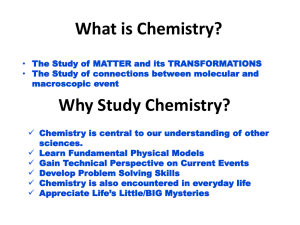
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Quick Notes
... (making it Neutrally Charged) Two types of Atoms: Ions- these are atoms that have LOST or GAINED an ELECTRON during a chemical reaction If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a Positive Ion If an atom gains an electron, it becomes a Negative Ion Ex: when Na reacts with Cl to form NaCl, the Na ...
... (making it Neutrally Charged) Two types of Atoms: Ions- these are atoms that have LOST or GAINED an ELECTRON during a chemical reaction If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a Positive Ion If an atom gains an electron, it becomes a Negative Ion Ex: when Na reacts with Cl to form NaCl, the Na ...
Atomic Theory - Hutchk12.org
... Hydrogen peroxide has a ratio of 1 g hydrogen to 16 grams of oxygen. ...
... Hydrogen peroxide has a ratio of 1 g hydrogen to 16 grams of oxygen. ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... of each element in a given compound is always the same. 3. Chemical reactions only involve the rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
... of each element in a given compound is always the same. 3. Chemical reactions only involve the rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
11/13 atoms powerpoint
... Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ...
... Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ...
Chapter 4: Introduction to Earth Chemistry Section 1 Notes
... Based on similarities in their _____________ properties, elements on the periodic table are arranged in columns, which are called ___________. An atom’s chemical properties are largely determined _________________________________________ _____________________________. These electrons are called ____ ...
... Based on similarities in their _____________ properties, elements on the periodic table are arranged in columns, which are called ___________. An atom’s chemical properties are largely determined _________________________________________ _____________________________. These electrons are called ____ ...
Exam #2
... (a) Electron affinities decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (b) Ionization energies decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (c) Chemical reactivity decreases going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (d) The second ionization energy ...
... (a) Electron affinities decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (b) Ionization energies decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (c) Chemical reactivity decreases going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (d) The second ionization energy ...
Chocolate Challenge - Waterford Public Schools
... Protons determine element’s identity # of protons is unique for each element Electrons determine element’s chemical properties Neutrons act as a “glue” for the protons to minimize charge repulsions ...
... Protons determine element’s identity # of protons is unique for each element Electrons determine element’s chemical properties Neutrons act as a “glue” for the protons to minimize charge repulsions ...
CHAPTER 2 - HCC Learning Web
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is mostly determined by the valence electrons • Elements with a full valence shell are chemically inert ...
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is mostly determined by the valence electrons • Elements with a full valence shell are chemically inert ...
PowerPoint Overview for Introduction
... The Elements o If a pure substance cannot be decomposed (at the macroscopic level ) into something else, then the substance is an element. o There are 118 Elements Known o Each element is given a unique chemical symbol (one or two letters). o Elements are Building Blocks of Matter. o Chemical symbo ...
... The Elements o If a pure substance cannot be decomposed (at the macroscopic level ) into something else, then the substance is an element. o There are 118 Elements Known o Each element is given a unique chemical symbol (one or two letters). o Elements are Building Blocks of Matter. o Chemical symbo ...
Chapter 2
... – Are numbered with Roman numeral and letter – (or just numbered with a number) • Main-group elements (labeled with A) • Transition elements (labeled with B) • Inner transition elements (shown below rest of table) ...
... – Are numbered with Roman numeral and letter – (or just numbered with a number) • Main-group elements (labeled with A) • Transition elements (labeled with B) • Inner transition elements (shown below rest of table) ...
Atomic Timeline - Ms Brown`s Chemistry Page
... • John Dalton formulated the Atomic Theory which states that: atoms of an element are different than atoms of other elements; atoms of one element are the same; that atoms of different elements can be combined; that atoms cannot be divided or separated; and that elements are made of tiny particles c ...
... • John Dalton formulated the Atomic Theory which states that: atoms of an element are different than atoms of other elements; atoms of one element are the same; that atoms of different elements can be combined; that atoms cannot be divided or separated; and that elements are made of tiny particles c ...
