OCR_AS_Level_Chemistry_Unit_F321_Atoms
... The first energy level (or shell) only contains an s orbital, labelled 1s The first shell can hold up to 2 electrons The second energy level contains an s orbital (labelled 2s) and three p orbitals (labelled 2p) The second shell can hold up to 8 electrons The third energy level contains an s orbital ...
... The first energy level (or shell) only contains an s orbital, labelled 1s The first shell can hold up to 2 electrons The second energy level contains an s orbital (labelled 2s) and three p orbitals (labelled 2p) The second shell can hold up to 8 electrons The third energy level contains an s orbital ...
Chemical Bonding Quiz
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
Chemistry 11 Exam 1 Spring 2006 When answering questions be
... When atoms form covalent bonds each can provide one electron. In molecular orbitals each atom possesses an atomic orbital. These two atomic orbitals combine to form new two new orbitals called molecular orbitals. In the MOs one is lower in energy than the atomic orbitals and the other is higher in e ...
... When atoms form covalent bonds each can provide one electron. In molecular orbitals each atom possesses an atomic orbital. These two atomic orbitals combine to form new two new orbitals called molecular orbitals. In the MOs one is lower in energy than the atomic orbitals and the other is higher in e ...
key to sample questions test 2
... Which one of the following statements is TRUE? Bond length tends to decrease as bond strength increases Bond length tends to increase as bond strength increases Single bonds tend to be shorter than double bonds Triple bonds tend to be longer than double bonds ...
... Which one of the following statements is TRUE? Bond length tends to decrease as bond strength increases Bond length tends to increase as bond strength increases Single bonds tend to be shorter than double bonds Triple bonds tend to be longer than double bonds ...
Exam Review
... In the free, or uncombined, state the number of protons in the nucleus of an element must equal the __. a) mass number c) mass number - atomic number b) number of neutrons in the nucleus d) number of electrons present Which of the following ideas of the Bohr model is not retained in the modern theor ...
... In the free, or uncombined, state the number of protons in the nucleus of an element must equal the __. a) mass number c) mass number - atomic number b) number of neutrons in the nucleus d) number of electrons present Which of the following ideas of the Bohr model is not retained in the modern theor ...
Here
... d. Bind each atom singly to central and subtract e. Fill octet of surrounding atoms and subtract f. Attempt to fill octet of central atom g. Check for multiple bonds or ion formation h. Recount to 8 4. Single Bonds – a covalent bond produced by the sharing of one pair of e- between two atoms: F2; HF ...
... d. Bind each atom singly to central and subtract e. Fill octet of surrounding atoms and subtract f. Attempt to fill octet of central atom g. Check for multiple bonds or ion formation h. Recount to 8 4. Single Bonds – a covalent bond produced by the sharing of one pair of e- between two atoms: F2; HF ...
The Periodic Table - Harlan Independent Schools
... One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called ...
... One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called ...
The ocean is a mixture.
... Halogen atoms only need to gain 1 electron to fill their outermost energy level. They react with alkali metals to form salts. Very ...
... Halogen atoms only need to gain 1 electron to fill their outermost energy level. They react with alkali metals to form salts. Very ...
1 st Nine Weeks Study Guide for Chemistry
... E. How do you tell an element from a compound? Element is one type of atom, a compound is two or more elements chemically combined. F. What are physical properties? Give at least five examples. Have to do with appearance, density, malleable, ductile. Boiling point G. What are chemical properties? Gi ...
... E. How do you tell an element from a compound? Element is one type of atom, a compound is two or more elements chemically combined. F. What are physical properties? Give at least five examples. Have to do with appearance, density, malleable, ductile. Boiling point G. What are chemical properties? Gi ...
File first semester final study guide key
... 2. How did Rutherford’s model of the atom differ from Thomson’s plum pudding model? Rutherford had a positively charged nucleus at the center of the atom. Thomson had positive charges spread throughout the entire atom. 3. What were two main conclusions of Rutherford’s gold foil experiment? 1. The at ...
... 2. How did Rutherford’s model of the atom differ from Thomson’s plum pudding model? Rutherford had a positively charged nucleus at the center of the atom. Thomson had positive charges spread throughout the entire atom. 3. What were two main conclusions of Rutherford’s gold foil experiment? 1. The at ...
