electron–domain geometry
... From this and knowing how many domains are due to nonbinding pairs, we can predict the molecular geometry ...
... From this and knowing how many domains are due to nonbinding pairs, we can predict the molecular geometry ...
Document
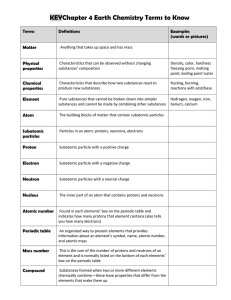
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
Lecture 2 - The Dionne Group
... A schematic illustration of a cross section from solid NaCl. NaCl is made of Cland Na+ ions arranged alternatingly so that the oppositely charged ions are closest to each other and attract each other. There are also repulsive forces between the like ions. In equilibrium the net force acting on any ...
... A schematic illustration of a cross section from solid NaCl. NaCl is made of Cland Na+ ions arranged alternatingly so that the oppositely charged ions are closest to each other and attract each other. There are also repulsive forces between the like ions. In equilibrium the net force acting on any ...
Chapter 2
... bonds form when atoms interact and complete their valence shells. A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms. Molecules consist of two or more covalently bonded atoms. Electrons of a polar covalent bond are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom. A covalent bo ...
... bonds form when atoms interact and complete their valence shells. A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms. Molecules consist of two or more covalently bonded atoms. Electrons of a polar covalent bond are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom. A covalent bo ...
AP Biology
... bonds form when atoms interact and complete their valence shells. A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms. Molecules consist of two or more covalently bonded atoms. Electrons of a polar covalent bond are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom. A covalent bo ...
... bonds form when atoms interact and complete their valence shells. A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms. Molecules consist of two or more covalently bonded atoms. Electrons of a polar covalent bond are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom. A covalent bo ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... Aluminum chloride, Al2Cl6 This forms an intermolecular Lewis acid-base dimer where one Cl atom on each AlCl3 donates a pair of electrons to the neighboring Al atom. Boron trifluoride, BF3 This forms partial pi bonds between the B and F atoms. Diborane, B2H6 B-H-B bridges are formed that use only two ...
... Aluminum chloride, Al2Cl6 This forms an intermolecular Lewis acid-base dimer where one Cl atom on each AlCl3 donates a pair of electrons to the neighboring Al atom. Boron trifluoride, BF3 This forms partial pi bonds between the B and F atoms. Diborane, B2H6 B-H-B bridges are formed that use only two ...
Ch 8 Bonding and Molecular Structure 06-Nov
... Χ = 4.0 – 2.2 = 1.8 Compound is covalent boind Because of the difference in Electronegativity for HF, the compound is polar. Nonpolar bonds form when the difference in electronegativity is less than 0.5 Polar bonds form when the difference in electronegativity is greater than 0.5 Ionic bonds form wh ...
... Χ = 4.0 – 2.2 = 1.8 Compound is covalent boind Because of the difference in Electronegativity for HF, the compound is polar. Nonpolar bonds form when the difference in electronegativity is less than 0.5 Polar bonds form when the difference in electronegativity is greater than 0.5 Ionic bonds form wh ...
It`s All in the Shape - Academic Computer Center
... Before we can uncover the molecular geometry of a molecule we need to gather information about the composition and covalent bonding in the molecule. Useful information will be the Lewis dot structure (or diagram) and a structural formula. The Lewis dot structure shows the arrangement of electrons ar ...
... Before we can uncover the molecular geometry of a molecule we need to gather information about the composition and covalent bonding in the molecule. Useful information will be the Lewis dot structure (or diagram) and a structural formula. The Lewis dot structure shows the arrangement of electrons ar ...
Bonding
... i. Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot structures for each molecule. ii.In terms of molecular geometry, account for the fact that the CF4 molecule is nonpolar, whereas the SF4 molecule is polar. ...
... i. Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot structures for each molecule. ii.In terms of molecular geometry, account for the fact that the CF4 molecule is nonpolar, whereas the SF4 molecule is polar. ...
Fall Final Exam Review Questions
... 40. Draw the Lewis Dot structures for the following: Potassium, Carbon, Iodine and Xenon? 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and w ...
... 40. Draw the Lewis Dot structures for the following: Potassium, Carbon, Iodine and Xenon? 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and w ...
Nature of Matter
... -Because they have the same # of electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. ...
... -Because they have the same # of electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. ...
Name Date
... up of two atoms that have very similar electronegativities. Because of this, carbon and hydrogen share the electrons just about equally and we say that a carbon-hydrogen bond is “nonpolar”. As a general measure, if the difference in electronegativity between two bonding atoms is less than about 0.5, ...
... up of two atoms that have very similar electronegativities. Because of this, carbon and hydrogen share the electrons just about equally and we say that a carbon-hydrogen bond is “nonpolar”. As a general measure, if the difference in electronegativity between two bonding atoms is less than about 0.5, ...
Stoichiometry Mole Concept Balancing Chemical Equations
... In a mixture of gases, the total pressure exerted is the sum of the partial pressures that each gas would exert if it were alone. ...
