Chemical Kinetics
... Reactions are reversible Choose conditions where the reverse has negligible contributions. Study at a point soon after they are mixed before product builds up. Reaction rate will depend only on concentration of the reactants. ...
... Reactions are reversible Choose conditions where the reverse has negligible contributions. Study at a point soon after they are mixed before product builds up. Reaction rate will depend only on concentration of the reactants. ...
17 ADSORPTION AND CATALYSIS S MODULE - 5
... surface area, more is the surface available for adsorption and greater is the adsorption. The surface area depends upon the particle size of the substance. A cube of each side equal to 1cm has six faces. Each of them is a square with surface area of 1cm2. Thus, the total surface area of this cube is ...
... surface area, more is the surface available for adsorption and greater is the adsorption. The surface area depends upon the particle size of the substance. A cube of each side equal to 1cm has six faces. Each of them is a square with surface area of 1cm2. Thus, the total surface area of this cube is ...
by John Mu
... If it is not decomposed entirely the Hydrocarbons are further decomposed by steam cracking − A mixture of alkanes with steam is passed through very hot metal tubes. ...
... If it is not decomposed entirely the Hydrocarbons are further decomposed by steam cracking − A mixture of alkanes with steam is passed through very hot metal tubes. ...
selection of chelating agents for remediation of radionuclide
... pattern of fused rings centered about the metal. Another group of macrocyclic ligands that have been extensively studied are the cyclic polyethers in which the donor atoms are either oxygen functions separated by two or three carbon atoms. Compounds having more than one kind of heterotom in the rin ...
... pattern of fused rings centered about the metal. Another group of macrocyclic ligands that have been extensively studied are the cyclic polyethers in which the donor atoms are either oxygen functions separated by two or three carbon atoms. Compounds having more than one kind of heterotom in the rin ...
Chapter 4: Chemical Reaction Dynamics
... 4.4 Reactive scattering: concepts, methods and examples 4.4.1 Motion on the PES The topology of the Born-Oppenheimer PES determines the dynamics of a chemical reaction. Even in the absence of exact QM reactive-scattering calculations, important insight into chemical dynamics can be gained from anal ...
... 4.4 Reactive scattering: concepts, methods and examples 4.4.1 Motion on the PES The topology of the Born-Oppenheimer PES determines the dynamics of a chemical reaction. Even in the absence of exact QM reactive-scattering calculations, important insight into chemical dynamics can be gained from anal ...
UNITS OF CONCENTRATION
... A 50.00 mL sample of water was treated as above and the I2 liberated was titrated with 8.11 mL of 0.01136 N Na2S2O3 to reach the end point. Determine the concentration of the dissolved O2 in equiv./L, moles/L and mg/L. ...
... A 50.00 mL sample of water was treated as above and the I2 liberated was titrated with 8.11 mL of 0.01136 N Na2S2O3 to reach the end point. Determine the concentration of the dissolved O2 in equiv./L, moles/L and mg/L. ...
Document
... Solve: (a) When bonded to a nonmetal, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 (rule 3b). Because the H 2S molecule is neutral, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal zero (rule 4). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we have 2(+1) + x = 0. Thus, S has an oxidation number of –2. (b) Becaus ...
... Solve: (a) When bonded to a nonmetal, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 (rule 3b). Because the H 2S molecule is neutral, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal zero (rule 4). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we have 2(+1) + x = 0. Thus, S has an oxidation number of –2. (b) Becaus ...
CHEM 30 REDOX
... Oxidation is a process in which e- are lost A reducing agent donates e- and is oxidized. A oxidizing agent gains e- and is reduced. ...
... Oxidation is a process in which e- are lost A reducing agent donates e- and is oxidized. A oxidizing agent gains e- and is reduced. ...
physical setting chemistry
... 50 In the laboratory, a student investigates the effect of concentration on the reaction between HCl(aq) and Mg(s), changing only the concentration of HCl(aq). Data for two trials in the investigation are shown in the table below. ...
... 50 In the laboratory, a student investigates the effect of concentration on the reaction between HCl(aq) and Mg(s), changing only the concentration of HCl(aq). Data for two trials in the investigation are shown in the table below. ...
Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical Enhancing
... when treated with sodium bromide afforded corresponding bromide that exhibited doublet at ı 6.61 (J = 12.4 Hz) indicating the presence of double bond [33] and upfield shift in the signal of saturated methylene protons containing alcoholic group. Monohalogenation of diols [34] is often a stubborn prob ...
... when treated with sodium bromide afforded corresponding bromide that exhibited doublet at ı 6.61 (J = 12.4 Hz) indicating the presence of double bond [33] and upfield shift in the signal of saturated methylene protons containing alcoholic group. Monohalogenation of diols [34] is often a stubborn prob ...
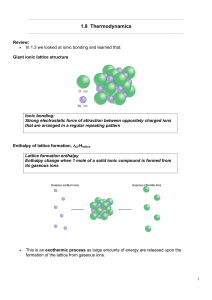
1.8 Thermodynamics
... • The entropy starts of with a low value (ordered) and leads to a higher value (disordered) • This means that reactants and products will have an entropy content, S • We are interested in the change in entropy of a chemical system. • This gives us an idea as to whether a reaction is feasible / spont ...
... • The entropy starts of with a low value (ordered) and leads to a higher value (disordered) • This means that reactants and products will have an entropy content, S • We are interested in the change in entropy of a chemical system. • This gives us an idea as to whether a reaction is feasible / spont ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.