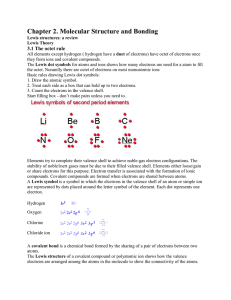
Chapter 7
... 2. The amount of a substance that contains the same number of particles as the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12 ...
... 2. The amount of a substance that contains the same number of particles as the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12 ...
2002 local exam - Virginia Section
... 33. The bond responsible for water’s high boiling point 34. The type of bonds in SO3 35. The strongest bond listed above 36. Generally in going from left to right across the third row of the periodic table (Na to Ar) the: (A) metallic character and electronegativity decreases (B) ionization energy a ...
... 33. The bond responsible for water’s high boiling point 34. The type of bonds in SO3 35. The strongest bond listed above 36. Generally in going from left to right across the third row of the periodic table (Na to Ar) the: (A) metallic character and electronegativity decreases (B) ionization energy a ...
Directed Reading
... a. how long it takes for chemical bonds to form b. how subatomic particles will split apart to form other atoms c. which kinds of atoms will form chemical bonds together d. the weather ______ 28. How many valence electrons can a hydrogen atom have? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 ______ 29. How can hydrogen rea ...
... a. how long it takes for chemical bonds to form b. how subatomic particles will split apart to form other atoms c. which kinds of atoms will form chemical bonds together d. the weather ______ 28. How many valence electrons can a hydrogen atom have? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 ______ 29. How can hydrogen rea ...
AP Chemistry Standards and Benchmarks
... Understands the difference between elements, atoms, compounds, and molecules Knows how to name compounds Understands the difference between ionic and covalent bonds Understands the properties of covalent bonds and their influence on molecular structure Knows how to use molar mass in calculations Und ...
... Understands the difference between elements, atoms, compounds, and molecules Knows how to name compounds Understands the difference between ionic and covalent bonds Understands the properties of covalent bonds and their influence on molecular structure Knows how to use molar mass in calculations Und ...
Topic 1 Test - A-Level Chemistry
... Write an equation, including state symbols, to show the reaction that occurs when the first ionisation energy of Kr is measured. Sometimes the mass spectrum of Kr has a very small peak with an m/z value of 42. Explain the occurrence of this peak. ...
... Write an equation, including state symbols, to show the reaction that occurs when the first ionisation energy of Kr is measured. Sometimes the mass spectrum of Kr has a very small peak with an m/z value of 42. Explain the occurrence of this peak. ...
Answers to Selected Problems
... nuclear charge in a Cs atom has a smaller effect on the electrons in the highest occupied energy level. c. It is relatively easy to remove all three electrons from an Al atom, but the third electron removed from a Mg atom is in a lower energy level. ...
... nuclear charge in a Cs atom has a smaller effect on the electrons in the highest occupied energy level. c. It is relatively easy to remove all three electrons from an Al atom, but the third electron removed from a Mg atom is in a lower energy level. ...
Exam 1 Format and Review
... exam. Not all of the topics listed are guaranteed to appear on the exam. Also, some topics not listed may be included The exam will focus on the (1) key course concepts, (2) lecture notes, (3) online homework assignments, and (4) additional recommended text problems (in syllabus). The exam will test ...
... exam. Not all of the topics listed are guaranteed to appear on the exam. Also, some topics not listed may be included The exam will focus on the (1) key course concepts, (2) lecture notes, (3) online homework assignments, and (4) additional recommended text problems (in syllabus). The exam will test ...
CMC Chapter 5
... Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom • Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. • Explain the impact of de Broglie's wave article duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the current view of electrons in atoms. • Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom's en ...
... Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom • Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. • Explain the impact of de Broglie's wave article duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the current view of electrons in atoms. • Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom's en ...
practice exercise - Needham.K12.ma.us
... ending, the acid is given a hydro- prefix and an -ic ending: hydrocyanic acid. Only water solutions of HCN are referred to as hydrocyanic acid: The pure compound, which is a gas under normal conditions, is called hydrogen cyanide. Both hydrocyanic acid and hydrogen cyanide are extremely toxic. (b) B ...
... ending, the acid is given a hydro- prefix and an -ic ending: hydrocyanic acid. Only water solutions of HCN are referred to as hydrocyanic acid: The pure compound, which is a gas under normal conditions, is called hydrogen cyanide. Both hydrocyanic acid and hydrogen cyanide are extremely toxic. (b) B ...
CHEM 400 - El Camino College
... two parts: multiple choice questions and open-end questions. You will need to bring a Scantron form No. 882E. Partial credit will be given for open-end questions only. Open-end questions will be of two categories: quantitative problems and short essay questions. They will be similar to those from yo ...
... two parts: multiple choice questions and open-end questions. You will need to bring a Scantron form No. 882E. Partial credit will be given for open-end questions only. Open-end questions will be of two categories: quantitative problems and short essay questions. They will be similar to those from yo ...
practice exercise
... ending, the acid is given a hydro- prefix and an -ic ending: hydrocyanic acid. Only water solutions of HCN are referred to as hydrocyanic acid: The pure compound, which is a gas under normal conditions, is called hydrogen cyanide. Both hydrocyanic acid and hydrogen cyanide are extremely toxic. (b) B ...
... ending, the acid is given a hydro- prefix and an -ic ending: hydrocyanic acid. Only water solutions of HCN are referred to as hydrocyanic acid: The pure compound, which is a gas under normal conditions, is called hydrogen cyanide. Both hydrocyanic acid and hydrogen cyanide are extremely toxic. (b) B ...
