Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... You can recognize an excited state electron configuration. If the configuration does not match that on the Periodic Table for that number of electrons, then it is an excited state. 9. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy ...
... You can recognize an excited state electron configuration. If the configuration does not match that on the Periodic Table for that number of electrons, then it is an excited state. 9. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy ...
Unit #8 - consumerchem
... 6) 4. Start with any element that appears only once on both sides of the equation. 7) 5. Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients in front of the formulas. a) Remember: no coefficient = 1. b) Multiply coefficients by the subscript to determine the number of atoms. c) Adjust coeffic ...
... 6) 4. Start with any element that appears only once on both sides of the equation. 7) 5. Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients in front of the formulas. a) Remember: no coefficient = 1. b) Multiply coefficients by the subscript to determine the number of atoms. c) Adjust coeffic ...
Class XII Chemistry IMPORTANT QUESTIONS and COMMON
... Ans.Dissolution of gas is exothermic process. Hence according to LeChatelier‘s principle, the solubility of gas should decrease with rise in temperature 7. Mention a large scale use of the phenomenon called ‘reverse osmosis’. Ans. Desalination of Sea water. 8 .Why it is advised to add ethylene glyco ...
... Ans.Dissolution of gas is exothermic process. Hence according to LeChatelier‘s principle, the solubility of gas should decrease with rise in temperature 7. Mention a large scale use of the phenomenon called ‘reverse osmosis’. Ans. Desalination of Sea water. 8 .Why it is advised to add ethylene glyco ...
No Slide Title
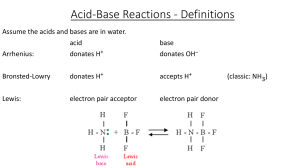
... A base is a substance that forms OH- ion when added to water (Arrhenius definition). A strong soluble base is a soluble hydroxide compound that completely dissociates when added to water. An insoluble base is an insoluble hydroxide compound. There are also a few substances that act as weak bases in ...
... A base is a substance that forms OH- ion when added to water (Arrhenius definition). A strong soluble base is a soluble hydroxide compound that completely dissociates when added to water. An insoluble base is an insoluble hydroxide compound. There are also a few substances that act as weak bases in ...
G - Senger Science
... At 650 K, the value of the equilibrium constant Kp for the ammonia synthesis reaction ...
... At 650 K, the value of the equilibrium constant Kp for the ammonia synthesis reaction ...
Net ionic equation
... A base is a substance that forms OH- ion when added to water (Arrhenius definition). A strong soluble base is a soluble hydroxide compound that completely dissociates when added to water. An insoluble base is an insoluble hydroxide compound. There are also a few substances that act as weak bases in ...
... A base is a substance that forms OH- ion when added to water (Arrhenius definition). A strong soluble base is a soluble hydroxide compound that completely dissociates when added to water. An insoluble base is an insoluble hydroxide compound. There are also a few substances that act as weak bases in ...
thermodynamics
... Mass, internal energy, pressure, heat capacity, molar heat capacity, density, mole fraction, specific heat, temperature and molarity. 60. The lattice enthalpy of an ionic compound is the enthalpy when one mole of an ionic compound present in its gaseous state, dissociates into its ions. It is imposs ...
... Mass, internal energy, pressure, heat capacity, molar heat capacity, density, mole fraction, specific heat, temperature and molarity. 60. The lattice enthalpy of an ionic compound is the enthalpy when one mole of an ionic compound present in its gaseous state, dissociates into its ions. It is imposs ...
Solute
... Temperature increases kinetic energy of solvent particles therefore more solute can be dissolved • For gases: Temperature solubility Temperature increases the kinetic energy of solute particles therefore more particles escape from solution ...
... Temperature increases kinetic energy of solvent particles therefore more solute can be dissolved • For gases: Temperature solubility Temperature increases the kinetic energy of solute particles therefore more particles escape from solution ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.