LEARNING WORKSHEET ON ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... For GCSE Chemistry you need to be able to give the FULL electron configurations for the elements up to and including Calcium (Atomic Number 20). The Periodic Table below shows the first four Periods (rows). The Atomic Number is given for each element. Remember that this tells you the number of elect ...
... For GCSE Chemistry you need to be able to give the FULL electron configurations for the elements up to and including Calcium (Atomic Number 20). The Periodic Table below shows the first four Periods (rows). The Atomic Number is given for each element. Remember that this tells you the number of elect ...
Atomic Structure
... • Fusion would be MUCH SAFER than fission • Products are “clean” – not radioactive • Accidents are much less likely and less dangerous (it can’t meltdown) ...
... • Fusion would be MUCH SAFER than fission • Products are “clean” – not radioactive • Accidents are much less likely and less dangerous (it can’t meltdown) ...
PSI AP CHEMISTRY Summer Assignment Review Unit Free
... 1. An element is found to gain three electrons when it forms an ion. a) What group number would this element be found in? b) Is there enough information provided to determine what period it is in? 2. Look at the average atomic mass of Ar and K. a) Explain why early scientists might have been tempted ...
... 1. An element is found to gain three electrons when it forms an ion. a) What group number would this element be found in? b) Is there enough information provided to determine what period it is in? 2. Look at the average atomic mass of Ar and K. a) Explain why early scientists might have been tempted ...
Document
... in successive ionization energies of the d electrons. Thus when elements of the first transition series react to form compounds, they can form ions of roughly the ___________________ by losing different numbers of electrons. * The higher oxidation states arise through ____________ bonding with more ...
... in successive ionization energies of the d electrons. Thus when elements of the first transition series react to form compounds, they can form ions of roughly the ___________________ by losing different numbers of electrons. * The higher oxidation states arise through ____________ bonding with more ...
PSI AP CHEMISTRY Atomic Theory and Models of the Atom Classwork:
... 1. An element is found to gain three electrons when it forms an ion. a) What group number would this element be found in? b) Is there enough information provided to determine what period it is in? 2. Look at the average atomic mass of Ar and K. a) Explain why early scientists might have been tempted ...
... 1. An element is found to gain three electrons when it forms an ion. a) What group number would this element be found in? b) Is there enough information provided to determine what period it is in? 2. Look at the average atomic mass of Ar and K. a) Explain why early scientists might have been tempted ...
Review Packet - Daigneault Chem.is.try
... 7. If element Z (fictitious) has two isotopes: Z-20 (20.00 amu) with 91.2% abundance, and Z-21 (21.00 amu) with 8.8% abundance. If element Z were an actual element, what mass would be displayed on the periodic table? 8. Show the location of each of the following on the periodic table: - periods - gr ...
... 7. If element Z (fictitious) has two isotopes: Z-20 (20.00 amu) with 91.2% abundance, and Z-21 (21.00 amu) with 8.8% abundance. If element Z were an actual element, what mass would be displayed on the periodic table? 8. Show the location of each of the following on the periodic table: - periods - gr ...
Chapter 2
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bonds ...
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bonds ...
introduction
... Perchloric tells you that the anion of this oxoacid is perchlorate, ClO 4. The correct formula is HClO4(aq). Remember that (aq) means that the substance is dissolved in water. Hydroiodic tells you that the anion of this binary acid is iodide, I. The correct formula is HI(aq). Na is an alkali metal ...
... Perchloric tells you that the anion of this oxoacid is perchlorate, ClO 4. The correct formula is HClO4(aq). Remember that (aq) means that the substance is dissolved in water. Hydroiodic tells you that the anion of this binary acid is iodide, I. The correct formula is HI(aq). Na is an alkali metal ...
Name - TeacherWeb
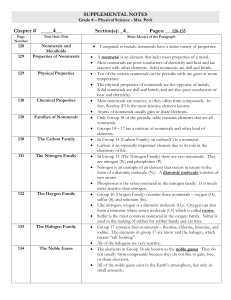
... The metalloids have some characteristics of both metals and nonmetals. All are a solid at room temperature. The most common metalloid is silicon. The most useful property of the metalloids is their varying ability to conduct electricity. (It can depend on the temperature, exposure to light, or the p ...
... The metalloids have some characteristics of both metals and nonmetals. All are a solid at room temperature. The most common metalloid is silicon. The most useful property of the metalloids is their varying ability to conduct electricity. (It can depend on the temperature, exposure to light, or the p ...
