2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
... • 8. A compound must at least 2 different elements bonded together, where a molecule is any 2 or more atoms bonded together ...
... • 8. A compound must at least 2 different elements bonded together, where a molecule is any 2 or more atoms bonded together ...
Matter
... Elements can join together to form all the different types of matter. That is why they are called the building blocks of matter. Elements can join together chemically to form compounds. Compounds are substances made of 2 or more elements which combine in a chemical reaction. The smallest unit of a c ...
... Elements can join together to form all the different types of matter. That is why they are called the building blocks of matter. Elements can join together chemically to form compounds. Compounds are substances made of 2 or more elements which combine in a chemical reaction. The smallest unit of a c ...
Protons Neutrons Electrons
... number of protons (with positive charge) as electrons (with negative charge). According to the chart, atoms A, B, E, G and H are neutral. ...
... number of protons (with positive charge) as electrons (with negative charge). According to the chart, atoms A, B, E, G and H are neutral. ...
Name - Quia
... Know how to tell if a bond is polar or nonpolar. Know how to tell if a bond is ionic or covalent. Be able to count valence electrons and understand their importance in bonding. Be able to draw Lewis Dot Structures. Be able tot use VSEPR theory to predict the molecular geometry (shape) of molecules. ...
... Know how to tell if a bond is polar or nonpolar. Know how to tell if a bond is ionic or covalent. Be able to count valence electrons and understand their importance in bonding. Be able to draw Lewis Dot Structures. Be able tot use VSEPR theory to predict the molecular geometry (shape) of molecules. ...
Chapter 1
... magnitude of the charges, the greater the electrostatic repulsion or attraction. As the charge on the plates is increased, the bending will increase. 11. How does Dalton’s atomic theory account for the fact that when 1.000 g of water is decomposed into its elements, 0.111 g of hydrogen and 0889 g of ...
... magnitude of the charges, the greater the electrostatic repulsion or attraction. As the charge on the plates is increased, the bending will increase. 11. How does Dalton’s atomic theory account for the fact that when 1.000 g of water is decomposed into its elements, 0.111 g of hydrogen and 0889 g of ...
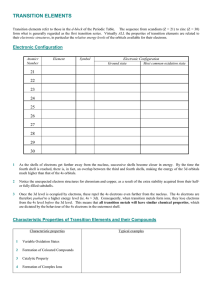
TRANSITION ELEMENTS
... In moving across the transition series, however, the nuclear charge is also increasing, but electrons are being added to an INNER d sub-shell. The outer 4s electrons, which determine the atomic radii, are more effectively shielded from the increasing nuclear charge (1° shielding effect). Consequentl ...
... In moving across the transition series, however, the nuclear charge is also increasing, but electrons are being added to an INNER d sub-shell. The outer 4s electrons, which determine the atomic radii, are more effectively shielded from the increasing nuclear charge (1° shielding effect). Consequentl ...
Chemistry Reference Table Review
... 24. The degree of polarity of a chemical bond in a molecule of a compound can be predicted by determining the difference in the (1) melting points of the elements in the compound (2) densities of the elements in the compound (3) electronegativities of the bonded atoms in a molecule of the compound ( ...
... 24. The degree of polarity of a chemical bond in a molecule of a compound can be predicted by determining the difference in the (1) melting points of the elements in the compound (2) densities of the elements in the compound (3) electronegativities of the bonded atoms in a molecule of the compound ( ...
File
... 6 = hex 3 = prop 7 = hept 4 = but 8 = oct Suffix is determined by the type of bond Alkane CnH2n+2 (all bonds are single) Alkene CnH2n (one bond is a double) Alkyne CnH2n-2 (one bond is a triple) ...
... 6 = hex 3 = prop 7 = hept 4 = but 8 = oct Suffix is determined by the type of bond Alkane CnH2n+2 (all bonds are single) Alkene CnH2n (one bond is a double) Alkyne CnH2n-2 (one bond is a triple) ...
