Periodic Table Puzzle
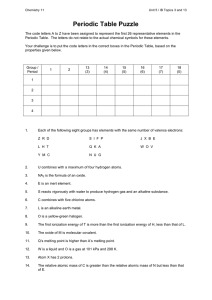
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the properti ...
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the properti ...
INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM MECHANICS I I mention in class
... two-dimensional space. When the electron is bound to one proton it has an energy E0 < 0. But there is always a small probability for it to tunnel through the other proton (with a probability amplitude T ) so the full hamiltonian (well, the crude approximation to it in the two-dimensional Hilbert spa ...
... two-dimensional space. When the electron is bound to one proton it has an energy E0 < 0. But there is always a small probability for it to tunnel through the other proton (with a probability amplitude T ) so the full hamiltonian (well, the crude approximation to it in the two-dimensional Hilbert spa ...
Chapter 19: Fermi
... • In this model, the free electrons move in a potential box or well whose walls coincide with the boundaries of the specimen. They occupy energy states up to the so-called Fermi level, which is the chemical potential μ(T) . The work function φ is the energy required to remove an electron at the Fer ...
... • In this model, the free electrons move in a potential box or well whose walls coincide with the boundaries of the specimen. They occupy energy states up to the so-called Fermi level, which is the chemical potential μ(T) . The work function φ is the energy required to remove an electron at the Fer ...
lecture 11 (zipped power point)
... Doubling the intensity of light wont change Kmax because the energy hn of individual photons wont change, nor is W0 (W0 is the intrinsic property of a given metal surface) ...
... Doubling the intensity of light wont change Kmax because the energy hn of individual photons wont change, nor is W0 (W0 is the intrinsic property of a given metal surface) ...
Chem 121 QU 78 Due in lecture
... 5. Solve the following problems from the text pages 353-357: →_________________________________________________________________ 10 What is Coulomb’s law↑? →_________________________________________________________________ 18 What are valence electrons?↑ →_____________________________________________ ...
... 5. Solve the following problems from the text pages 353-357: →_________________________________________________________________ 10 What is Coulomb’s law↑? →_________________________________________________________________ 18 What are valence electrons?↑ →_____________________________________________ ...
PHYS420 (Spring 2002) Riq Parra Homework # 7
... In the typical experimental photoelectric set-up, a Geissler tube (two electrodes in a evacuated glass tube) is connected to some voltage source. In this context, state the difference between the stopping potential, a retarding voltage and an accelerating voltage. Feel free to draw diagrams/graphs t ...
... In the typical experimental photoelectric set-up, a Geissler tube (two electrodes in a evacuated glass tube) is connected to some voltage source. In this context, state the difference between the stopping potential, a retarding voltage and an accelerating voltage. Feel free to draw diagrams/graphs t ...
Document
... • Energy is quantized. It comes in chunks. • A quanta is the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. • Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. • Schrödinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the e ...
... • Energy is quantized. It comes in chunks. • A quanta is the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. • Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. • Schrödinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the e ...
Random Laser - Department of Physics
... photons. This recombination is a non-equilibrium process and energy must be conserved. Cathodoluminescence from semiconductors is most commonly characterized via spectroscopic techniques. These techniques involve measuring the energy distribution of ...
... photons. This recombination is a non-equilibrium process and energy must be conserved. Cathodoluminescence from semiconductors is most commonly characterized via spectroscopic techniques. These techniques involve measuring the energy distribution of ...
Semester Exam Practice Questions
... a. atomic numbers c. numbers of electrons b. mass numbers d. numbers of protons 16. Einstein’s theory, summarized by the equation E=mc2 , indicates that __________. a. matter can neither be created nor destroyed b. energy exists in discrete packets called quanta c. energy is proportional to the wave ...
... a. atomic numbers c. numbers of electrons b. mass numbers d. numbers of protons 16. Einstein’s theory, summarized by the equation E=mc2 , indicates that __________. a. matter can neither be created nor destroyed b. energy exists in discrete packets called quanta c. energy is proportional to the wave ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.