5 Energetics/thermochemistry
... causes what we perceive through sense perception as warmth. Whenever a substance becomes warmer, the average kinetic energy of its particles has increased. The random kinetic energy of particles in matter can be increased in a number of ways. For example, solar energy from the Sun being absorbed by ...
... causes what we perceive through sense perception as warmth. Whenever a substance becomes warmer, the average kinetic energy of its particles has increased. The random kinetic energy of particles in matter can be increased in a number of ways. For example, solar energy from the Sun being absorbed by ...
enthalpy 2
... standard conditions, all products and reactants in the standard state. The standard state is important, it means the way that the element is, at standard conditions (see above). So you would have H2(g) NOT H on its own. Therefore you sometimes need to do fractions of elements, as with the standard e ...
... standard conditions, all products and reactants in the standard state. The standard state is important, it means the way that the element is, at standard conditions (see above). So you would have H2(g) NOT H on its own. Therefore you sometimes need to do fractions of elements, as with the standard e ...
solliqsol - chemmybear.com
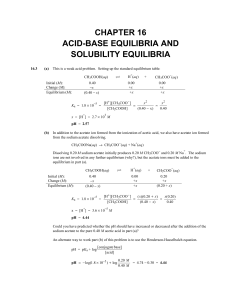
... AgBr(s) Ag+(aq) + Br-(aq); As KBr dissolves, the concentration of Br- ions increase and force the equilibrium to shift to the left (LeChatelier’s principle) where the concentrations of the ions in solution decrease and less can dissolve. The diverse (“uncommon”) ion effect – “the salt effect”. As ...
... AgBr(s) Ag+(aq) + Br-(aq); As KBr dissolves, the concentration of Br- ions increase and force the equilibrium to shift to the left (LeChatelier’s principle) where the concentrations of the ions in solution decrease and less can dissolve. The diverse (“uncommon”) ion effect – “the salt effect”. As ...
CHAPTER 12 Study Guide
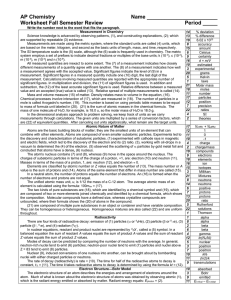
... of writing a ratio using the coefficients of two substances from a balanced equation as the number of moles of each substance reacting or being formed. 40. a. 0.54 mol b. 13.6 mol c. 0.984 mol d. 236 mol 41. a. 11.3 mol CO, 22.5 mol H2 b. 112 g CO, 16.0 g H2 c. 11.4 g H2 42. a. 372 g F2 b. 1.32 g NH ...
... of writing a ratio using the coefficients of two substances from a balanced equation as the number of moles of each substance reacting or being formed. 40. a. 0.54 mol b. 13.6 mol c. 0.984 mol d. 236 mol 41. a. 11.3 mol CO, 22.5 mol H2 b. 112 g CO, 16.0 g H2 c. 11.4 g H2 42. a. 372 g F2 b. 1.32 g NH ...
chapter 8 - Denton ISD
... For example, sometimes a gaseous product is indicated by an arrow pointing upward,↑, instead of (g). A downward arrow, ↓, is often used to show the formation of a precipitate during a reaction in solution. The conditions under which a reaction takes place are often indicated by placing information a ...
... For example, sometimes a gaseous product is indicated by an arrow pointing upward,↑, instead of (g). A downward arrow, ↓, is often used to show the formation of a precipitate during a reaction in solution. The conditions under which a reaction takes place are often indicated by placing information a ...
The Hydroxylation of Aromatic Nitro Compounds by Alkalies
... should diminish the yield; but no such diminution occurs. The only remaining product is water; and this is now believed to render the potassium hydroxide incapable of further reaction by coating the surface. Wohl's statement that the hydroxylation proceeds in the absence of air Is true. but then the ...
... should diminish the yield; but no such diminution occurs. The only remaining product is water; and this is now believed to render the potassium hydroxide incapable of further reaction by coating the surface. Wohl's statement that the hydroxylation proceeds in the absence of air Is true. but then the ...
Study Modules XII Chemistry 2017
... ordered arrangements of constituent particles in a crystal. Types of defects (Imperfections) 1. Point defects: Irregularities from ideal arrangement around a point (or an atom) in a crystalline substance. 2. Line defects: Irregularities from ideal arrangement in entire rows of lattice points Types o ...
... ordered arrangements of constituent particles in a crystal. Types of defects (Imperfections) 1. Point defects: Irregularities from ideal arrangement around a point (or an atom) in a crystalline substance. 2. Line defects: Irregularities from ideal arrangement in entire rows of lattice points Types o ...
chapter 8
... For example, sometimes a gaseous product is indicated by an arrow pointing upward,↑, instead of (g). A downward arrow, ↓, is often used to show the formation of a precipitate during a reaction in solution. The conditions under which a reaction takes place are often indicated by placing information a ...
... For example, sometimes a gaseous product is indicated by an arrow pointing upward,↑, instead of (g). A downward arrow, ↓, is often used to show the formation of a precipitate during a reaction in solution. The conditions under which a reaction takes place are often indicated by placing information a ...
File
... What is the molar concentration of a solution made from 12.0 g of sodium bromide dissolved in 40.0 ml of solution? (2%) ...
... What is the molar concentration of a solution made from 12.0 g of sodium bromide dissolved in 40.0 ml of solution? (2%) ...
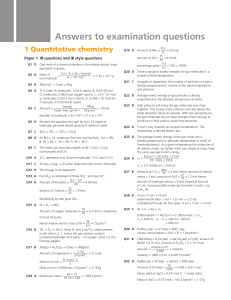
Answers to examination questions
... Q6 A B is trigonal planar (bond angles 120°); A, C and D are based upon a tetrahedral arrangement with four regions of high electron density. However, the water molecule has two lone pairs around the central atom, compared with one for ammonia and none for methane. Lone pair repulsion is greater ...
... Q6 A B is trigonal planar (bond angles 120°); A, C and D are based upon a tetrahedral arrangement with four regions of high electron density. However, the water molecule has two lone pairs around the central atom, compared with one for ammonia and none for methane. Lone pair repulsion is greater ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.