coordination compounds
... oxygen transport to the tissues of the body. Permanent exchange of substances to the environment enables to the body maintain a certain level of concentration of the compounds involved in the equilibrium of the complexation processes, providing metal-ligand homeostasis. In addition, complex compound ...
... oxygen transport to the tissues of the body. Permanent exchange of substances to the environment enables to the body maintain a certain level of concentration of the compounds involved in the equilibrium of the complexation processes, providing metal-ligand homeostasis. In addition, complex compound ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... Example – Estimate the mass of CO2 produced in 2004 by the combustion of 3.4 x 1015 g gasoline • assuming that gasoline is octane, C8H18, the equation for the reaction is: 2 C8H18(l) + 25 O2(g) 16 CO2(g) + 18 H2O(g) • the equation for the reaction gives the mole relationship between amount of C8H ...
... Example – Estimate the mass of CO2 produced in 2004 by the combustion of 3.4 x 1015 g gasoline • assuming that gasoline is octane, C8H18, the equation for the reaction is: 2 C8H18(l) + 25 O2(g) 16 CO2(g) + 18 H2O(g) • the equation for the reaction gives the mole relationship between amount of C8H ...
1 mol H 2
... quantitative relationships between amounts of reactants used and the products formed by a chemical reaction. It is based on the Law of Conservation of Mass: the amount of matter present at the end of a reaction is the same as was present at the beginning. The total mass of the reactants equals the ...
... quantitative relationships between amounts of reactants used and the products formed by a chemical reaction. It is based on the Law of Conservation of Mass: the amount of matter present at the end of a reaction is the same as was present at the beginning. The total mass of the reactants equals the ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
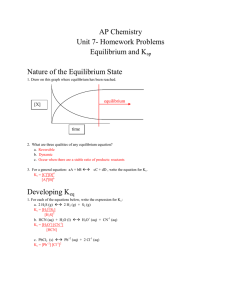
... Things Don’t Always Go as Planned! • many things can happen during the course of an experiment that cause the loss of product • the amount of product that is made in a reaction is called the actual yield generally less than the theoretical yield, never more! ...
... Things Don’t Always Go as Planned! • many things can happen during the course of an experiment that cause the loss of product • the amount of product that is made in a reaction is called the actual yield generally less than the theoretical yield, never more! ...
Document
... Things Don’t Always Go as Planned! • many things can happen during the course of an experiment that cause the loss of product • the amount of product that is made in a reaction is called the actual yield generally less than the theoretical yield, never more! ...
... Things Don’t Always Go as Planned! • many things can happen during the course of an experiment that cause the loss of product • the amount of product that is made in a reaction is called the actual yield generally less than the theoretical yield, never more! ...
TRO Chapter 4
... Things Don’t Always Go as Planned! • many things can happen during the course of an experiment that cause the loss of product • the amount of product that is made in a reaction is called the actual yield generally less than the theoretical yield, never more! ...
... Things Don’t Always Go as Planned! • many things can happen during the course of an experiment that cause the loss of product • the amount of product that is made in a reaction is called the actual yield generally less than the theoretical yield, never more! ...
CHAPTER 12 | The Chemistry of Solids
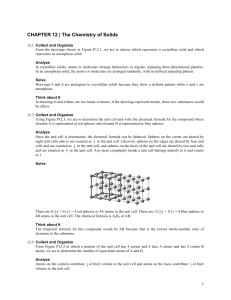
... In crystalline solids, atoms or molecules arrange themselves in regular, repeating three-dimensional patterns. In an amorphous solid, the atoms or molecules are arranged randomly, with no defined repeating pattern. Solve Drawings b and d are analogous to crystalline solids because they show a defini ...
... In crystalline solids, atoms or molecules arrange themselves in regular, repeating three-dimensional patterns. In an amorphous solid, the atoms or molecules are arranged randomly, with no defined repeating pattern. Solve Drawings b and d are analogous to crystalline solids because they show a defini ...
National German competition
... In contrast to pure water that has a pH of 7, rainwater reacts to show a slightly acid reaction because of dissolved carbon dioxide. Some of the reasons for this phenomenon are natural and some are caused by man. In air, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen monooxide are oxidized to sulfur trioxide and nitro ...
... In contrast to pure water that has a pH of 7, rainwater reacts to show a slightly acid reaction because of dissolved carbon dioxide. Some of the reasons for this phenomenon are natural and some are caused by man. In air, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen monooxide are oxidized to sulfur trioxide and nitro ...
ANNEX (Manuscrits posteriors a la Comissió de Doctorat de Juliol del...
... Synthesis of Cs[8,8’-I2-3,3’-Co(1,2-C2B9H10)2] (Cs[2]). Iodine monochloride (3.0 g, 18.48 mmol) was added to a solution of Cs[3,3’-Co(1,2-C2B9H11)2)] (3.92 g, 8.58 mmol) in 80 mL of EtOH. The reaction mixture was refluxed for 10 hours. The excess of iodine monochloride was descomposed by addition of ...
... Synthesis of Cs[8,8’-I2-3,3’-Co(1,2-C2B9H10)2] (Cs[2]). Iodine monochloride (3.0 g, 18.48 mmol) was added to a solution of Cs[3,3’-Co(1,2-C2B9H11)2)] (3.92 g, 8.58 mmol) in 80 mL of EtOH. The reaction mixture was refluxed for 10 hours. The excess of iodine monochloride was descomposed by addition of ...
BSc Honours chemistry CBCS Syllabus 2016-17
... The question paper will consist of five sections A, B, C, D and E. Section E will be compulsory. Examiner will set nine questions in all, selecting two questions from section A, B, C, and D of 10 marks each and may contain more than one part. Section E will be of 10 marks and consists of objective t ...
... The question paper will consist of five sections A, B, C, D and E. Section E will be compulsory. Examiner will set nine questions in all, selecting two questions from section A, B, C, and D of 10 marks each and may contain more than one part. Section E will be of 10 marks and consists of objective t ...
APPROACHES TO CARBOHYDRATE-BASED CHEMICAL LIBRARIES: THE
... isolated from animal sources, plant extracts, and microbial fermentations. The leads are then laboriously refined into drug candidates through a process of systematic optimization. Sequential modifications of the lead compounds are individually synthesized and tested for activity, with beneficial ch ...
... isolated from animal sources, plant extracts, and microbial fermentations. The leads are then laboriously refined into drug candidates through a process of systematic optimization. Sequential modifications of the lead compounds are individually synthesized and tested for activity, with beneficial ch ...
Grade XII Unit 1 - Ethiopian Ministry of Education
... Solution of liquids in liquids Ethanol mixes with water but oil does not. Why? Solubility is a measure of how much solute will dissolve in a solvent at a specific temperature. Do you know the principle “like dissolves like”? The “like dissolves like” principle is helpful in predicting the solubility ...
... Solution of liquids in liquids Ethanol mixes with water but oil does not. Why? Solubility is a measure of how much solute will dissolve in a solvent at a specific temperature. Do you know the principle “like dissolves like”? The “like dissolves like” principle is helpful in predicting the solubility ...
Stoichiometry
... The empirical formulas of benzene and acetylene are both CH. Indeed, there are hundreds of compounds with that empirical formula. Yet, there are no molecules that are composed of a single carbon atom and a single hydrogen atom. Formulas that represent the actual numbers of atoms in a molecule are ca ...
... The empirical formulas of benzene and acetylene are both CH. Indeed, there are hundreds of compounds with that empirical formula. Yet, there are no molecules that are composed of a single carbon atom and a single hydrogen atom. Formulas that represent the actual numbers of atoms in a molecule are ca ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.