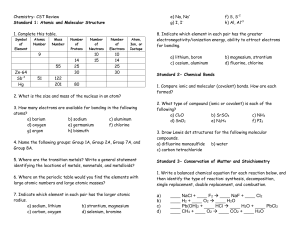
Review Sheet: Unit 6 Name__________________ CHEMISTRY: A
... reactants are two or more ____________ and/or compounds and a more ____________ product is formed. A ____________ reaction is just the opposite; a single compound is broken down into two or more simpler substances. In a ____________ ____________ reaction, the reactants and products take the general ...
... reactants are two or more ____________ and/or compounds and a more ____________ product is formed. A ____________ reaction is just the opposite; a single compound is broken down into two or more simpler substances. In a ____________ ____________ reaction, the reactants and products take the general ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... skeleton equation = formulas of the reactants & products only, no balancing of # of atoms due to the Law of Conservation of Mass, mass of reactants = mass of products o we cannot change the formulas therefore we must change the number of molecules o we do this by adding coefficients in front of th ...
... skeleton equation = formulas of the reactants & products only, no balancing of # of atoms due to the Law of Conservation of Mass, mass of reactants = mass of products o we cannot change the formulas therefore we must change the number of molecules o we do this by adding coefficients in front of th ...
Mock Final Exam
... Lecture 11: Equilibrium (abridged) 11.1: Concept of equilibrium 91. At equilibrium, which of the following statements is true? a. All chemical processes have ceased. b. The rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. c. The rate constants of the forward and reverse reaction ...
... Lecture 11: Equilibrium (abridged) 11.1: Concept of equilibrium 91. At equilibrium, which of the following statements is true? a. All chemical processes have ceased. b. The rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. c. The rate constants of the forward and reverse reaction ...
chemical equilibrium
... • an increase in temperature is used to speed up chemical reactions • it can have an undesired effect when the reaction is reversible and exothermic • you get to the equilibrium position quicker but with a reduced yield because the increased temperature moves the equilibrium to the left • In many in ...
... • an increase in temperature is used to speed up chemical reactions • it can have an undesired effect when the reaction is reversible and exothermic • you get to the equilibrium position quicker but with a reduced yield because the increased temperature moves the equilibrium to the left • In many in ...
Exercise 2 PARTITION COEFFICIENT OF SUCCINIC ACID
... Consider a system consisting of two liquid layers (phases) of two immiscible or partiallly miscible liquids. If a third substance, which is soluble in both liquids, is added into the system it is found to distribute, or divide, itself between the two layers in a definite manner. It has been shown ex ...
... Consider a system consisting of two liquid layers (phases) of two immiscible or partiallly miscible liquids. If a third substance, which is soluble in both liquids, is added into the system it is found to distribute, or divide, itself between the two layers in a definite manner. It has been shown ex ...
Unit 9 – Behavior of Gases
... 45. How many milliliters of 0.45M hydrochloric acid must be added to 25.0mL of 1.00M potassium hydroxide to make a neutral solution? 46. Explain how you used titration to determine the molarity of an unknown acid. 47. Explain in terms of collision theory how each of the following would affect the ra ...
... 45. How many milliliters of 0.45M hydrochloric acid must be added to 25.0mL of 1.00M potassium hydroxide to make a neutral solution? 46. Explain how you used titration to determine the molarity of an unknown acid. 47. Explain in terms of collision theory how each of the following would affect the ra ...
Equilibrium - AP Chemistry
... • At some time, the color stops changing and we have a mixture of N2O4 and NO2. • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as ...
... • At some time, the color stops changing and we have a mixture of N2O4 and NO2. • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as ...
The Equilibrium Constant
... • At some time, the color stops changing and we have a mixture of N2O4 and NO2. • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as ...
... • At some time, the color stops changing and we have a mixture of N2O4 and NO2. • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as ...
Ch. 3 - Chemical Reactions
... Chemical Equations Coefficients and Subscripts Which is What •Subscript : the number located slightly below any element in a formula. Represents the ratio of numbers present in a molecule. ...
... Chemical Equations Coefficients and Subscripts Which is What •Subscript : the number located slightly below any element in a formula. Represents the ratio of numbers present in a molecule. ...
File
... 5. At 25 °C, Kc =0.0146 for the following reaction: PCl5 PCl3 + Cl2 If, at equilibrium, the molar concentrations for PCl5 and PCl3 are 0.500 M and 0.200 M respectfully, calculate the concentration of chlorine gas. (0.0365M) 6. Consider the reaction: CO + 2H2 CH3OH. All substances are in the ga ...
... 5. At 25 °C, Kc =0.0146 for the following reaction: PCl5 PCl3 + Cl2 If, at equilibrium, the molar concentrations for PCl5 and PCl3 are 0.500 M and 0.200 M respectfully, calculate the concentration of chlorine gas. (0.0365M) 6. Consider the reaction: CO + 2H2 CH3OH. All substances are in the ga ...
12 Chemical Potential
... Here we derive the probability that a system with accessible energy levels E1, E2,... and particle numbers N1, N2,... at temperature T is in any particular state with an energy level Ei and particle number Nj. Again define the Helmholtz free energy F as the average work required to assemble the syst ...
... Here we derive the probability that a system with accessible energy levels E1, E2,... and particle numbers N1, N2,... at temperature T is in any particular state with an energy level Ei and particle number Nj. Again define the Helmholtz free energy F as the average work required to assemble the syst ...
Chemistry 1: Second Semester Practice Exam Read each question
... 24. Given the reaction: 2KClO3 Æ 2 KCl + 3O2, What is the total number of moles of KCl produced when 1.50 moles of potassium chlorate is decomposed? C. 3.00 A. 1.50 B. 4.50 D. 0.750 25. Given the reaction: N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) Æ 2 NH3 (g). How many liters of ammonia measured at STP are produced when 2 ...
... 24. Given the reaction: 2KClO3 Æ 2 KCl + 3O2, What is the total number of moles of KCl produced when 1.50 moles of potassium chlorate is decomposed? C. 3.00 A. 1.50 B. 4.50 D. 0.750 25. Given the reaction: N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) Æ 2 NH3 (g). How many liters of ammonia measured at STP are produced when 2 ...
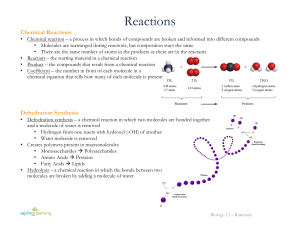
Reactions
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
Learning Outcomes for CHEM1001 in 2015
... 3. recognize that elements are labelled using their chemical symbol 4. explain the differences between elements, compounds and mixtures 5. explain the difference between allotropes and the physical state of an element 6. explain what atoms are and how they combine to form compounds 7. appreciate the ...
... 3. recognize that elements are labelled using their chemical symbol 4. explain the differences between elements, compounds and mixtures 5. explain the difference between allotropes and the physical state of an element 6. explain what atoms are and how they combine to form compounds 7. appreciate the ...
Semester 2 Review
... 12. The reactant that runs out first and limits the amount of product formed is called the _____________ _____________. The left over reactant is called the ____________ ___________. 13. How do you determine actual yield? (Experiment / Calculation) How do you determine theoretical yield? (Experiment ...
... 12. The reactant that runs out first and limits the amount of product formed is called the _____________ _____________. The left over reactant is called the ____________ ___________. 13. How do you determine actual yield? (Experiment / Calculation) How do you determine theoretical yield? (Experiment ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.