Unit 13, Lesson 1
... These titrations involve the titration of an oxidizing agent with a reducing agent or vice versa. There must be a sufficiently large difference between the oxidizing and reducing capabilities of these agents for the reaction to undergo completion with a sharp end point. The endpoint or equivalence p ...
... These titrations involve the titration of an oxidizing agent with a reducing agent or vice versa. There must be a sufficiently large difference between the oxidizing and reducing capabilities of these agents for the reaction to undergo completion with a sharp end point. The endpoint or equivalence p ...
Chapter 2 power point File
... water) Solubility – the amount of solute that is capable of being dissolved in a solvent Solubility is often listed as grams dissolved per 100 ml of solvent Solubility is often given with a temperature because it changes with temperature Things are called insoluble when they do not dissolve ...
... water) Solubility – the amount of solute that is capable of being dissolved in a solvent Solubility is often listed as grams dissolved per 100 ml of solvent Solubility is often given with a temperature because it changes with temperature Things are called insoluble when they do not dissolve ...
Full text in PDF form
... the limiting case for a refraction index unity. In this limit the optical metric coincides with the spacetime metric. Moreover, we show that a time dependent refraction index may be regarded as a consequence of the action of self-interacting forces on the microscopic constituents of an ultrarelativi ...
... the limiting case for a refraction index unity. In this limit the optical metric coincides with the spacetime metric. Moreover, we show that a time dependent refraction index may be regarded as a consequence of the action of self-interacting forces on the microscopic constituents of an ultrarelativi ...
C5H12 + 8 O2 → 5 CO2 + 6 H2O
... Steps to solve stoichiometry problems 1. Write the balanced chemical equation (or process) 2. Make a table & fill in given information Recognize: ...
... Steps to solve stoichiometry problems 1. Write the balanced chemical equation (or process) 2. Make a table & fill in given information Recognize: ...
Energy Practice
... m = mass of substance to be considered (usually g or kg) c = the specific heat of the substance (the amount of energy required or released when one kilogram of the substance changes in temperature by 1°C (usually expressed in J/g•°C). ∆T = change in temperature (°C): tf - ti (final temperature minus ...
... m = mass of substance to be considered (usually g or kg) c = the specific heat of the substance (the amount of energy required or released when one kilogram of the substance changes in temperature by 1°C (usually expressed in J/g•°C). ∆T = change in temperature (°C): tf - ti (final temperature minus ...
examination review
... Changes to the AP Chemistry Exam format for 2007 include modification to Question 4 in Section II. Previously, students were asked to write chemical equations for any five of eight given sets of chemical reactions. The new format requires students to write balanced chemical equations showing only th ...
... Changes to the AP Chemistry Exam format for 2007 include modification to Question 4 in Section II. Previously, students were asked to write chemical equations for any five of eight given sets of chemical reactions. The new format requires students to write balanced chemical equations showing only th ...
SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
... toluene / phenyl methane methyl benzene acetate ethanoate acetamide ethanamide ...
... toluene / phenyl methane methyl benzene acetate ethanoate acetamide ethanamide ...
From (2)
... Solids:(1) Nucleation, (2)formation of the reaction interface and (3) propagation of the reaction interface Liquids: nucleation may take place at the walls of the container. Example: Many hydrometallurgical processes are accelerated by introducing nuclei in the solution Gases: Production of metallic ...
... Solids:(1) Nucleation, (2)formation of the reaction interface and (3) propagation of the reaction interface Liquids: nucleation may take place at the walls of the container. Example: Many hydrometallurgical processes are accelerated by introducing nuclei in the solution Gases: Production of metallic ...
0922085
... A closed empty cargo tank with a volume of 240 m has an excess pressure of 10 kPa. The tank receives a liquid cargo of 80 m3. The temperature remains constant. What is then the excess pressure in the cargo tank? A ...
... A closed empty cargo tank with a volume of 240 m has an excess pressure of 10 kPa. The tank receives a liquid cargo of 80 m3. The temperature remains constant. What is then the excess pressure in the cargo tank? A ...
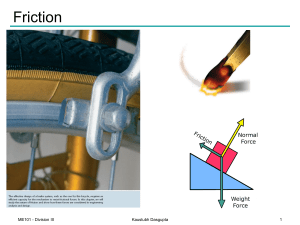
Friction
... Determine the maximum angle Ө before the block begins to slip. μs = Coefficient of static friction between the block and the inclined surface Solution: Draw the FBD of the block ...
... Determine the maximum angle Ө before the block begins to slip. μs = Coefficient of static friction between the block and the inclined surface Solution: Draw the FBD of the block ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.