The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The physical and chemical properties of elements is determined by the atomic structure. The atomic structure is, in turn, determined by the electrons and which shells, subshells and orbitals they reside in. The rules of placing electrons within shells is known as the Aufbau principle. As protons are ...
... The physical and chemical properties of elements is determined by the atomic structure. The atomic structure is, in turn, determined by the electrons and which shells, subshells and orbitals they reside in. The rules of placing electrons within shells is known as the Aufbau principle. As protons are ...
Name: Period
... 1. Another name for the representative elements is ________________. Where are these elements located on the periodic table? 2. Who was the first scientist to arrange the elements according to similar chemical and physical properties in order of increasing atomic mass? 3. What is characteristic of t ...
... 1. Another name for the representative elements is ________________. Where are these elements located on the periodic table? 2. Who was the first scientist to arrange the elements according to similar chemical and physical properties in order of increasing atomic mass? 3. What is characteristic of t ...
Structure of matter.
... The solution of the Schrödinger equation often leads to numerical coefficients which determine the possible values of energy. These numerical coefficients are called quantum numbers ...
... The solution of the Schrödinger equation often leads to numerical coefficients which determine the possible values of energy. These numerical coefficients are called quantum numbers ...
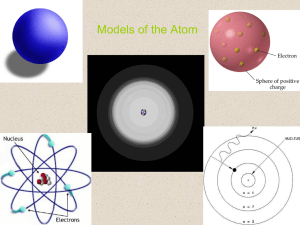
Models of the Atom
... The Bohr Model • Niels Bohr (1885 – 1962) – Danish Physicist/ Student of Rutherford – An electron is found only in specific circular paths, or orbits, around the nucleus. – The energy of an atom changes when it absorbs or emits light. – Each orbit has a fixed energy (each orbital is a different ene ...
... The Bohr Model • Niels Bohr (1885 – 1962) – Danish Physicist/ Student of Rutherford – An electron is found only in specific circular paths, or orbits, around the nucleus. – The energy of an atom changes when it absorbs or emits light. – Each orbit has a fixed energy (each orbital is a different ene ...
Chem 2 AP Ch 7 MC Review Key
... B) No, fluorescent materials only emit purple and green visible light. C) Yes, fluorescent materials emit a broad spectrum of light. D) Yes, after storing enough visible light energy, the fluorescent material can emit ultraviolet light. ...
... B) No, fluorescent materials only emit purple and green visible light. C) Yes, fluorescent materials emit a broad spectrum of light. D) Yes, after storing enough visible light energy, the fluorescent material can emit ultraviolet light. ...
DPPs 1 - Career Point
... (D) An electron of kinetic energy 2.6 eV may emerge from the atom when electron of kinetic energy 125 eV collides with this atom. ...
... (D) An electron of kinetic energy 2.6 eV may emerge from the atom when electron of kinetic energy 125 eV collides with this atom. ...
Quantum Numbers Primer The quantum numbers
... Consider the hydrogen atom. When the electron occupies the n = 1 orbital (the lowest value allowed), the atom is at the lowest energy and the radius is the smallest. We call this lowest energy state the ground state. We can promote an electron in the n = 1 energy level to a higher level; such as n = ...
... Consider the hydrogen atom. When the electron occupies the n = 1 orbital (the lowest value allowed), the atom is at the lowest energy and the radius is the smallest. We call this lowest energy state the ground state. We can promote an electron in the n = 1 energy level to a higher level; such as n = ...
SCH3U Course Review
... Ionization energies tend to increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
... Ionization energies tend to increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
Unit 2 Review KEY
... Electromagnetic Radiation – form of energy that exhibits wavelength behavior as it travels through space. Wavelength (λ) – the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. Frequency (v) – number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time (1 sec) Photoelectric Effect – an emissio ...
... Electromagnetic Radiation – form of energy that exhibits wavelength behavior as it travels through space. Wavelength (λ) – the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. Frequency (v) – number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time (1 sec) Photoelectric Effect – an emissio ...
Lecture 24: Quantum mechanics
... Question then arose how do we prove the wave nature of electrons. In a brilliant experiment, Stern and Gerlach proved this. They exploited Huygen’s principle that was used to prove light is wave. The primary effect of wave nature is the observation of diffraction or interference phenomena. Using sin ...
... Question then arose how do we prove the wave nature of electrons. In a brilliant experiment, Stern and Gerlach proved this. They exploited Huygen’s principle that was used to prove light is wave. The primary effect of wave nature is the observation of diffraction or interference phenomena. Using sin ...
Modern Atomic Theory
... puzzling scientists in the late 19th century. His model began the basis for the field of quantum mechanics . ...
... puzzling scientists in the late 19th century. His model began the basis for the field of quantum mechanics . ...
Quantum dots and radio-frequency electrometers in silicon
... Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge An important goal for solid-state quantum computing is to confine a single electron in silicon, then manipulate and subsequently determine its spin state. Silicon has a low nuclear spin density which, together with the low spin-orbit coupling in this mat ...
... Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge An important goal for solid-state quantum computing is to confine a single electron in silicon, then manipulate and subsequently determine its spin state. Silicon has a low nuclear spin density which, together with the low spin-orbit coupling in this mat ...
IONIZATION METHODS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY
... Chemical ionisation has become very popular for structural elucidation since it was first developed in the mid-1960s. Here, the concept of ionisation relies on the interaction of ions with neutral molecules and the further production of new ions. In general, the amount of fragments ions produced is ...
... Chemical ionisation has become very popular for structural elucidation since it was first developed in the mid-1960s. Here, the concept of ionisation relies on the interaction of ions with neutral molecules and the further production of new ions. In general, the amount of fragments ions produced is ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.