Subatomic Particles - Ciencias Esmeralda
... Thomson (1912) found 2 types of neon atoms and Soddy (1910) found 2 types of uranium atoms. 2 elements that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers Based on atomic structure: 2 elements that have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. For example: Cl-35 and Cl-37 ...
... Thomson (1912) found 2 types of neon atoms and Soddy (1910) found 2 types of uranium atoms. 2 elements that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers Based on atomic structure: 2 elements that have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. For example: Cl-35 and Cl-37 ...
chem – mixtures elements compounds for ib 1 10-10
... I can write and recognize a chemical symbol for an element using the periodic table. I can give examples of chemical compounds. I can explain that elements are the basic building blocks of matter and discuss how they can physically mix or chemically combine. I can suggest experimental techniques to ...
... I can write and recognize a chemical symbol for an element using the periodic table. I can give examples of chemical compounds. I can explain that elements are the basic building blocks of matter and discuss how they can physically mix or chemically combine. I can suggest experimental techniques to ...
File
... The Quantum Hypothesis • Max Planck, a German physicist, hypothesized that warm bodies emit radiant energy in discrete bundles called quanta. The energy in each energy bundle is proportional to the frequency of the radiation. • Einstein stated that light itself is quantized. A beam of light is not ...
... The Quantum Hypothesis • Max Planck, a German physicist, hypothesized that warm bodies emit radiant energy in discrete bundles called quanta. The energy in each energy bundle is proportional to the frequency of the radiation. • Einstein stated that light itself is quantized. A beam of light is not ...
Chemistry Unit Outcomes
... List 5 qualitative and 3quantitative observations about the candle before it is lit. Explain whether the candle changed chemically or physically or both physically and chemically during the burning process. List one clue or piece of evidence to support your answer. 3. List 3 physical properties of t ...
... List 5 qualitative and 3quantitative observations about the candle before it is lit. Explain whether the candle changed chemically or physically or both physically and chemically during the burning process. List one clue or piece of evidence to support your answer. 3. List 3 physical properties of t ...
Energy and Matter in Chemical Change Science 10
... repetition of characteristics • The success of this model was that it was predictive ...
... repetition of characteristics • The success of this model was that it was predictive ...
Cumulative Review, entire quarter
... Electrons in atoms are located in orbitals, regions of space where electrons form standing waves. The basic shapes are s orbitals, spherical cloud centered on nucleus p: two-lobed orbitals, 3 per set, oriented along the xy&z axes; from period 2 and up. d set of 5 four-lobed orbitals, beginning with ...
... Electrons in atoms are located in orbitals, regions of space where electrons form standing waves. The basic shapes are s orbitals, spherical cloud centered on nucleus p: two-lobed orbitals, 3 per set, oriented along the xy&z axes; from period 2 and up. d set of 5 four-lobed orbitals, beginning with ...
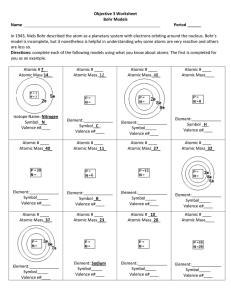
Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name Period In 1943, Niels
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
1. The Greek philosopher Democritus coined what word for a tiny
... B. The atom in an excited state has one fewer electron than the atom in the ground state. C. The atom in an excited state has more energy and is less stable than the atom in the ...
... B. The atom in an excited state has one fewer electron than the atom in the ground state. C. The atom in an excited state has more energy and is less stable than the atom in the ...
Chemistry: Unit 2
... • Element A – atomic mass of 2 mass units • Element B – atomic mass of 3 mass units • What is the expected mass of AB? ...
... • Element A – atomic mass of 2 mass units • Element B – atomic mass of 3 mass units • What is the expected mass of AB? ...
Chemistry - School District of Springfield Township
... o The half-life of a radioactive element is the time it takes for one-half of the unstable nuclei in a sample to decay. o This reaction (either through fission or fusion) can convert a small mass into a large amount of energy according to Einstein’s equation: E = mc2. o This radiation has many usefu ...
... o The half-life of a radioactive element is the time it takes for one-half of the unstable nuclei in a sample to decay. o This reaction (either through fission or fusion) can convert a small mass into a large amount of energy according to Einstein’s equation: E = mc2. o This radiation has many usefu ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons in electron shells • The periodic table of the elements shows the ...
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons in electron shells • The periodic table of the elements shows the ...
Select as many as apply.
... 1. 8O Like the halogens, these atoms like to gain electrons and a smaller atom does that more vigorously because it is the nucleus (protons) pulling in the electron to be gained, and the closer it comes to the nucleus, the more vigorously it comes. 2. 16S 3. 34Se 4. 52Te 5. They are equally reactive ...
... 1. 8O Like the halogens, these atoms like to gain electrons and a smaller atom does that more vigorously because it is the nucleus (protons) pulling in the electron to be gained, and the closer it comes to the nucleus, the more vigorously it comes. 2. 16S 3. 34Se 4. 52Te 5. They are equally reactive ...
Electron Configurations
... A list of all the electrons in an atom (or ion) • Must go in order (Aufbau principle) • 2 electrons per orbital, maximum • We need electron configurations so that we can determine the number of electrons in the outermost energy level. These are called valence electrons. • The number of valence elect ...
... A list of all the electrons in an atom (or ion) • Must go in order (Aufbau principle) • 2 electrons per orbital, maximum • We need electron configurations so that we can determine the number of electrons in the outermost energy level. These are called valence electrons. • The number of valence elect ...
Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review Study Island
... 53. In the electron cloud model, if you begin at the electron shell closest to the nucleus of an atom and move out, what is the number of electrons that each energy level or electron shell needs to fill the first four electron shells? A. 2, 8, 18, 32 B. 2, 6, 10, 14 C. 2, 8, 6, 2 D. 8, 8, 8, 8 ...
... 53. In the electron cloud model, if you begin at the electron shell closest to the nucleus of an atom and move out, what is the number of electrons that each energy level or electron shell needs to fill the first four electron shells? A. 2, 8, 18, 32 B. 2, 6, 10, 14 C. 2, 8, 6, 2 D. 8, 8, 8, 8 ...
presentation1-elements-atoms-and-isotopes
... The isotopes of an element are virtually identical in their chemical reactions. This is because they have the same number of protons and the same number of electrons. The uncharged neutrons make little difference to chemical properties but do affect physical properties such as melting point and dens ...
... The isotopes of an element are virtually identical in their chemical reactions. This is because they have the same number of protons and the same number of electrons. The uncharged neutrons make little difference to chemical properties but do affect physical properties such as melting point and dens ...
physics webquest - Walden University ePortfolio for Mike Dillon
... by their atomic number. • Elements in the same group (column) have similar physical properties. • Elements in the same row have similar electron shells. ...
... by their atomic number. • Elements in the same group (column) have similar physical properties. • Elements in the same row have similar electron shells. ...
Document
... electron is known as a. Low state b. Ground state c. Basement state d. Excited state ...
... electron is known as a. Low state b. Ground state c. Basement state d. Excited state ...
Section 3.1
... physical and chemical properties. 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged but never created, destro ...
... physical and chemical properties. 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged but never created, destro ...