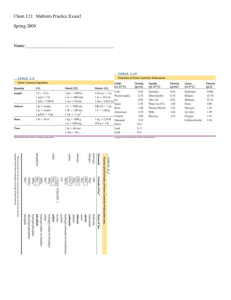
Unit 4 Chemical Kinetics and Chemical Equilibrium
... Le Chatelier’s Principle Reducing the volume (thereby increasing the partial pressures) of a gaseous system at equilibrium causes the reaction to shift in the direction that reduces the total number of moles of gas Increasing the volume (thereby decreasing the partial pressure) of a gaseous equ ...
... Le Chatelier’s Principle Reducing the volume (thereby increasing the partial pressures) of a gaseous system at equilibrium causes the reaction to shift in the direction that reduces the total number of moles of gas Increasing the volume (thereby decreasing the partial pressure) of a gaseous equ ...
Chapter 2 Study Guides
... 7. Before a chemical reaction can start, ____________________ must be absorbed by the reactants. The amount that must be absorbed to start the reaction is called the ...
... 7. Before a chemical reaction can start, ____________________ must be absorbed by the reactants. The amount that must be absorbed to start the reaction is called the ...
Free Energy I
... Burning two moles of H2 in O2 (under conditions of constant P) would decrease the entropy of the system by 326.3 J/K for every mole of O2 or every two moles of water or H2. How much does the entropy change when 0.275 g of H2 is ignited with O2 in a constant-pressure system? ...
... Burning two moles of H2 in O2 (under conditions of constant P) would decrease the entropy of the system by 326.3 J/K for every mole of O2 or every two moles of water or H2. How much does the entropy change when 0.275 g of H2 is ignited with O2 in a constant-pressure system? ...
HS-PS1-6
... simple reactions in which there are only two reactants; evidence from temperature, concentration, and rate data; and qualitative relationships between rate and temperature.] HS-PS1-6: Refine the design of a chemical system by specifying a change in conditions that would produce increased amounts of ...
... simple reactions in which there are only two reactants; evidence from temperature, concentration, and rate data; and qualitative relationships between rate and temperature.] HS-PS1-6: Refine the design of a chemical system by specifying a change in conditions that would produce increased amounts of ...
Ch 17 Equilibrium
... • The equilibrium constant, K, is the ratio of products to reactants. • Therefore, the larger K the more products are present at equilibrium. • Conversely, the smaller K the more reactants are present at equilibrium. • If K >> 1, then products dominate at equilibrium and equilibrium lies to the righ ...
... • The equilibrium constant, K, is the ratio of products to reactants. • Therefore, the larger K the more products are present at equilibrium. • Conversely, the smaller K the more reactants are present at equilibrium. • If K >> 1, then products dominate at equilibrium and equilibrium lies to the righ ...
Chapter 17 lecture notes on Chemical Equilibria
... Some rules for relating Q to K We can calculate the value of Q anywhere along the course of the reaction. Note that in the reaction of A and B forming C and D, the value of Q starts off very small (reactants in denominator) compared to the final K value. Q increases until the point that the forward ...
... Some rules for relating Q to K We can calculate the value of Q anywhere along the course of the reaction. Note that in the reaction of A and B forming C and D, the value of Q starts off very small (reactants in denominator) compared to the final K value. Q increases until the point that the forward ...
practice test2(Answers)
... When some of the sugar added to iced tea remains undissolved at the bottom of the glass, the solution is A) dilute B) unsaturated C) saturated D) polar ...
... When some of the sugar added to iced tea remains undissolved at the bottom of the glass, the solution is A) dilute B) unsaturated C) saturated D) polar ...
Chapter 17 - Cengage Learning
... cause the reaction rate to increase without increasing the temperature. These substances are called catalysts. Catalysts are useful because they increase the reaction rate without necessitating an increase in temperature or concentration. Many reactions do not continue until all of the reactants hav ...
... cause the reaction rate to increase without increasing the temperature. These substances are called catalysts. Catalysts are useful because they increase the reaction rate without necessitating an increase in temperature or concentration. Many reactions do not continue until all of the reactants hav ...
Principles of Reactivity: Chemical Equilibria
... If the concentration of a reactant or product is changed from its equilibrium value at a given temperature, equilibrium will be reestablished eventually. The value of K will still be the same! ...
... If the concentration of a reactant or product is changed from its equilibrium value at a given temperature, equilibrium will be reestablished eventually. The value of K will still be the same! ...
普通化学 (全英文) 教学大纲
... 10.4.Relationship between K and ΔGoT: ΔGoT = – R∙T∙ln K 10.5.Predict the reaction direction by comparing the magnitude of Q and K: (Q < K, Q > K) 10.6.Hess law for ΔG and K Multiple ionic equilibria in solution (using Hess Law to find out combination coefficients) Pay attention to K: e.g. if (re ...
... 10.4.Relationship between K and ΔGoT: ΔGoT = – R∙T∙ln K 10.5.Predict the reaction direction by comparing the magnitude of Q and K: (Q < K, Q > K) 10.6.Hess law for ΔG and K Multiple ionic equilibria in solution (using Hess Law to find out combination coefficients) Pay attention to K: e.g. if (re ...
2. Covalent network
... Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures: Ptotal=ntotal(RT/V) Used to find pressure of a gas that is in a mixture of gases in a container. Only total number of moles matters. Mole Fraction: X1=P1/Ptotal (Pressure is directly related to moles) ...
... Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures: Ptotal=ntotal(RT/V) Used to find pressure of a gas that is in a mixture of gases in a container. Only total number of moles matters. Mole Fraction: X1=P1/Ptotal (Pressure is directly related to moles) ...
Material Equilibrium
... ENTROPY AND EQUILIBRIUM Example: In isolated system (not in material equilibrium) The spontaneous chemical reaction or transport of matter are irreversible process that increase the ENTROPY The process was continued until the system’s entropy is maximized. Once it is maximized, any further pr ...
... ENTROPY AND EQUILIBRIUM Example: In isolated system (not in material equilibrium) The spontaneous chemical reaction or transport of matter are irreversible process that increase the ENTROPY The process was continued until the system’s entropy is maximized. Once it is maximized, any further pr ...
Unit 5 • What Do Atoms Look Like
... Arrhenius only dealt with aqueous solutions. When NH3 and HCl meet in the air, a proton (H+) is transferred from the HCl to the NH3. The two resulting ions immediately are attracted to each other to form the solid, NH4Cl(s) which we see as smoke. HCl(g) is a B-L acid because it donates a proton. NH3 ...
... Arrhenius only dealt with aqueous solutions. When NH3 and HCl meet in the air, a proton (H+) is transferred from the HCl to the NH3. The two resulting ions immediately are attracted to each other to form the solid, NH4Cl(s) which we see as smoke. HCl(g) is a B-L acid because it donates a proton. NH3 ...
IA Velikanova, AK Bolvako PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
... 13. Which statement is true for a liquid/gas mixture in equilibrium? (a) the equilibrium constant is dependent on temperature; (b) the amount of the gas present at equilibrium is independent of pressure; (c) all interchange between the liquid and gas phases has ceased; (d) all of the above. 14. Why ...
... 13. Which statement is true for a liquid/gas mixture in equilibrium? (a) the equilibrium constant is dependent on temperature; (b) the amount of the gas present at equilibrium is independent of pressure; (c) all interchange between the liquid and gas phases has ceased; (d) all of the above. 14. Why ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.