Chemistry
... 1) The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element is the: a) cell b) proton c) electron d) neutron e) none of the above 2) Which of the following is not a part of Dalton’s atomic theory? a) All elements are composed of atoms. b) The positive charge of the atom is loc ...
... 1) The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element is the: a) cell b) proton c) electron d) neutron e) none of the above 2) Which of the following is not a part of Dalton’s atomic theory? a) All elements are composed of atoms. b) The positive charge of the atom is loc ...
2.2 The Discovery of Atomic Structure
... • Gravity forces the drops downward. The applied electric field forces the drops upward. • When a drop is perfectly balanced, then the weight of the drop is equal to the electrostatic force of attraction between the drop and the positive plate. • Millikan carried out the above experiment and determi ...
... • Gravity forces the drops downward. The applied electric field forces the drops upward. • When a drop is perfectly balanced, then the weight of the drop is equal to the electrostatic force of attraction between the drop and the positive plate. • Millikan carried out the above experiment and determi ...
Class IX Chemistry Chapter 4: Structure of the Atom
... These particles constituting the cathode rays were later called electrons. Since it was observed that the nature of cathode rays was the same irrespective of the metal used for the cathode or the gas filled in the cathode ray tube. This led Thomson to conclude that all atoms must contain electrons. ...
... These particles constituting the cathode rays were later called electrons. Since it was observed that the nature of cathode rays was the same irrespective of the metal used for the cathode or the gas filled in the cathode ray tube. This led Thomson to conclude that all atoms must contain electrons. ...
Document
... c) However, for species in groups 14-17 and those transition metals with multiple oxidation state possibilities, the oxidation number will be calculated ...
... c) However, for species in groups 14-17 and those transition metals with multiple oxidation state possibilities, the oxidation number will be calculated ...
Thomson`s Model of the Atom
... Bohr’s Model of the Atom As did Rutherford's atomic model, Bohr’s atomic model had a nucleus surrounded by a large volume of space. But Bohr’s model focused on the electrons and their arrangement. In Bohr’s model, electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets a ...
... Bohr’s Model of the Atom As did Rutherford's atomic model, Bohr’s atomic model had a nucleus surrounded by a large volume of space. But Bohr’s model focused on the electrons and their arrangement. In Bohr’s model, electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets a ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... A. These molecules are composed of positive and negative ions that are combined in a lattice (3D cube) like structure that looks “like” a crystal (crystalline). 1. The ions alternate (positive- negative) so as to maintain neutrality and reduce repulsive forces between like charged ions. 2. The attra ...
... A. These molecules are composed of positive and negative ions that are combined in a lattice (3D cube) like structure that looks “like” a crystal (crystalline). 1. The ions alternate (positive- negative) so as to maintain neutrality and reduce repulsive forces between like charged ions. 2. The attra ...
File - Riske Science
... Use of the nuclear symbol notation A Z X to deduce the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in atoms and ions. ●● Calculations involving non-integer relative atomic masses and abundance of isotopes from given data, including mass spectra. ...
... Use of the nuclear symbol notation A Z X to deduce the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in atoms and ions. ●● Calculations involving non-integer relative atomic masses and abundance of isotopes from given data, including mass spectra. ...
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... pattern relative to one another because the intermolecular forces are too weak to hold the atoms or molecules in a solid ...
... pattern relative to one another because the intermolecular forces are too weak to hold the atoms or molecules in a solid ...
ion
... An ion is an electrically charged particle obtained from an atom or chemically bonded group of atoms by adding or removing one or more electrons. A cation is a positively charged ion formed by losing one or more electrons. A cation is named by its element name followed by the word ion. For example, ...
... An ion is an electrically charged particle obtained from an atom or chemically bonded group of atoms by adding or removing one or more electrons. A cation is a positively charged ion formed by losing one or more electrons. A cation is named by its element name followed by the word ion. For example, ...
SIA Chapter 12 Atoms PP
... The term “element” is used when referring to macroscopic quantities. The term “atom” is used when discussing the submicroscopic. ...
... The term “element” is used when referring to macroscopic quantities. The term “atom” is used when discussing the submicroscopic. ...
chapter 1 activity 4 powerpoint
... beam of particles that traveled through a chamber of gas when exposed to an electrical current. ...
... beam of particles that traveled through a chamber of gas when exposed to an electrical current. ...
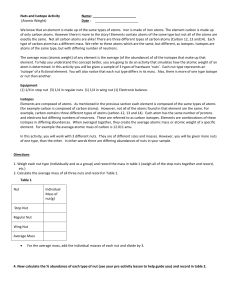
Nuts,Bolts and Isotopes- Average Atomic Mass Activity
... (for example carbon is composed of carbon atoms). However, not all of the atoms found in that element are the same. For example, carbon contains three different types of atoms (carbon-12, 13 and 14). Each atom has the same number of protons and electrons but differing numbers of neutrons. These are ...
... (for example carbon is composed of carbon atoms). However, not all of the atoms found in that element are the same. For example, carbon contains three different types of atoms (carbon-12, 13 and 14). Each atom has the same number of protons and electrons but differing numbers of neutrons. These are ...
Assignment 20 ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF ATOMS AND IONS I
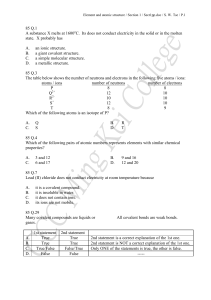
... eighteen elements, and the sixth period expands even more to include thirty-two elements. A vertical column on the Periodic Table is called a column or group. The Periodic Table contains a total of 18 different columns or groups, within which there are recurrences of chemical characteristics. In ea ...
... eighteen elements, and the sixth period expands even more to include thirty-two elements. A vertical column on the Periodic Table is called a column or group. The Periodic Table contains a total of 18 different columns or groups, within which there are recurrences of chemical characteristics. In ea ...
Atomic orbital An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that
... Sometimes the ψ function will be graphed to show its phases, rather than the |ψ(r,θ,φ)|2 which shows probability density but has no phases (which have been lost in the process of taking the absolute value, since ψ(r,θ,φ) is a complex number). |ψ(r,θ,φ)|2 orbital graphs tend to have less spherical, t ...
... Sometimes the ψ function will be graphed to show its phases, rather than the |ψ(r,θ,φ)|2 which shows probability density but has no phases (which have been lost in the process of taking the absolute value, since ψ(r,θ,φ) is a complex number). |ψ(r,θ,φ)|2 orbital graphs tend to have less spherical, t ...
Glossary: Chemical bonds
... f = 1 / n x V (where n is the number of metallic atoms in the compound, and V is the valency of the metal). Number of equivalents: n = m / МE (for any substance); n = V / VE (for gaseous substances), VE is the equivalent volume of the gas (the volume occupied by one equivalent of a gas under normal ...
... f = 1 / n x V (where n is the number of metallic atoms in the compound, and V is the valency of the metal). Number of equivalents: n = m / МE (for any substance); n = V / VE (for gaseous substances), VE is the equivalent volume of the gas (the volume occupied by one equivalent of a gas under normal ...
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been ...
... – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been ...