... In a mixture of gases, the total pressure exerted is the sum of the partial pressures that each gas would exert if it were alone. ...
Prescriptive #54
... When nonmetal atoms bond together to form covalent compounds, they will either share the electrons equally between the atoms, or the electrons will be more attracted to one atom than another. This unequal attraction results in a polar bond and is very important in determining the properties of subst ...
... When nonmetal atoms bond together to form covalent compounds, they will either share the electrons equally between the atoms, or the electrons will be more attracted to one atom than another. This unequal attraction results in a polar bond and is very important in determining the properties of subst ...
Chapter 3 : Simple Bonding Theory Why do they make chemical
... Covalent Bond Localized electron bonding models •Lewis dot structure •VSEPR (Valence shell electron pair repulsion) •Valence bond theory (hybridization) ...
... Covalent Bond Localized electron bonding models •Lewis dot structure •VSEPR (Valence shell electron pair repulsion) •Valence bond theory (hybridization) ...
File
... Pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances and cannot be made by combining other substances ...
... Pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances and cannot be made by combining other substances ...
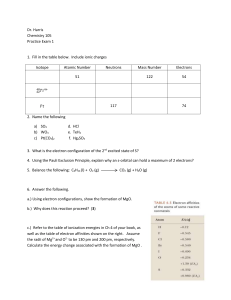
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... 12. A certain element, X, has 3 isotopes (49X, 50X, and 51X). The isotope masses are 49.122 amu, 50.456 amu, and 51.246 amu. Analysis confirms that 3.00% of all X is 51X. Given that the average mass of X is 50.000, determine the percent abundances of the other isotopes. ...
... 12. A certain element, X, has 3 isotopes (49X, 50X, and 51X). The isotope masses are 49.122 amu, 50.456 amu, and 51.246 amu. Analysis confirms that 3.00% of all X is 51X. Given that the average mass of X is 50.000, determine the percent abundances of the other isotopes. ...
Module 1 : Introduction Lecture 2-3 : VSEPR theory and its
... Another term called steric number is often used in VSEPR theory. Steric number (SN) = No. of attached atom + No. of lone pairs. Since the lone pair—lone pair repulsions are maximum, the most stable geometry can be obtained by maximizing the distance between steric numbers on the central atom. Molecu ...
... Another term called steric number is often used in VSEPR theory. Steric number (SN) = No. of attached atom + No. of lone pairs. Since the lone pair—lone pair repulsions are maximum, the most stable geometry can be obtained by maximizing the distance between steric numbers on the central atom. Molecu ...
CHM 101 - Academic Computer Center
... Oxygen can form either covalent or ionic bonds. Explain the nature of each bond, the conditions under which each forms and the type of substances in each bond. ...
... Oxygen can form either covalent or ionic bonds. Explain the nature of each bond, the conditions under which each forms and the type of substances in each bond. ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry comes alive
... produces polar molecules Atoms with six or seven valence shell electrons are electronegative Atoms with one or two valence shell electrons are electropositive ...
... produces polar molecules Atoms with six or seven valence shell electrons are electronegative Atoms with one or two valence shell electrons are electropositive ...
Chapter 2: Chemistry of Life
... • Radioisotopes – isotopes in which the nucleus is unstable and tends to release particles or radiant energy or both – Can help determine age of fossils – Can help trace movement of chemicals through organisms ...
... • Radioisotopes – isotopes in which the nucleus is unstable and tends to release particles or radiant energy or both – Can help determine age of fossils – Can help trace movement of chemicals through organisms ...
COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
... compounds Effective atomic number (EAN) rule : based on the octet theory of Lewis this is the first attempt to account for the bonding in complexes The formation of a complex was described as an acid - base reaction according to Lewis The sum of the electrons on the central atom (Lewis acid) includi ...
... compounds Effective atomic number (EAN) rule : based on the octet theory of Lewis this is the first attempt to account for the bonding in complexes The formation of a complex was described as an acid - base reaction according to Lewis The sum of the electrons on the central atom (Lewis acid) includi ...
Review questions
... The sulfur atom in each compound has three sets of electron pairs around the central atom, so sp2 hybrids overlapping with oxygen 2p orbitals describe the σ bonds: two in SO2 and three in SO3. SO2 is bent, like O3 and SO3 is trigonal planar, like NO3–. The Lewis structures indicate the presence of t ...
... The sulfur atom in each compound has three sets of electron pairs around the central atom, so sp2 hybrids overlapping with oxygen 2p orbitals describe the σ bonds: two in SO2 and three in SO3. SO2 is bent, like O3 and SO3 is trigonal planar, like NO3–. The Lewis structures indicate the presence of t ...
Covalent Bonds
... more time closer to the electronegative oxygen atom • Individually, hydrogen bonds are weak, but are collectively strong in large numbers ...
... more time closer to the electronegative oxygen atom • Individually, hydrogen bonds are weak, but are collectively strong in large numbers ...