Hybridization and St..
... orbitals all have identical energies, and each is referred to as an sp3 hybrid orbital. ...
... orbitals all have identical energies, and each is referred to as an sp3 hybrid orbital. ...
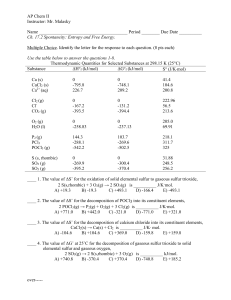
AP Chem II Instructor: Mr. Malasky Name Period ______ Due Date
... ____ 5. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2(g) → 2 S (s,rhombic) + O2(g) is __________ kJ/mol. A) +395.2 B) +269.9 C) -269.9 D) +300.4 E) -300.4 ____ 6. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the formation of POCl3 from it ...
... ____ 5. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2(g) → 2 S (s,rhombic) + O2(g) is __________ kJ/mol. A) +395.2 B) +269.9 C) -269.9 D) +300.4 E) -300.4 ____ 6. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the formation of POCl3 from it ...
Gr 9 Atomic Structure_Gizmo Element Builder - OISE
... We have noted before that the outer shell of an atom has a special name, the valence shell. We also now that each orbital has a maximum number of electrons that it can accommodate. Most atoms prefer to have an outer shell/valence shell that is either full with the maximum number of electrons, or oth ...
... We have noted before that the outer shell of an atom has a special name, the valence shell. We also now that each orbital has a maximum number of electrons that it can accommodate. Most atoms prefer to have an outer shell/valence shell that is either full with the maximum number of electrons, or oth ...
NCERT SOLUTIONS STRUCTURE OF ATOM Question 1: What are
... is determined by the number of valence electrons present in the atom of that element. If the number of valence electrons of the atom of an element is less than or equal to four, then the valency of that element is equal to the number of valence electrons. For example, the atom of silicon has four va ...
... is determined by the number of valence electrons present in the atom of that element. If the number of valence electrons of the atom of an element is less than or equal to four, then the valency of that element is equal to the number of valence electrons. For example, the atom of silicon has four va ...
Building Atoms Unit Interactive Science Notebook III
... Question: How many isotopes can one element have? Can an atom have just any number of neutrons? The number of isotopes varies from atom to atom. There are "preferred" combinations of neutrons and protons, at which the forces holding nuclei together seem to balance best. Light elements tend to have a ...
... Question: How many isotopes can one element have? Can an atom have just any number of neutrons? The number of isotopes varies from atom to atom. There are "preferred" combinations of neutrons and protons, at which the forces holding nuclei together seem to balance best. Light elements tend to have a ...
AS CHECKLISTS File
... Explain in terms of van der Waals’ forces the variations in the boiling points of alkanes with different carbon-chain length and branching. Describe the combustion of alkanes, leading to their use as fuels in industry, in the home and in transport. Explain using equations the incomplete combustion o ...
... Explain in terms of van der Waals’ forces the variations in the boiling points of alkanes with different carbon-chain length and branching. Describe the combustion of alkanes, leading to their use as fuels in industry, in the home and in transport. Explain using equations the incomplete combustion o ...
Chemistry - Beachwood City Schools
... 1. In gases, the particles are far apart, move independently in the ideal case, take the shape of their container and can have a variety of volumes. In ideal gases, the particles are not attracted to each other at all. In liquids, the particles are close together giving them a constant volume althou ...
... 1. In gases, the particles are far apart, move independently in the ideal case, take the shape of their container and can have a variety of volumes. In ideal gases, the particles are not attracted to each other at all. In liquids, the particles are close together giving them a constant volume althou ...
atoms - HCC Learning Web
... • Most “neon” signs don’t actually contain neon gas. • True neon signs are red in color. • Each noble gas has its own emission spectrum, and signs made with each have a different color. ...
... • Most “neon” signs don’t actually contain neon gas. • True neon signs are red in color. • Each noble gas has its own emission spectrum, and signs made with each have a different color. ...
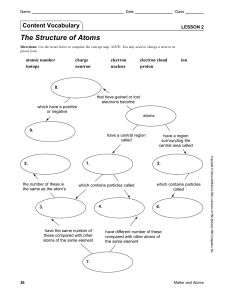
Lesson 2 | The Structure of Atoms
... Lesson 2: The Structure of Atoms A. The Parts of an Atom 1. Every kind of element is made up of its own kind of atoms. 2. Atoms are composed of several basic types of very small particles; the number of each of these particles gives the different kinds of atoms their unique identity. 3. The region ...
