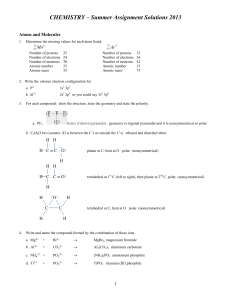
Chapter 4 Notes
... The Atomic Theory 1. All matter is composed of extremely small, indivisible particles, called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike. Atoms of different elements are chemically different. . 3. Atoms combine in whole # ratios to form compounds. 4. Atoms are combined, separated, or r ...
... The Atomic Theory 1. All matter is composed of extremely small, indivisible particles, called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike. Atoms of different elements are chemically different. . 3. Atoms combine in whole # ratios to form compounds. 4. Atoms are combined, separated, or r ...
Main-group elements as transition metals
... labels. This type of activation by main-group species is general, as shown by the fact that several other unsaturated heavier main-group molecules, including the carbene-like :GeAr2 and :SnAr2 as well as the monovalent :GaAr species, have been recently shown to react directly with H2 (Fig. 3a and b) ...
... labels. This type of activation by main-group species is general, as shown by the fact that several other unsaturated heavier main-group molecules, including the carbene-like :GeAr2 and :SnAr2 as well as the monovalent :GaAr species, have been recently shown to react directly with H2 (Fig. 3a and b) ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
Atomic Mass
... number of protons in one an atom of an element. It also tells you the number of electrons in a neutral atom of that element. The atomic number gives the identity of an element as well as its location on the periodic table. No two different elements will have the same atomic number ...
... number of protons in one an atom of an element. It also tells you the number of electrons in a neutral atom of that element. The atomic number gives the identity of an element as well as its location on the periodic table. No two different elements will have the same atomic number ...
Campbell Biology, 10e (Reece) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of
... A) the number of electrons in the element B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column ...
... A) the number of electrons in the element B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
inorganic chemistry
... compared to chlorine is due to very small size of the fluorine atom. As a result, there are strong inter-electronic repulsions in the relatively small 2p subshell of fluorine and thus the incoming electron does not feel much attraction. Therefore, its electron affinity is small. Thus, electron affin ...
... compared to chlorine is due to very small size of the fluorine atom. As a result, there are strong inter-electronic repulsions in the relatively small 2p subshell of fluorine and thus the incoming electron does not feel much attraction. Therefore, its electron affinity is small. Thus, electron affin ...
atm-atomic structure - Discovery Education
... Much of what we know about atomic structure today is the result of indirect observation of atoms and the particles that compose them. Democritus was the first to realize that the forces that hold together the atom cannot be divided except by the most powerful reactions. When the nucleus of an atom i ...
... Much of what we know about atomic structure today is the result of indirect observation of atoms and the particles that compose them. Democritus was the first to realize that the forces that hold together the atom cannot be divided except by the most powerful reactions. When the nucleus of an atom i ...
2 Atomic structure
... central nucleus (Figure 2.1). The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons (except for a hydrogen atom, which has no neutrons). The actual mass of a proton is 1.67 × 10−27 kg and the charge on a proton is +1.6 × 10−19 C. Relative masses and charges, shown in Table 2.1, are used to compare the mass ...
... central nucleus (Figure 2.1). The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons (except for a hydrogen atom, which has no neutrons). The actual mass of a proton is 1.67 × 10−27 kg and the charge on a proton is +1.6 × 10−19 C. Relative masses and charges, shown in Table 2.1, are used to compare the mass ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
total review package - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... Consider the following ideas: Compounds are made up of molecules which are combinations of atoms All atoms of an element are the same Atoms of different elements are different Atoms are indivisible particles Who came up with these ideas? ______________________ He called the ideas, the ______ ...
... Consider the following ideas: Compounds are made up of molecules which are combinations of atoms All atoms of an element are the same Atoms of different elements are different Atoms are indivisible particles Who came up with these ideas? ______________________ He called the ideas, the ______ ...
Chapter 2 ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... Copper has two stable isotopes, Cu-63 and Cu-65. If the masses are 62.929599 u and 64.927793 u respectively, what are the relative % abundances of the two isotopes? The weighted average atomic mass is reported as 63.546 u. Solution: Recall that the sum of the fractions that represent the two isotope ...
... Copper has two stable isotopes, Cu-63 and Cu-65. If the masses are 62.929599 u and 64.927793 u respectively, what are the relative % abundances of the two isotopes? The weighted average atomic mass is reported as 63.546 u. Solution: Recall that the sum of the fractions that represent the two isotope ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Element “X” is actually the real element ________________________________. Regions in space occupied by electrons are called ___________________________ Write the ground state electron configurations (eg. 1s2 2s2 2p6) for the following atoms or ions. You may use the core notation. a) ...
... Element “X” is actually the real element ________________________________. Regions in space occupied by electrons are called ___________________________ Write the ground state electron configurations (eg. 1s2 2s2 2p6) for the following atoms or ions. You may use the core notation. a) ...
Problem Solving Drill - Rapid Learning Center
... 3. A complete chemical symbol displays all the information about an atom’s protons, neutrons and electrons. Such a symbol contains an element symbol, surrounded by the atomic number, the mass number of the isotope and the charge of the ion. For the following, give the number of protons (p), neutrons ...
... 3. A complete chemical symbol displays all the information about an atom’s protons, neutrons and electrons. Such a symbol contains an element symbol, surrounded by the atomic number, the mass number of the isotope and the charge of the ion. For the following, give the number of protons (p), neutrons ...
Problem Solving Drill - Rapid Learning Center
... 3. A complete chemical symbol displays all the information about an atom’s protons, neutrons and electrons. Such a symbol contains an element symbol, surrounded by the atomic number, the mass number of the isotope and the charge of the ion. For the following, give the number of protons (p), neutrons ...
... 3. A complete chemical symbol displays all the information about an atom’s protons, neutrons and electrons. Such a symbol contains an element symbol, surrounded by the atomic number, the mass number of the isotope and the charge of the ion. For the following, give the number of protons (p), neutrons ...
Chemistry - Kendriya Vidyalaya Raigarh
... Q.5. H3PO3 can be represented by structures 1 and 2 shown below. Can these two structures be taken as the canonical forms of the resonance hybrid representing H3PO3? If not, give reasons for the same. ...
... Q.5. H3PO3 can be represented by structures 1 and 2 shown below. Can these two structures be taken as the canonical forms of the resonance hybrid representing H3PO3? If not, give reasons for the same. ...
H He - Science PowerPoints
... • Activity! Going outside and creating the atom Nitrogen #7 – Students need to be protons, neutrons, and electrons in the correct orbitals. • Boys neutrons, girls protons in nucleus? ...
... • Activity! Going outside and creating the atom Nitrogen #7 – Students need to be protons, neutrons, and electrons in the correct orbitals. • Boys neutrons, girls protons in nucleus? ...
atoms
... If two elements, A and B, form more than one compound, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Dalton predicted this law and observed it while developing his atomic theory. When two or more compounds exist from the same elements, they can not h ...
... If two elements, A and B, form more than one compound, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Dalton predicted this law and observed it while developing his atomic theory. When two or more compounds exist from the same elements, they can not h ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Ø If two elements, A and B, form more than one compound, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Ø Dalton predicted this law and observed it while developing his atomic theory. Ø When two or more compounds exist from the same elements, they can ...
... Ø If two elements, A and B, form more than one compound, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Ø Dalton predicted this law and observed it while developing his atomic theory. Ø When two or more compounds exist from the same elements, they can ...