Chemistry Tests Questions
... 4. When silver nitrate solution is added to iron(II) nitrate solution a grey-black precipitate is formed and after a few minutes there is no further change. The mixture is now in dynamic equilibrium. Explain what this term means. ...
... 4. When silver nitrate solution is added to iron(II) nitrate solution a grey-black precipitate is formed and after a few minutes there is no further change. The mixture is now in dynamic equilibrium. Explain what this term means. ...
Quiz contsts questions chemistry
... The square of the mean velocity of molecules is equal to square of the rms velocity at a certain temperature. (c) The ratio of the mean velocity to the rms velocity is independent of temperature. (d) The mean K.E. of the gas molecules at any given temperature does and depend on the mean velocity. ...
... The square of the mean velocity of molecules is equal to square of the rms velocity at a certain temperature. (c) The ratio of the mean velocity to the rms velocity is independent of temperature. (d) The mean K.E. of the gas molecules at any given temperature does and depend on the mean velocity. ...
5548-4.pdf
... a result of the aluminum pickup. The multi-layer diffusion equation for the nickel – aluminum system was then solved by an analytical method to obtain the concentration profiles for various aluminum activities in the pack. They obtained the concentration profiles that were more realistic than that o ...
... a result of the aluminum pickup. The multi-layer diffusion equation for the nickel – aluminum system was then solved by an analytical method to obtain the concentration profiles for various aluminum activities in the pack. They obtained the concentration profiles that were more realistic than that o ...
2.0 Chem 20 Final Review
... Chemists believe that molecules are made up of charged particles (electrons and nuclei). A polar molecule is one in which the negative (electron) charge is not distributed symmetrically among the atoms making up the molecule. Thus, it will have partial positive and negative charges on opposite s ...
... Chemists believe that molecules are made up of charged particles (electrons and nuclei). A polar molecule is one in which the negative (electron) charge is not distributed symmetrically among the atoms making up the molecule. Thus, it will have partial positive and negative charges on opposite s ...
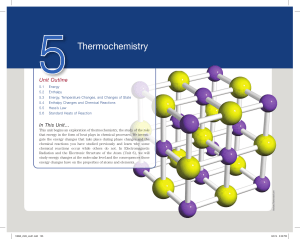
Chapter 2: Mass Relations in Formulas, Chemical Reactions, and
... with each substance. The number in front of each substance is called the stoichiometric coefficients or more simply the coefficient. The bulk of this information is often referred to as the stoichiometry of the chemical reaction. For the above reaction, the stoichiometric coefficients are 2, 1, 1 an ...
... with each substance. The number in front of each substance is called the stoichiometric coefficients or more simply the coefficient. The bulk of this information is often referred to as the stoichiometry of the chemical reaction. For the above reaction, the stoichiometric coefficients are 2, 1, 1 an ...
Magic of Chemical Reactions 2. - mt
... What are the steps of writing a chemical equation? 1. The symbols or molecular formulae of the reactants are written on the left hand side and products are on the right hand side. 2. Reactants and products are connected with an arrow () pointing towards product side. 3. Whenever there are two or mo ...
... What are the steps of writing a chemical equation? 1. The symbols or molecular formulae of the reactants are written on the left hand side and products are on the right hand side. 2. Reactants and products are connected with an arrow () pointing towards product side. 3. Whenever there are two or mo ...
Transition State Theory
... Calculate the rotational partition function, q r , for the following transition ...
... Calculate the rotational partition function, q r , for the following transition ...
Minimum Learning Competencies - Ministry of Education, Ethiopia
... Explain the difference between voltaic cell and electrolytic cell Describe the difference types of voltaic cell Describe how voltaic cells can be used to make commercially useful batteries Describe selected industrial applications of electrolysis ...
... Explain the difference between voltaic cell and electrolytic cell Describe the difference types of voltaic cell Describe how voltaic cells can be used to make commercially useful batteries Describe selected industrial applications of electrolysis ...
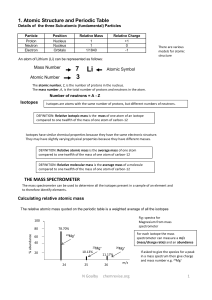
1. Atomic Structure and Periodic Table THE MASS SPECTROMETER
... 2. Add electrons equal to the change in oxidation number For reduction add e’s to reactants For oxidation add e’s to products ...
... 2. Add electrons equal to the change in oxidation number For reduction add e’s to reactants For oxidation add e’s to products ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.