4 1 introduction to atoms 65-68
... nucleus of an atom was ________________________. 7. In the atomic model proposed by ________________________ , electrons move in specific orbits, similar to how planets orbit the sun. 8. What particle did Chadwick discover in 1932 that was hard to detect because it had no electrical charge? ________ ...
... nucleus of an atom was ________________________. 7. In the atomic model proposed by ________________________ , electrons move in specific orbits, similar to how planets orbit the sun. 8. What particle did Chadwick discover in 1932 that was hard to detect because it had no electrical charge? ________ ...
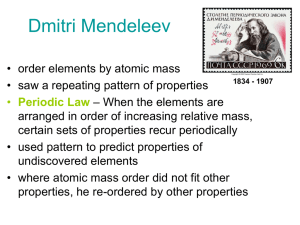
Dmitri Mendeleev
... periodic in the table same is composed family have of periods similar (rows) properties, and and areorcommonly referred to by their traditional groups families (columns). names. ...
... periodic in the table same is composed family have of periods similar (rows) properties, and and areorcommonly referred to by their traditional groups families (columns). names. ...
Chemistry Module 1- Basic Revision Notes 1.1a Atomic Structure 1.1
... 1.1.3 Elements (H, He, Li, Be,…..) are the basic building blocks of all matter, and cannot be broken down into simpler parts by chemical means. 1.1.4 There is a clear relationship between an elements electronic structure and its position in the periodic table. P E r i o d ...
... 1.1.3 Elements (H, He, Li, Be,…..) are the basic building blocks of all matter, and cannot be broken down into simpler parts by chemical means. 1.1.4 There is a clear relationship between an elements electronic structure and its position in the periodic table. P E r i o d ...
Science 9 Topic 3 What Are Elements Name
... Compounds are pure substances that contain two or more elements combined together in fixed (or definite) proportions. Water is an example of this law. Pure water always contains 11% Hydrogen and 89% Oxygen. Law of Multiple Proportions states that the masses of one element, which combine with a fixed ...
... Compounds are pure substances that contain two or more elements combined together in fixed (or definite) proportions. Water is an example of this law. Pure water always contains 11% Hydrogen and 89% Oxygen. Law of Multiple Proportions states that the masses of one element, which combine with a fixed ...
SECTION 3.1 Atomic Structure
... The last are the d orbitals, which occur 5 ways in space and the f orbitals, which occur 7 ways in space. Each orbital can only hold 2 electrons Electrons will occupy the lowest energy levels first, which mean they occupy orbitals with the lowest energy. Orbitals are occupied in this order: s ...
... The last are the d orbitals, which occur 5 ways in space and the f orbitals, which occur 7 ways in space. Each orbital can only hold 2 electrons Electrons will occupy the lowest energy levels first, which mean they occupy orbitals with the lowest energy. Orbitals are occupied in this order: s ...
Atomic Structure Test Review
... is 14, and so on until the p orbitals are full with 6. These are group 18. The entire energy level is full. That is why noble gases are unreactive. If there are s and d, it is a d-block metal. ...
... is 14, and so on until the p orbitals are full with 6. These are group 18. The entire energy level is full. That is why noble gases are unreactive. If there are s and d, it is a d-block metal. ...
Name: Date: Period: Who is the Father of Atomic Theory? What
... Characteristics of Elements: 5. Fill in the following descriptions of nonmetals: Location on the Periodic Table: Characteristics of Elements: 6. Fill in the following descriptions of metalloids: Location on the Periodic Table: Characteristics of Elements: 7. Can “groups be described as columns (↕) o ...
... Characteristics of Elements: 5. Fill in the following descriptions of nonmetals: Location on the Periodic Table: Characteristics of Elements: 6. Fill in the following descriptions of metalloids: Location on the Periodic Table: Characteristics of Elements: 7. Can “groups be described as columns (↕) o ...
study guide - atomic srtucture/_classification of matter
... idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still believed today. They are: 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles too small to see 2. In reactio ...
... idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still believed today. They are: 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles too small to see 2. In reactio ...