... Lesson 2: The Structure of Atoms A. The Parts of an Atom 1. Every kind of element is made up of its own kind of atoms. 2. Atoms are composed of several basic types of very small particles; the number of each of these particles gives the different kinds of atoms their unique identity. 3. The region ...
File
... contains as many particles as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12. • A mole is the SI unit for the amount of a ...
... contains as many particles as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12. • A mole is the SI unit for the amount of a ...
1.1 - cloudfront.net
... contains six electrons, allowing the atom to remain electrically neutral. However the number of neutrons varies from six to eight. Isotopes are atoms that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to a change in the number of neutrons. The three isotopes of carbon can be referred to ...
... contains six electrons, allowing the atom to remain electrically neutral. However the number of neutrons varies from six to eight. Isotopes are atoms that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to a change in the number of neutrons. The three isotopes of carbon can be referred to ...
Synopses - Mindfiesta
... The formal charge is a factor based on a pure covalent view of bonding in which electron pairs are shared equally by neighbouring atoms. Drawbacks of the octet theory : (1) It is clear that octet rule is based upon the chemical inertness of noble gases. However, some noble gases (for example xenon a ...
... The formal charge is a factor based on a pure covalent view of bonding in which electron pairs are shared equally by neighbouring atoms. Drawbacks of the octet theory : (1) It is clear that octet rule is based upon the chemical inertness of noble gases. However, some noble gases (for example xenon a ...
1 - Cathedral High School
... 3.2.1 Describe and explain the periodic trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed i ...
... 3.2.1 Describe and explain the periodic trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed i ...
Atomic Theory and Isotopes powerpoint
... called atoms. The atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different in some fundamental way or ways. ...
... called atoms. The atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different in some fundamental way or ways. ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2 (2015)
... A) B B) Be 7) Which fourth period transition element has the highest atomic number? A) Ca B) Cd C) Kr D) Zn C) Sb and Te D) Po and At C) Ca D) none of the above 8) Which of the following elements are fourth period metalloids? A) Si and Ge B) Ge and As 9) Which of the following is an alkali metal? A ...
... A) B B) Be 7) Which fourth period transition element has the highest atomic number? A) Ca B) Cd C) Kr D) Zn C) Sb and Te D) Po and At C) Ca D) none of the above 8) Which of the following elements are fourth period metalloids? A) Si and Ge B) Ge and As 9) Which of the following is an alkali metal? A ...
as PDF - Halbleiter.org
... The bond energy of the chemical bonds is in the range of several hundreds to several thousands kilojoule/mol (kJ/mol). The bond energy of hydrogen bonds is up to a hundred kJ/mol and the bond energy of van der Waals forces is in the range of 0.5 to 5 kJ/mol. ...
... The bond energy of the chemical bonds is in the range of several hundreds to several thousands kilojoule/mol (kJ/mol). The bond energy of hydrogen bonds is up to a hundred kJ/mol and the bond energy of van der Waals forces is in the range of 0.5 to 5 kJ/mol. ...
KHOA: HÓA HỌC - CCS - Trường Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội
... element is a substance comprised of a single type of atom. The elements are the building blocks of our nature. An element is either discovered in nature or synthesized in the laboratory in pure form that cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical methods. Currently, there are about 118 ...
... element is a substance comprised of a single type of atom. The elements are the building blocks of our nature. An element is either discovered in nature or synthesized in the laboratory in pure form that cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical methods. Currently, there are about 118 ...
IGCSE Revision Guide (Double Award) | PDF
... Say that ionic compounds, such as NaCl and MgO, have high melting point and high boiling points because ionic bonds are strong and a large amount of heat energy is needed to separate the ions. ...
... Say that ionic compounds, such as NaCl and MgO, have high melting point and high boiling points because ionic bonds are strong and a large amount of heat energy is needed to separate the ions. ...
CHAPTER -4 “STRUCTURE OF ATOM” CONCEPT DETAILS Pre
... “Atomic number of an element is defined as the number of unit positive charges on the nucleus (nuclear charge) of the atom of that element or as the number of protons present in the nucleus.” Atomic number, Z = Number of unit positive charge on the nucleus = Total number of unit positive charges car ...
... “Atomic number of an element is defined as the number of unit positive charges on the nucleus (nuclear charge) of the atom of that element or as the number of protons present in the nucleus.” Atomic number, Z = Number of unit positive charge on the nucleus = Total number of unit positive charges car ...