin, or absolute zero. ...
Final Exam Review Packet
... - The molecular mass is the mass of one mole of any substance. 6. The advantage of using moles is that the quantity will be much smaller and a number that is easier to deal with than if you use grams or pounds. Also, you can compare two quantities of moles to each other, but you cannot compare grams ...
... - The molecular mass is the mass of one mole of any substance. 6. The advantage of using moles is that the quantity will be much smaller and a number that is easier to deal with than if you use grams or pounds. Also, you can compare two quantities of moles to each other, but you cannot compare grams ...
Chapter 3 Molecules Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical
... their atoms, the order of atom attachment, and the kind of attachment. They do not directly describe the three-dimensional shape but an experienced chemist can make a good shape, guess at it. use lines to represent covalent bonds Each line describes the number of electrons shared by the bonded ...
... their atoms, the order of atom attachment, and the kind of attachment. They do not directly describe the three-dimensional shape but an experienced chemist can make a good shape, guess at it. use lines to represent covalent bonds Each line describes the number of electrons shared by the bonded ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.