Experiment 1
... The experimental variable that appears in equations (1), (3), and (4) in the preceding discussion is not the freezing point of a solution but the freezing point depression: the difference between the freezing point of the solution and the freezing point of pure water (calculated as a positive differ ...
... The experimental variable that appears in equations (1), (3), and (4) in the preceding discussion is not the freezing point of a solution but the freezing point depression: the difference between the freezing point of the solution and the freezing point of pure water (calculated as a positive differ ...
Reaction Analysis and PAT Tools
... useful and meaningful information about chemical reactions, in real time. The result of an extensive research project on how scientists analyze reactions, iC IR allows chemists and engineers to quickly gain an understanding of their chemistry. ReactIR collects data in the mid infrared spectral regio ...
... useful and meaningful information about chemical reactions, in real time. The result of an extensive research project on how scientists analyze reactions, iC IR allows chemists and engineers to quickly gain an understanding of their chemistry. ReactIR collects data in the mid infrared spectral regio ...
X012/12/02
... 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of ...
... 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of ...
Document
... Instructions for completion of Section 1 are given on Page 02. SECTION 2 — 80 marks Attempt ALL questions Reference may be made to the Chemistry Higher and Advanced Higher Data Booklet. Write your answers clearly in the spaces provided in this booklet. Additional space for answers and rough work is ...
... Instructions for completion of Section 1 are given on Page 02. SECTION 2 — 80 marks Attempt ALL questions Reference may be made to the Chemistry Higher and Advanced Higher Data Booklet. Write your answers clearly in the spaces provided in this booklet. Additional space for answers and rough work is ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... 12 One mole of magnesium, aluminium and sulphur are each completely burned in an excess of oxygen gas. Which graph shows the moles of oxygen used in each case? ...
... 12 One mole of magnesium, aluminium and sulphur are each completely burned in an excess of oxygen gas. Which graph shows the moles of oxygen used in each case? ...
Thermal Diffusion and Partial Molar Enthalpy Variations of n
... 2.2. Fluxes and Forces from Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics. Consider next the butane adsorbed in the zeolite phase. The amount of zeolite is constant in the system, and it is taken as frame of reference (thus, its mass flux is zero). We are interested in the transport properties of butane and heat. T ...
... 2.2. Fluxes and Forces from Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics. Consider next the butane adsorbed in the zeolite phase. The amount of zeolite is constant in the system, and it is taken as frame of reference (thus, its mass flux is zero). We are interested in the transport properties of butane and heat. T ...
2013 Chemistry examination report
... On dilution, the concentration of all the species present decreases and the system is pushed out of equilibrium. The system tries to partially oppose this change, and increase the overall concentration, by favouring the direction that produces more particles – i.e. the forward reaction – thus increa ...
... On dilution, the concentration of all the species present decreases and the system is pushed out of equilibrium. The system tries to partially oppose this change, and increase the overall concentration, by favouring the direction that produces more particles – i.e. the forward reaction – thus increa ...
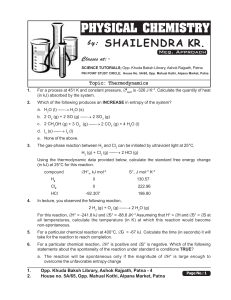
Thermodynamics - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... If the initial concentration of CH3OH (g) is 1.5 M and the initial concentration of CO (g) is 2.0 M, what is the concentration (in M) of CH3OH (g) at equilibrium, at 298 K? ...
... If the initial concentration of CH3OH (g) is 1.5 M and the initial concentration of CO (g) is 2.0 M, what is the concentration (in M) of CH3OH (g) at equilibrium, at 298 K? ...
Unit-II - GDC Memorial College
... process. Concept of heat and work. Zeroth Law of thermodynamics, First law of thermodynamics: statement, definition of internal energy and enthalpy. Heat capacity, heat capacities at constant volume and pressure and their relationship. Joule’s law – Joule – Thomson coefficient for ideal gass and rea ...
... process. Concept of heat and work. Zeroth Law of thermodynamics, First law of thermodynamics: statement, definition of internal energy and enthalpy. Heat capacity, heat capacities at constant volume and pressure and their relationship. Joule’s law – Joule – Thomson coefficient for ideal gass and rea ...
