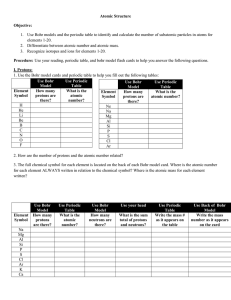
4.80 Chapter Outline
... Atoms and molecules are called the building blocks of matter because if you attempt to break down an atom, you no longer have gold or water or any other recognizable substance. If broken apart, almost all atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Because these pa ...
... Atoms and molecules are called the building blocks of matter because if you attempt to break down an atom, you no longer have gold or water or any other recognizable substance. If broken apart, almost all atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Because these pa ...
What are elements?
... • In the center is circles. Each circle represents a single neutron or proton. Protons should have a plus or P written on them. Neutrons should be blank or have an N. • In a circle around the nucleus are the electrons. Electrons should have a dot for Created by G.Baker each electron ...
... • In the center is circles. Each circle represents a single neutron or proton. Protons should have a plus or P written on them. Neutrons should be blank or have an N. • In a circle around the nucleus are the electrons. Electrons should have a dot for Created by G.Baker each electron ...
Period:______ Table Number
... they are combined together in different ways and in different amounts. P. 9, 70, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 46. The smallest particle of any element that you can have which still possesses all of the physical and chemical properties of that element is a single ATOM of that element. P. 10, VCR: Atoms a ...
... they are combined together in different ways and in different amounts. P. 9, 70, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 46. The smallest particle of any element that you can have which still possesses all of the physical and chemical properties of that element is a single ATOM of that element. P. 10, VCR: Atoms a ...
Atomic Structure_Bohr Flashcards
... 8. a. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in H-1 to H-2 to H-3. List any similarities and differences. b. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in C-12 to C-13 to C-14. List any similarities and differences. ...
... 8. a. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in H-1 to H-2 to H-3. List any similarities and differences. b. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in C-12 to C-13 to C-14. List any similarities and differences. ...
Tutorial 3 - Atomic Theory
... -tells you about the size of the orbital, i.e., the distance from the nucleus -tells you about the energy of the orbital; the bigger the number, the higher the energy level -the orbitals form a series of shells (like the layers of an onion). Shells of higher n surround shells of lower n. 2. The Angu ...
... -tells you about the size of the orbital, i.e., the distance from the nucleus -tells you about the energy of the orbital; the bigger the number, the higher the energy level -the orbitals form a series of shells (like the layers of an onion). Shells of higher n surround shells of lower n. 2. The Angu ...
Chemistry pacing map - City School District of Albany
... Identify elements by comparing bright-line spectrum to given. Differentiate & explain differences between Thomson (Plum pudding), Rutherford, Bohr, and Modern (Quantum mechanical model) of atoms. Define orbital. Classify elements as metals, nonmetals, metalloids, or noble gases by their location on ...
... Identify elements by comparing bright-line spectrum to given. Differentiate & explain differences between Thomson (Plum pudding), Rutherford, Bohr, and Modern (Quantum mechanical model) of atoms. Define orbital. Classify elements as metals, nonmetals, metalloids, or noble gases by their location on ...
chapter04
... more than a couple of dozen noble-gas compounds of all types are known. This group of elements is far less reactive chemically than any other. ...
... more than a couple of dozen noble-gas compounds of all types are known. This group of elements is far less reactive chemically than any other. ...
Document
... Atoms of an element that have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes of each other. ...
... Atoms of an element that have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes of each other. ...
The science of chemistry is concerned with the
... more than a couple of dozen noble-gas compounds of all types are known. This group of elements is far less reactive chemically than any other. ...
... more than a couple of dozen noble-gas compounds of all types are known. This group of elements is far less reactive chemically than any other. ...
Chapter 2.4 Periodic properties of the elements
... y suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it. ...
... y suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it. ...
Slide 1
... ago, scientists found that certain types of matter couldn’t be broken down into any other simpler substances They called these special pure substances: elements ...
... ago, scientists found that certain types of matter couldn’t be broken down into any other simpler substances They called these special pure substances: elements ...
What Are Atoms, and Why Do They Join Together?
... understanding of what atoms are and how they behave. In particular, they learned that while atoms are the smallest particles that have the properties of an element, atoms are made up of even smaller particles. These particles, known as subatomic particles, are the proton, neutron, and electron. Prot ...
... understanding of what atoms are and how they behave. In particular, they learned that while atoms are the smallest particles that have the properties of an element, atoms are made up of even smaller particles. These particles, known as subatomic particles, are the proton, neutron, and electron. Prot ...
Lesson 5 Atomic Theory File
... - the nucleus of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons, while the electrons move freely around the nucleus Orally: it is the number of protons that give an element its characteristics (i.e. if you change the number of protons in a nucleus, you have changed the element!!!) - unlike charges (i.e. ...
... - the nucleus of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons, while the electrons move freely around the nucleus Orally: it is the number of protons that give an element its characteristics (i.e. if you change the number of protons in a nucleus, you have changed the element!!!) - unlike charges (i.e. ...
Chemistry Chapter 4 (Due October 24) [Test
... b. atoms of an element can have different numbers of protons c. atoms are divisible d. all atoms of an element are not identical but they must all have the same mass ____ 16. Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of all elements? a. Cathode rays are negatively-charg ...
... b. atoms of an element can have different numbers of protons c. atoms are divisible d. all atoms of an element are not identical but they must all have the same mass ____ 16. Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of all elements? a. Cathode rays are negatively-charg ...
9/6/12 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... - A chemical property of many substances is their reactivity with oxygen. o Rusting, corrosion - Some substances break down into new substances when heated Classifying Matter - An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. - Matter exists in many different ...
... - A chemical property of many substances is their reactivity with oxygen. o Rusting, corrosion - Some substances break down into new substances when heated Classifying Matter - An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. - Matter exists in many different ...
3.1 The Atom: From Philosophical Idea to Theory
... Cathode ray tubes pass electricity through a gas that is contained at a very low pressure. ...
... Cathode ray tubes pass electricity through a gas that is contained at a very low pressure. ...
Chapter 3
... Cathode ray tubes pass electricity through a gas that is contained at a very low pressure. ...
... Cathode ray tubes pass electricity through a gas that is contained at a very low pressure. ...
Chemistry Basics Review
... Represented by a symbol; all are found on the Periodic Table Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model The positive particle in the nucleus ...
... Represented by a symbol; all are found on the Periodic Table Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model The positive particle in the nucleus ...
Chp 1,2 rev
... 3) If a sample starts at 200g how much will be left after 5 half-life’s have gone by? ...
... 3) If a sample starts at 200g how much will be left after 5 half-life’s have gone by? ...