42.89 KB
... B) real gases will condense to form solids at 1000 atm pressure. C) gas phase collisions prevent molecules from colliding with the walls of the ...
... B) real gases will condense to form solids at 1000 atm pressure. C) gas phase collisions prevent molecules from colliding with the walls of the ...
Fall.2008.Week9.Lesson.2 - reich
... • 1-Berylium chloride and aluminum react together. What is the reaction type? Balance the chemical reaction. • 2-Magnesium chloride and sodium phosphate undergo a double displacement reaction. Go through all the steps to show the net ionic equation. • 3- When you cook with a propane grill you burn p ...
... • 1-Berylium chloride and aluminum react together. What is the reaction type? Balance the chemical reaction. • 2-Magnesium chloride and sodium phosphate undergo a double displacement reaction. Go through all the steps to show the net ionic equation. • 3- When you cook with a propane grill you burn p ...
AP Chemistry Summer Study Guide
... Galvanic / Voltaic Cell: Redox reaction that is spontaneous Gamma Ray: 0 protons, mass number = 0, Low ionizing ability, high energy Halogen: Elements in group 17. Form halides as ions Hydrogen Bonding: Strong dipole that results when H is bonded to F, O, or N Indirect relationship: Relationship bet ...
... Galvanic / Voltaic Cell: Redox reaction that is spontaneous Gamma Ray: 0 protons, mass number = 0, Low ionizing ability, high energy Halogen: Elements in group 17. Form halides as ions Hydrogen Bonding: Strong dipole that results when H is bonded to F, O, or N Indirect relationship: Relationship bet ...
Stoichiometry
... Carbonates – oxides and carbon dioxide BaCO3(s) BaO(s) + CO2(g) Hydroxides – metal oxide and water NaOH(l) Na2O(s) + H2O(l) Acids – nonmetallic oxide and water H2SO4(s) SO3(g) + H2O(l) ...
... Carbonates – oxides and carbon dioxide BaCO3(s) BaO(s) + CO2(g) Hydroxides – metal oxide and water NaOH(l) Na2O(s) + H2O(l) Acids – nonmetallic oxide and water H2SO4(s) SO3(g) + H2O(l) ...
Naming Binary Inorganic Compounds
... Naming of Compounds that contain Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic ions are ___________ molecules. The atoms within a polyatomic ion are usually very tightly bound together, so the ion retains its identity within ionic compounds and over the course of many chemical reactions. o o o o ...
... Naming of Compounds that contain Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic ions are ___________ molecules. The atoms within a polyatomic ion are usually very tightly bound together, so the ion retains its identity within ionic compounds and over the course of many chemical reactions. o o o o ...
File - Grade 12 Chemistry
... 20. Draw the Lewis structure for SO2. How many bonded pairs of electrons and how many lone pairs of electrons are around the sulfur atom 21. Draw orbital diagrams and Lewis structures to show how each pair of elements can combine. Write the chemical formula of the product. a) Al and Cl b) Mg and O ...
... 20. Draw the Lewis structure for SO2. How many bonded pairs of electrons and how many lone pairs of electrons are around the sulfur atom 21. Draw orbital diagrams and Lewis structures to show how each pair of elements can combine. Write the chemical formula of the product. a) Al and Cl b) Mg and O ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... on the reactants side of the equation, and only one on the products side of the equation. To balance the equation, you cannot change the structure of any of the molecules, but you can change the number of molecules that are used. Question: How are chemical equations balanced? 1. Balance: Turn on Sho ...
... on the reactants side of the equation, and only one on the products side of the equation. To balance the equation, you cannot change the structure of any of the molecules, but you can change the number of molecules that are used. Question: How are chemical equations balanced? 1. Balance: Turn on Sho ...