Chemistry Skills Practice Assignments
... 2. For which substance, A or B, does the freezing point decrease as the pressure is increased? 3. One of the substances behaves more like most other substances. Which substance and what property allows you to tell? 4. Assuming that the temperature scales for both phase diagrams are the same, which c ...
... 2. For which substance, A or B, does the freezing point decrease as the pressure is increased? 3. One of the substances behaves more like most other substances. Which substance and what property allows you to tell? 4. Assuming that the temperature scales for both phase diagrams are the same, which c ...
Presentation 3
... Since the concentrations, nio, are in ions per mL and the final form of this model for a single ion activity coefficient is written in terms of ionic strength (I = ½ Σzi2mi, m is moles / kg), log γi = - zi2 [NA2e3 / (2.303 (DRT)3/2)][2πρ /1000]1/2 I1/2 where ρ is solution density. For water at 25 o ...
... Since the concentrations, nio, are in ions per mL and the final form of this model for a single ion activity coefficient is written in terms of ionic strength (I = ½ Σzi2mi, m is moles / kg), log γi = - zi2 [NA2e3 / (2.303 (DRT)3/2)][2πρ /1000]1/2 I1/2 where ρ is solution density. For water at 25 o ...
GCSE ADDITIONAL CHEMISTRY (C2) REVISION BOOKLET
... The rate of a chemical reaction can be found by measuring how ........................ the reactants are ............................ or how quickly the products are ....................... . An example of a chemical reaction is the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid: CaCO3(s) ...
... The rate of a chemical reaction can be found by measuring how ........................ the reactants are ............................ or how quickly the products are ....................... . An example of a chemical reaction is the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid: CaCO3(s) ...
Chapter 8
... Note: If polyatomic ions do not change, they can be balanced as a “unit”. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Note: If polyatomic ions do not change, they can be balanced as a “unit”. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... These reactions will be further discussed in Chapter 8 2. Neutralization: The most important reaction of acids and bases is called neutralization. In these reactions an acid combines with a base to form a salt and water. For example: ...
... These reactions will be further discussed in Chapter 8 2. Neutralization: The most important reaction of acids and bases is called neutralization. In these reactions an acid combines with a base to form a salt and water. For example: ...
Philicities, Fugalities, and Equilibrium Constants
... In a reaction series, the Leffler−Hammond parameter α = δΔG⧧/δΔG° describes the fraction of the change in the Gibbs energy of reaction, which is reflected in the change of the Gibbs energy of activation. It has long been considered as a measure for the position of the transition state; thus, an α value ...
... In a reaction series, the Leffler−Hammond parameter α = δΔG⧧/δΔG° describes the fraction of the change in the Gibbs energy of reaction, which is reflected in the change of the Gibbs energy of activation. It has long been considered as a measure for the position of the transition state; thus, an α value ...
2015_Final Exam Study Guide
... In a balanced chemical equation, the coefficients represent the relative numbers of a. uncombined atoms. c. moles. b. molecules. d. all of these. What is the term that represents the sum of the atomic masses of the atoms in 1 mole of a compound? a. atomic weight c. density b. relative mass d. molar ...
... In a balanced chemical equation, the coefficients represent the relative numbers of a. uncombined atoms. c. moles. b. molecules. d. all of these. What is the term that represents the sum of the atomic masses of the atoms in 1 mole of a compound? a. atomic weight c. density b. relative mass d. molar ...
Page 1
... 57. Compare fission and fusion. (define and identify uses) Fission: the splitting of a nucleus into fragments Fusion: the combining of atomic nuclei 58. Compare alpha, beta and gamma particles. Alpha: a particle with twp protons and two neutrons, with a 2+ charge; is equivalent to a helium -4 nucleu ...
... 57. Compare fission and fusion. (define and identify uses) Fission: the splitting of a nucleus into fragments Fusion: the combining of atomic nuclei 58. Compare alpha, beta and gamma particles. Alpha: a particle with twp protons and two neutrons, with a 2+ charge; is equivalent to a helium -4 nucleu ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.