ChE 215, Physical Chemistry
... 2) To study the kinetics of hydrolysis of ethyl acetate solution to ethanol and acetic acid and to determine the reaction rate constant (K). 3) To study the adsorption isotherm using charcoal and acetic acid solution. 4) To determine the refractive index and densities of liquids at various temperatu ...
... 2) To study the kinetics of hydrolysis of ethyl acetate solution to ethanol and acetic acid and to determine the reaction rate constant (K). 3) To study the adsorption isotherm using charcoal and acetic acid solution. 4) To determine the refractive index and densities of liquids at various temperatu ...
printable version
... made and used up-but at the same speed (rate). • Equilibrium is symbolized by the use of a double arrow ( ) or an equals sign (=) ...
... made and used up-but at the same speed (rate). • Equilibrium is symbolized by the use of a double arrow ( ) or an equals sign (=) ...
Combustion Chemistry
... Reaction – due to chemical composition change Enthalpy of formation – the heat released from producing 1 mole of a substance from its elements at a constant temperature T – the enthalpy of formation is zero for the reference ...
... Reaction – due to chemical composition change Enthalpy of formation – the heat released from producing 1 mole of a substance from its elements at a constant temperature T – the enthalpy of formation is zero for the reference ...
1 - 嘉義大學
... 40. Which form of electromagnetic radiation has the longest wavelengths? (A) gamma rays (B) microwaves (C) radio waves ...
... 40. Which form of electromagnetic radiation has the longest wavelengths? (A) gamma rays (B) microwaves (C) radio waves ...
Topics 7 and 17 Outlines
... • Physical and chemical systems should be covered. • Relationship between Kc values for reactions that are multiples or inverses of one another should be covered. • Specific details of any industrial process are not required. 17.1 The equilibrium law Essential idea: The position of equilibrium can b ...
... • Physical and chemical systems should be covered. • Relationship between Kc values for reactions that are multiples or inverses of one another should be covered. • Specific details of any industrial process are not required. 17.1 The equilibrium law Essential idea: The position of equilibrium can b ...
Balanced Equations And Equilibrium Constants
... power of each of their respective coefficients. We use the chemical equilibrium to determine the extent and drive of the chemical reaction. Recall that when solving for equilibrium constants, the activities of pure solids and liquids are one, so (NH4)2CO3(s) is not included in the equation. Kc = [NH ...
... power of each of their respective coefficients. We use the chemical equilibrium to determine the extent and drive of the chemical reaction. Recall that when solving for equilibrium constants, the activities of pure solids and liquids are one, so (NH4)2CO3(s) is not included in the equation. Kc = [NH ...
The following list of topics for an AP Chemistry course is intended to
... 2. Precipitation reactions 3. Oxidation-reduction reactions a. Oxidation number b. The role of the electron in oxidation-reduction c. Electrochemistry; electrolytic and galvanic cells; Faraday’s laws; standard half-cell potentials; Nernst equation; prediction of the direction of redox reactions B. S ...
... 2. Precipitation reactions 3. Oxidation-reduction reactions a. Oxidation number b. The role of the electron in oxidation-reduction c. Electrochemistry; electrolytic and galvanic cells; Faraday’s laws; standard half-cell potentials; Nernst equation; prediction of the direction of redox reactions B. S ...
EXAM REVIEW !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! The examination is scheduled
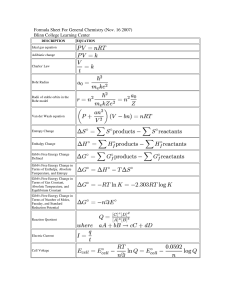
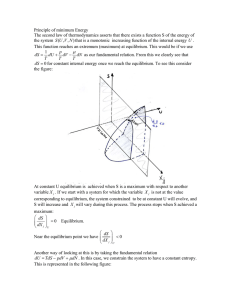
... What is the fundamental equation of chemical thermodynamics? The chemical potential of a pure substance is (G/n)p,T and for a perfect gas = o + RT ln(p/po) how does this change for a real gas. In general = o + RT ln a where a is the activity. For ideal gas a = p/po. For real gas a = f/po. Wh ...
... What is the fundamental equation of chemical thermodynamics? The chemical potential of a pure substance is (G/n)p,T and for a perfect gas = o + RT ln(p/po) how does this change for a real gas. In general = o + RT ln a where a is the activity. For ideal gas a = p/po. For real gas a = f/po. Wh ...
Tall: 1) The decomposition of CaCO3 is an endothermic process:
... The reaction below has an equilibrium constant, Keq, of 171 at 25oC. Using the reaction conditions given, determine if the reaction is product-favored, reactant-favored, or at equilibrium. Don’t forget to find Molarity first! 2 NO2(g) N2O4(g) a) 2.0x10-3 mol NO2, 1.5x10-5 mol N2O4, 10.0 L flask ...
... The reaction below has an equilibrium constant, Keq, of 171 at 25oC. Using the reaction conditions given, determine if the reaction is product-favored, reactant-favored, or at equilibrium. Don’t forget to find Molarity first! 2 NO2(g) N2O4(g) a) 2.0x10-3 mol NO2, 1.5x10-5 mol N2O4, 10.0 L flask ...
Thermodynamics and kinetics
... external conditions are constant • Change in external conditions can change equilibrium A stressed system at equilibrium will shift to reduce stress concentration, pressure, temperature • N2 + 3 H2 <--> 2 NH3 + 22 kcal What is the shift due to Increased temperature? Increased N2? Reduction o ...
... external conditions are constant • Change in external conditions can change equilibrium A stressed system at equilibrium will shift to reduce stress concentration, pressure, temperature • N2 + 3 H2 <--> 2 NH3 + 22 kcal What is the shift due to Increased temperature? Increased N2? Reduction o ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.