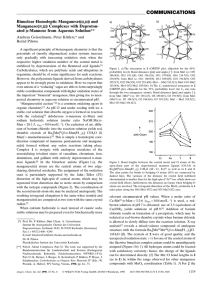
theodore l. brown h. eugene lemay, jr. bruce e. bursten catherine j
... system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. To obtain permission(s) to use material from this work, please submit a written request to Pearson Education, Inc., Permissions Department, 1900 E. Lake Ave., Glenview, IL 60025. Many o ...
... system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. To obtain permission(s) to use material from this work, please submit a written request to Pearson Education, Inc., Permissions Department, 1900 E. Lake Ave., Glenview, IL 60025. Many o ...
N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 2.5 Transition Metals Substitution
... Learn the two bidentate ligands mentioned above but it is not necessary to remember the structure of EDTA. ...
... Learn the two bidentate ligands mentioned above but it is not necessary to remember the structure of EDTA. ...
Chapter 4
... This was written as a molecular equation in which all reactants and products are shown as complete, neutral chemical formulas. ...
... This was written as a molecular equation in which all reactants and products are shown as complete, neutral chemical formulas. ...
Theoretical problems
... for the 43rd International Chemistry Olympiad easier for both students and mentors. We restricted ourselves to the inclusion of only a few topics that are not usually covered in secondary schools. There are six such advanced topics in theoretical part that we expect the participants to be familiar w ...
... for the 43rd International Chemistry Olympiad easier for both students and mentors. We restricted ourselves to the inclusion of only a few topics that are not usually covered in secondary schools. There are six such advanced topics in theoretical part that we expect the participants to be familiar w ...
Chemistry
... 1. If 495g of NaOH is dissolved to a final total volume of 20.0 L, what is the molarity of the solution? 2. How many moles of the indicated solute does each of the following solutions contain? a) 2.50 L of 13.1 M HCl b) 15.6 mL of 0.155 M NaOH 3. What mass of the indicated solute does each of the fo ...
... 1. If 495g of NaOH is dissolved to a final total volume of 20.0 L, what is the molarity of the solution? 2. How many moles of the indicated solute does each of the following solutions contain? a) 2.50 L of 13.1 M HCl b) 15.6 mL of 0.155 M NaOH 3. What mass of the indicated solute does each of the fo ...
updated chem cp final review key
... f. Adding an enzyme Increases rate of reaction g. Breaking a reactant into smaller pieces Increases rate of reaction 43. Know what conditions are true of a chemical reaction at equilibrium. (1) rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal. (2) The concentrations of all substances involved stop ...
... f. Adding an enzyme Increases rate of reaction g. Breaking a reactant into smaller pieces Increases rate of reaction 43. Know what conditions are true of a chemical reaction at equilibrium. (1) rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal. (2) The concentrations of all substances involved stop ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry - Byron Senior High School
... Plan: We will use Hess’s law. In doing so, we first note the numbers of moles of substances among the reactants and products in the target equation, (3). We then manipulate equations (1) and (2) to give the same number of moles of these substances, so that when the resulting equations are added, we ...
... Plan: We will use Hess’s law. In doing so, we first note the numbers of moles of substances among the reactants and products in the target equation, (3). We then manipulate equations (1) and (2) to give the same number of moles of these substances, so that when the resulting equations are added, we ...
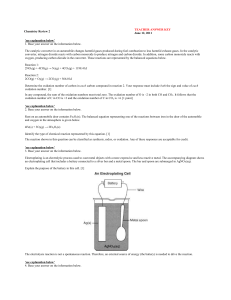
Chemistry Review 2 answer key
... must equal 0, the oxidation number of the nitrogen must be +2. 'see explanation below' 23. Base your answer on the information below. Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and ex ...
... must equal 0, the oxidation number of the nitrogen must be +2. 'see explanation below' 23. Base your answer on the information below. Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and ex ...
Reactions Balancing Chemical Equations uses Law of conservation
... Not all reactions go to completion. Theoretical yield = maximum amount of product that can be obtained under the experimental conditions. Actual yield = amount of product obtained. ...
... Not all reactions go to completion. Theoretical yield = maximum amount of product that can be obtained under the experimental conditions. Actual yield = amount of product obtained. ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.