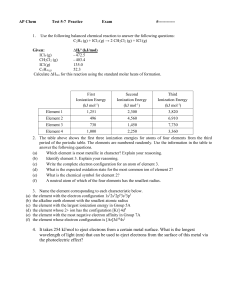
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
... Fe2O3(s) + 3 CO(g) 2 Fe(s) + 3CO2(g) ΔH = -28.0 kJ 3Fe(s) + 4 CO2(g) 4CO(g) + Fe3O4(s) ΔH = +12.5 kJ the enthalpy of the reaction of Fe2O3 with CO 3 Fe2O3(s) + CO(g) CO2(g) + 2 Fe3O4(s) is __________ kJ. A) -59.0 B) 40.5 C) -15.5 D) -109 E) +109 ...
... Fe2O3(s) + 3 CO(g) 2 Fe(s) + 3CO2(g) ΔH = -28.0 kJ 3Fe(s) + 4 CO2(g) 4CO(g) + Fe3O4(s) ΔH = +12.5 kJ the enthalpy of the reaction of Fe2O3 with CO 3 Fe2O3(s) + CO(g) CO2(g) + 2 Fe3O4(s) is __________ kJ. A) -59.0 B) 40.5 C) -15.5 D) -109 E) +109 ...
General and Organic Chemistry Review Primer
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
Periodic Trends & the Periodic Table
... • Metalloids have some chemical and physical properties of metals and other properties of nonmetals. • In the periodic table, the metalloids lie along the border between metals and ...
... • Metalloids have some chemical and physical properties of metals and other properties of nonmetals. • In the periodic table, the metalloids lie along the border between metals and ...
MYP 10 PeriodicityWS
... 3.2.1 Define the terms first ionization energy and electronegativity. 3.2.2 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (FI). 3.2.3. Describe and explain the trends i ...
... 3.2.1 Define the terms first ionization energy and electronegativity. 3.2.2 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (FI). 3.2.3. Describe and explain the trends i ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment - Belle Vernon Area School District
... 2. You need to master the formulas, charges, and names of the common ions. On the first week of the school year, you will be given a quiz on these ions. You will be asked to: • write the names of these ions when given the formula and charge • write the formula and charge when given the names I have ...
... 2. You need to master the formulas, charges, and names of the common ions. On the first week of the school year, you will be given a quiz on these ions. You will be asked to: • write the names of these ions when given the formula and charge • write the formula and charge when given the names I have ...
Ionic and Covalent Compounds: Naming, Formulas, Properties 1
... b) What is the mole ratio of oxygen gas to carbon dioxide gas? ___mol O 2 :___mol CO 2 [10 points] c) If one mole of oxygen gas reacts, how many moles of carbon dioxide gas are produced? [8 points] d) What are the molar masses of isopentane, C 5 H 12 , AND carbon dioxide, CO 2 ? [8 points] e) The vo ...
... b) What is the mole ratio of oxygen gas to carbon dioxide gas? ___mol O 2 :___mol CO 2 [10 points] c) If one mole of oxygen gas reacts, how many moles of carbon dioxide gas are produced? [8 points] d) What are the molar masses of isopentane, C 5 H 12 , AND carbon dioxide, CO 2 ? [8 points] e) The vo ...
Fall 2013 Final practice questions w/o solution
... 8. Which statement best explains why the electron affinity of B is less positive than that of Li? A) B has electrons in p orbitals, so it is lower in energy. B) Li does not want to gain an electron because it already has a half-full s orbital. C) B is a smaller atom, so its valence electrons are mo ...
... 8. Which statement best explains why the electron affinity of B is less positive than that of Li? A) B has electrons in p orbitals, so it is lower in energy. B) Li does not want to gain an electron because it already has a half-full s orbital. C) B is a smaller atom, so its valence electrons are mo ...
Unit 1 Powerpoint
... particular preference or point of view that is personal, rather than scientific. Science aims to be objective, but scientists are human, too. Sometimes scientific data can be misinterpreted or misapplied by scientists who want to prove a particular point. Recommendations made by scientists with pers ...
... particular preference or point of view that is personal, rather than scientific. Science aims to be objective, but scientists are human, too. Sometimes scientific data can be misinterpreted or misapplied by scientists who want to prove a particular point. Recommendations made by scientists with pers ...
Dr. Audrey Lugo`s AP Chemistry Course Syllabus
... 5. Periodic relationships including, for example, atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidation states B. Chemical bonding 1. Binding forces a. Types: ionic, covalent, metallic, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals (including London dispersion forces) b. Relationships to states, struc ...
... 5. Periodic relationships including, for example, atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidation states B. Chemical bonding 1. Binding forces a. Types: ionic, covalent, metallic, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals (including London dispersion forces) b. Relationships to states, struc ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.