Redox
... The oxidation number is used to express the oxidation state of an element, whether as the uncombined element or when combined in a compound; it consists of a + or – sign followed by a number, or it is zero. Atoms of elements have no overall charge and are therefore given an oxidation number of zero. ...
... The oxidation number is used to express the oxidation state of an element, whether as the uncombined element or when combined in a compound; it consists of a + or – sign followed by a number, or it is zero. Atoms of elements have no overall charge and are therefore given an oxidation number of zero. ...
File - Science With BLT
... a. The metal electrons are being transferred to the methane gas. Since each metal has a different number of electrons, this causes the flame to be a certain color. b. The flame is the same color as the salt solution being investigated. c. Metal electrons that are excited will emit colored light when ...
... a. The metal electrons are being transferred to the methane gas. Since each metal has a different number of electrons, this causes the flame to be a certain color. b. The flame is the same color as the salt solution being investigated. c. Metal electrons that are excited will emit colored light when ...
Atoms,molecules,nomenclature.
... Solution Elements that are in the same group of the periodic table are most likely to exhibit similar chemical and physical properties. We therefore expect that Ca and Mg should be most alike because they are in the same group (2A, the alkaline earth metals). Locate Na (sodium) and Br (bromine) on t ...
... Solution Elements that are in the same group of the periodic table are most likely to exhibit similar chemical and physical properties. We therefore expect that Ca and Mg should be most alike because they are in the same group (2A, the alkaline earth metals). Locate Na (sodium) and Br (bromine) on t ...
Atom
... also known as radioactive decay three different kind of particles released – each with different energy levels ...
... also known as radioactive decay three different kind of particles released – each with different energy levels ...
Atomic Nature of Matter
... Atoms consist of three basic subatomic particles. These particles are the proton, the neutron, and the electron. Protons are particles that have a positive charge, have about the same mass as a hydrogen atom, and exist in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are particles that have no electrical charge, ...
... Atoms consist of three basic subatomic particles. These particles are the proton, the neutron, and the electron. Protons are particles that have a positive charge, have about the same mass as a hydrogen atom, and exist in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are particles that have no electrical charge, ...
Review
... 5. What is the average atomic mass of silicon if 92.21 % of its atoms have a mass of 27.977 amu, 4.07 % have a mass of 28.976 amu, and 3.09 % have a mass of 29.974 amu? ...
... 5. What is the average atomic mass of silicon if 92.21 % of its atoms have a mass of 27.977 amu, 4.07 % have a mass of 28.976 amu, and 3.09 % have a mass of 29.974 amu? ...
H 2
... 2. Single Replacement Reactions: The reactants are an element and a compound and the products are a different element and compound. A metallic element will replace the positive part of a compound or a nonmetallic element will replace the negative part of a compound. 3. Synthesis (Combination) Reacti ...
... 2. Single Replacement Reactions: The reactants are an element and a compound and the products are a different element and compound. A metallic element will replace the positive part of a compound or a nonmetallic element will replace the negative part of a compound. 3. Synthesis (Combination) Reacti ...
Unit 13: Electrochemistry (Link to Prentice Hall Text: Chapters 22
... A car battery powers the car through a spontaneous reaction, but what can you do if the battery dies? (c) To coat one metal on top of another one, as with jewelry, or exhaust pipes. a. To make something look more expensive or shinier b. To improve corrosion resistance ...
... A car battery powers the car through a spontaneous reaction, but what can you do if the battery dies? (c) To coat one metal on top of another one, as with jewelry, or exhaust pipes. a. To make something look more expensive or shinier b. To improve corrosion resistance ...
Chapter 2 - Phillips Scientific Methods
... Ionic Bonds: Transfer electrons • Atoms sometimes strip electrons from their bonding partners. • An example is the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine. • After the transfer of an electron, both atoms have charges. ...
... Ionic Bonds: Transfer electrons • Atoms sometimes strip electrons from their bonding partners. • An example is the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine. • After the transfer of an electron, both atoms have charges. ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions Chapter 2
... • An atom or molecule can gain or lose more than one electron. • Many atoms gain or lose enough electrons to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas (group 8A). ...
... • An atom or molecule can gain or lose more than one electron. • Many atoms gain or lose enough electrons to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas (group 8A). ...