PART 2 – CHEMISTRY
... neutrons. Around this, electrons orbit at high speed. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. For example, the atomic number of fluorine is 9. This means that there are 9 protons in the nucleus and 9 elec ...
... neutrons. Around this, electrons orbit at high speed. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. For example, the atomic number of fluorine is 9. This means that there are 9 protons in the nucleus and 9 elec ...
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... This paper reports unusual two-coordinate nickel complexes. The nickel can only bind two ligands because the ligands are so huge (also called bulky or sterically large or sterically encumbered). Figures 1 and 3 show the large size of the ligands. They are the results of Xray diffraction experiments ...
... This paper reports unusual two-coordinate nickel complexes. The nickel can only bind two ligands because the ligands are so huge (also called bulky or sterically large or sterically encumbered). Figures 1 and 3 show the large size of the ligands. They are the results of Xray diffraction experiments ...
Document
... The noble gases are unreactive in chemical reactions In 1916, Gilbert Lewis used this fact to explain why atoms form certain kinds of ions and molecules The Octet Rule: in forming compounds, atoms tend to achieve a noble gas configuration; 8 in the outer level is stable l Each noble gas (except He, ...
... The noble gases are unreactive in chemical reactions In 1916, Gilbert Lewis used this fact to explain why atoms form certain kinds of ions and molecules The Octet Rule: in forming compounds, atoms tend to achieve a noble gas configuration; 8 in the outer level is stable l Each noble gas (except He, ...
Chemistry-5th-Edition-Brady-Solution-Manual
... Nonmetals are more frequently found in compounds because of the large variety of ways they may combine. A particularly illustrative example is the combination of carbon, a nonmetal, with other elements. So many compounds are possible that there is one entire area of chemistry devoted to the study of ...
... Nonmetals are more frequently found in compounds because of the large variety of ways they may combine. A particularly illustrative example is the combination of carbon, a nonmetal, with other elements. So many compounds are possible that there is one entire area of chemistry devoted to the study of ...
Section 4.8: The Structure and Properties of Solids
... in manufacturing, repair, or delivery might find themselves out of a job if a 3-D photocopier could replicate any three-dimensional object. People who work in design might find that they were no longer paid for their work, since a 3-D photocopier could reproduce it with little effort. In addition, m ...
... in manufacturing, repair, or delivery might find themselves out of a job if a 3-D photocopier could replicate any three-dimensional object. People who work in design might find that they were no longer paid for their work, since a 3-D photocopier could reproduce it with little effort. In addition, m ...
FORMULA WRITNG
... b. Calcium shavings are placed into a solution of copper (II) nitrate. molecular: total ionic: net ionic: c. Balls of aluminum foil are placed into a solution of lithium chloride. molecular: total ionic: net ionic: d. Aluminum metal is placed into a solution of hydrochloric acid. molecular: total io ...
... b. Calcium shavings are placed into a solution of copper (II) nitrate. molecular: total ionic: net ionic: c. Balls of aluminum foil are placed into a solution of lithium chloride. molecular: total ionic: net ionic: d. Aluminum metal is placed into a solution of hydrochloric acid. molecular: total io ...
Notes on Chapter 12 Chemical Equilibrium
... c. catalyst = anything that speeds up the rate of reactions by lowering the energy of activation for the reaction. The catalyst is not changed or used up during the chemical reaction. ...
... c. catalyst = anything that speeds up the rate of reactions by lowering the energy of activation for the reaction. The catalyst is not changed or used up during the chemical reaction. ...
BS5-Ch 2.
... (sodium), and K (potassium) Many non-metals occur in groups of 2 (as diatomic molecules)- H, O, N, F, Cl, I, Br Some elements occur as molecules: P4, S, S8, P10, O3 , etc… ...
... (sodium), and K (potassium) Many non-metals occur in groups of 2 (as diatomic molecules)- H, O, N, F, Cl, I, Br Some elements occur as molecules: P4, S, S8, P10, O3 , etc… ...