4.2 3-D Structure
... 1. The words that make up the initialism “VSEPR”—valence shell electron-pair repulsion —describe the concept of the theory very well. The main concept of the theory is that pairs of electrons, both bonding and non-bonding, will repel one another and maximize the distance between themselves around an ...
... 1. The words that make up the initialism “VSEPR”—valence shell electron-pair repulsion —describe the concept of the theory very well. The main concept of the theory is that pairs of electrons, both bonding and non-bonding, will repel one another and maximize the distance between themselves around an ...
Acid-Base Reactions
... Oxidation = loss of electrons, Reduction = Gain of electrons (OIL RIG) Assigning oxidation numbers Displacement reactions (single replacement) need to be balanced for mass and charge Activity Series ...
... Oxidation = loss of electrons, Reduction = Gain of electrons (OIL RIG) Assigning oxidation numbers Displacement reactions (single replacement) need to be balanced for mass and charge Activity Series ...
Section 16.1 A Model for Reaction Rates
... • Q5: Explain why the average rate of a reaction depends on the length of the time interval over which the rate is measured. • The rate of change of a reactant or product in a chemical reaction is not linear in time • Q6: Describe the relationship between activation energy and the rate of a reactio ...
... • Q5: Explain why the average rate of a reaction depends on the length of the time interval over which the rate is measured. • The rate of change of a reactant or product in a chemical reaction is not linear in time • Q6: Describe the relationship between activation energy and the rate of a reactio ...
Chemistry 11th
... (ii) The oxides of alkali and alkaline earth metal dissolve in water to form their respective hydroxides. These oxides are strong bases. However, the oxides of alkali metals are more basic than those of alkaline earth metals. This is because the ionization enthalpy of alkali metals is lower. The e ...
... (ii) The oxides of alkali and alkaline earth metal dissolve in water to form their respective hydroxides. These oxides are strong bases. However, the oxides of alkali metals are more basic than those of alkaline earth metals. This is because the ionization enthalpy of alkali metals is lower. The e ...
jyvaskla2 - School of Chemistry
... very much like the balls and spheres of molecular models !!! The simple binary hydrides of the second period elements show that the relative volumes of space associated with each element is determined by their relative electronegativities. Surfaces are truncated at 0.001 au. ...
... very much like the balls and spheres of molecular models !!! The simple binary hydrides of the second period elements show that the relative volumes of space associated with each element is determined by their relative electronegativities. Surfaces are truncated at 0.001 au. ...
Understanding the Role of Aqueous Solution in Chemical Reactions
... Due to its properties, solvent effects in aqueous chemical reactions are often significant. Both beneficial and negative effects of water in chemical reactions are well documented. Compared to the organic alternatives, water is an environmentally friendly, cheap and safe solvent. To date, the role o ...
... Due to its properties, solvent effects in aqueous chemical reactions are often significant. Both beneficial and negative effects of water in chemical reactions are well documented. Compared to the organic alternatives, water is an environmentally friendly, cheap and safe solvent. To date, the role o ...
CHAPTER-4 STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
... 2. If it is the outermost orbit, then it should have not more than 8 electrons. 3. There should be step-wise filling of electrons in different orbits, i.e., electrons are not accompanied in a given orbit if the earlier orbits or shells are incompletely filled. Q.7: Define valency by taking examples ...
... 2. If it is the outermost orbit, then it should have not more than 8 electrons. 3. There should be step-wise filling of electrons in different orbits, i.e., electrons are not accompanied in a given orbit if the earlier orbits or shells are incompletely filled. Q.7: Define valency by taking examples ...
Chemistry with Physics Structure for Quiz
... How do you read a graduated cylinder? By reading the bottom of the meniscus at eye level. Read the volume using all certain digits and one uncertain digit. ...
... How do you read a graduated cylinder? By reading the bottom of the meniscus at eye level. Read the volume using all certain digits and one uncertain digit. ...
Chapter 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... • The concept of an isotope (specifically 12C) will be useful when defining the mole in Chapter 3. • Because the atomic number signifies the number of electrons in an atom, it will be commonly used to write electron configurations of atoms (Chapter 6), draw Lewis structures (Chapter 8), and understa ...
... • The concept of an isotope (specifically 12C) will be useful when defining the mole in Chapter 3. • Because the atomic number signifies the number of electrons in an atom, it will be commonly used to write electron configurations of atoms (Chapter 6), draw Lewis structures (Chapter 8), and understa ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide
... ____ 92. Which region contains elements with two valence electrons? a. A c. C b. B d. D ____ 93. Which is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from an atom of an element in the gaseous state? a. ionization energy c. ionic radius b. electronegativity d. law of octets ____ 94. Which co ...
... ____ 92. Which region contains elements with two valence electrons? a. A c. C b. B d. D ____ 93. Which is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from an atom of an element in the gaseous state? a. ionization energy c. ionic radius b. electronegativity d. law of octets ____ 94. Which co ...
- TestbankU
... A) Because atoms are so small that you can't see them with the unaided eye. B) Because bits of paper are so massive [or heavy] that they do not respond noticeably to atomic impacts. C) Because only living organisms such as bacteria exhibit Brownian motion. D) Because only individual atoms and molecu ...
... A) Because atoms are so small that you can't see them with the unaided eye. B) Because bits of paper are so massive [or heavy] that they do not respond noticeably to atomic impacts. C) Because only living organisms such as bacteria exhibit Brownian motion. D) Because only individual atoms and molecu ...