CH225h - Oregon State chemistry
... The rms speeds are inversely proportional to the square root of mass, so the ratio of Ar speed / He speed is ≈ sqrt (4/40) ≈ 0.3 (b) If Ar, He, and Xe are mixed with equal partial pressures in a gas sample, which will effuse most rapidly through a small hole in the container ? Explain briefly. He. E ...
... The rms speeds are inversely proportional to the square root of mass, so the ratio of Ar speed / He speed is ≈ sqrt (4/40) ≈ 0.3 (b) If Ar, He, and Xe are mixed with equal partial pressures in a gas sample, which will effuse most rapidly through a small hole in the container ? Explain briefly. He. E ...
4. Which of the following describes how a Keq value is related to the
... III Forward and reverse reactions are occurring. IV The forward and reverse reaction rates are equal. A. I and II only B. I, III and IV only C. II, III and IV only D. III and IV only ...
... III Forward and reverse reactions are occurring. IV The forward and reverse reaction rates are equal. A. I and II only B. I, III and IV only C. II, III and IV only D. III and IV only ...
Exam Review Chapter 18-Equilibrium
... a. More H2CO3 is produced. b. More H2O is produced. c. The equilibrium d. No Change 7. Two opposing reactions (A + B ↔C + D) occurring simultaneously at the same rate is an example of: a. reversibility. c. neither a nor b b. chemical equilibrium. d. both a and b 8. According to collision theory, in ...
... a. More H2CO3 is produced. b. More H2O is produced. c. The equilibrium d. No Change 7. Two opposing reactions (A + B ↔C + D) occurring simultaneously at the same rate is an example of: a. reversibility. c. neither a nor b b. chemical equilibrium. d. both a and b 8. According to collision theory, in ...
Chapter one
... * 15-4 Explore - Colder then ice water - in this activity you have discovered what happens to the freezing point of water when a substance is dissolved ...
... * 15-4 Explore - Colder then ice water - in this activity you have discovered what happens to the freezing point of water when a substance is dissolved ...
Equilibrium Constant
... react to give back the original reactants, even as the reactants are forming more products. After some time, both the forward and reverse reactions will be going on at the same rate. When this occurs, the reaction is said to have reached equilibrium. ...
... react to give back the original reactants, even as the reactants are forming more products. After some time, both the forward and reverse reactions will be going on at the same rate. When this occurs, the reaction is said to have reached equilibrium. ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry Test
... At equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of the reverse reaction. At equilibrium, the number of moles of SO3 present in the reaction vessel will always be the same as the number of moles of SO2 present, regardless of the temperature. Changing the volume of the vessel ...
... At equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of the reverse reaction. At equilibrium, the number of moles of SO3 present in the reaction vessel will always be the same as the number of moles of SO2 present, regardless of the temperature. Changing the volume of the vessel ...
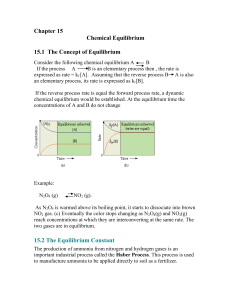
Consider the following chemical equilibrium A B
... B If the process A B is an elementary process then , the rate is expressed as rate = kf [A]. Assuming that the reverse process B A is also an elementary process, its rate is expressed as kr[B]. If the reverse process rate is equal the forward process rate, a dynamic chemical equilibrium would be est ...
... B If the process A B is an elementary process then , the rate is expressed as rate = kf [A]. Assuming that the reverse process B A is also an elementary process, its rate is expressed as kr[B]. If the reverse process rate is equal the forward process rate, a dynamic chemical equilibrium would be est ...
solving equilibrium problems with the ti-92
... the correct answer. Remember the computer maxim, Garbage in, garbage out! The key to correctly solving equilibrium problems is in setting up the ICE table, or reaction stoichiometry matrix. This will be covered in detail by your instructor, and the textbook; here, we are only interested in solving t ...
... the correct answer. Remember the computer maxim, Garbage in, garbage out! The key to correctly solving equilibrium problems is in setting up the ICE table, or reaction stoichiometry matrix. This will be covered in detail by your instructor, and the textbook; here, we are only interested in solving t ...
Diapositiva 1
... These closely connected ideas of temperature and thermal equilibrium are expressed formally in the “Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics:” Zeroth Law: There exists for every thermodynamic system in equilibrium a property called temperature. Equality of temperature is a necessary and sufficient condition for ...
... These closely connected ideas of temperature and thermal equilibrium are expressed formally in the “Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics:” Zeroth Law: There exists for every thermodynamic system in equilibrium a property called temperature. Equality of temperature is a necessary and sufficient condition for ...
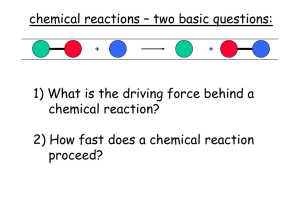
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.