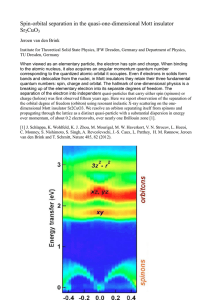
Spin-orbital separation in the quasi-one
... to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the quantized atomic orbital it occupies. Even if electrons in solids form bands and delocalize from the nuclei, in Mott insulators they retain their three fundamental quantum numbers: spin, charge and orbita ...
... to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the quantized atomic orbital it occupies. Even if electrons in solids form bands and delocalize from the nuclei, in Mott insulators they retain their three fundamental quantum numbers: spin, charge and orbita ...
4 slides per page() - Wayne State University Physics and
... Atomic Transitions – Energy Levels An atom may have many possible energy levels At ordinary temperatures, most of the atoms in a sample are in the ground state Only photons with energies corresponding to differences between energy levels can be absorbed ...
... Atomic Transitions – Energy Levels An atom may have many possible energy levels At ordinary temperatures, most of the atoms in a sample are in the ground state Only photons with energies corresponding to differences between energy levels can be absorbed ...
1st Term Review
... 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, what did Rutherford conclude about the atom? 15. An atom of chromium-60 contains how many protons, neutron and electrons? 16. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 17. What is the electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom? 18. Atomic ...
... 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, what did Rutherford conclude about the atom? 15. An atom of chromium-60 contains how many protons, neutron and electrons? 16. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 17. What is the electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom? 18. Atomic ...
WS on obj. 1-11
... 23. _____ (T/F) Cations are formed by the gain of protons. 24. ____________________________ ions are the ions of the halogens and have a 1- charge, 25. _____________________________________ compounds are composed of positive and negative ions. 26. _____ (T/F) A formula unit shows the smallest whole- ...
... 23. _____ (T/F) Cations are formed by the gain of protons. 24. ____________________________ ions are the ions of the halogens and have a 1- charge, 25. _____________________________________ compounds are composed of positive and negative ions. 26. _____ (T/F) A formula unit shows the smallest whole- ...
There are a total of n subshells, each specified by an
... …and apparently 5s comes before 4d, and 6s comes before 5d… ...
... …and apparently 5s comes before 4d, and 6s comes before 5d… ...
Quantum Theory Chapter 27
... showed that all of optics was explained by electromagnetic theory, but……. ...
... showed that all of optics was explained by electromagnetic theory, but……. ...
Atomic Structure Zumdahl Chemistry Chapter 7
... m )corresponds to the three dimensional orientation of the particular orbital an electron is in and has integral values between and - ,including zero. The magnetic spin number ( ms ) corresponds to the direction of the electrons magnetic moment and can have two values +1/2 and –1/2. Wolfgang Pa ...
... m )corresponds to the three dimensional orientation of the particular orbital an electron is in and has integral values between and - ,including zero. The magnetic spin number ( ms ) corresponds to the direction of the electrons magnetic moment and can have two values +1/2 and –1/2. Wolfgang Pa ...
Relativity Problem Set 7 - Solutions Prof. J. Gerton October 24, 2011
... to the quantization of the angular momentum. Plugging in numbers, 6.81 eV ...
... to the quantization of the angular momentum. Plugging in numbers, 6.81 eV ...
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
... atom estimates the probability of finding an electron in a certain position. true ______________________ ...
... atom estimates the probability of finding an electron in a certain position. true ______________________ ...
Radiation Equilibrium (in Everything Including Direct Semiconductors)
... But how about hν = Eg/2 or any other energy inside the band gap? After all, photons with these energies can not be created in the semiconductor, while they have a certain density according to Plancks formula. Well, as in the free electron gas model (which does not have band gaps after all) we have m ...
... But how about hν = Eg/2 or any other energy inside the band gap? After all, photons with these energies can not be created in the semiconductor, while they have a certain density according to Plancks formula. Well, as in the free electron gas model (which does not have band gaps after all) we have m ...
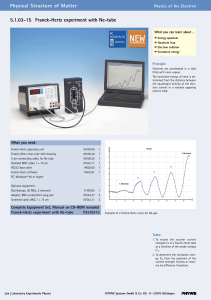
5.1.03-15 Franck-Hertz experiment with Ne
... angular momentum of the electron is an integral multiple of h/2p, i.e. n*h/2p, where n is an integer and h is Planck’s constant. Bohr’s picture of electrons in discrete states with transitions among those states producing radiation whose frequency is determined by the energy differences between stat ...
... angular momentum of the electron is an integral multiple of h/2p, i.e. n*h/2p, where n is an integer and h is Planck’s constant. Bohr’s picture of electrons in discrete states with transitions among those states producing radiation whose frequency is determined by the energy differences between stat ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.