Ionic Bonding - petersonORHS
... dot notation for the first two elements in each group. The other elements in that group will be the same. >Use these example to help you draw dot notations. ...
... dot notation for the first two elements in each group. The other elements in that group will be the same. >Use these example to help you draw dot notations. ...
Atom - U of L Class Index
... identical in mass and in all other properties. 3. Different elements have different kinds of atoms; these atoms differ in mass from element to element. 4. Atoms are indestructible & retain their identity in all chemical reactions. 5. The formation of a compound from its elements occurs through the c ...
... identical in mass and in all other properties. 3. Different elements have different kinds of atoms; these atoms differ in mass from element to element. 4. Atoms are indestructible & retain their identity in all chemical reactions. 5. The formation of a compound from its elements occurs through the c ...
Condition - Future Website of mrbentley2
... 6. Draw the Lewis dot structures of the following ionic compounds. Then, using a different colored pen, show how one element “steals” the other’s electrons, resulting in two ions. (Hint: Some of the compounds may require multiple numbers of one type of element - be sure to draw in the extra element ...
... 6. Draw the Lewis dot structures of the following ionic compounds. Then, using a different colored pen, show how one element “steals” the other’s electrons, resulting in two ions. (Hint: Some of the compounds may require multiple numbers of one type of element - be sure to draw in the extra element ...
Atomic Structure Tick Sheet
... I know that electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom in SHELLS or ENERGY LEVELS. I know that the shell nearest to the nucleus is FULL when it has a maximum of 2 electrons. I know that the other shells can hold a maximum of 8 electrons. I know that the combining power (valency) of an elem ...
... I know that electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom in SHELLS or ENERGY LEVELS. I know that the shell nearest to the nucleus is FULL when it has a maximum of 2 electrons. I know that the other shells can hold a maximum of 8 electrons. I know that the combining power (valency) of an elem ...
Pb2+ +2I- → PbI2 (s)
... 1st IE = 400, 2nd IE = 800, 3rd IE = 4000, 4th IE = 4500 – what element could this be? Jump in energy is at 2nd electron, it could be Mg, Be, Ca, Sr, or Br ...
... 1st IE = 400, 2nd IE = 800, 3rd IE = 4000, 4th IE = 4500 – what element could this be? Jump in energy is at 2nd electron, it could be Mg, Be, Ca, Sr, or Br ...
atomic theory of matter
... • Name these the same way that ionic binary compounds are named replacing the name of the anion (in a few cases cation) with the name of the polyatomic ion. – Oxy anions (anions containing at least 1 oxygen atom): difficult because there are often several possible anions. – Add -ate to the stem (car ...
... • Name these the same way that ionic binary compounds are named replacing the name of the anion (in a few cases cation) with the name of the polyatomic ion. – Oxy anions (anions containing at least 1 oxygen atom): difficult because there are often several possible anions. – Add -ate to the stem (car ...
(iii) Formation of Hydrogen chloride molecule
... Each atom uses three hybrid orbitals to form three sigma bonds, two with two carbon atoms and one with a hydrogen atom. ...
... Each atom uses three hybrid orbitals to form three sigma bonds, two with two carbon atoms and one with a hydrogen atom. ...
Transition-Metal Carbides. A Comparison of Bonding in Extended
... clusters have exposed surfacelike carbon atoms and are considered in a separate paper.’ The smallest “bulklike” carbides have six metal atoms, which may be arranged either octahedrally or trigonal prismatically around a central carbon atom. Each of these clusters has a welldefined electron count. Fo ...
... clusters have exposed surfacelike carbon atoms and are considered in a separate paper.’ The smallest “bulklike” carbides have six metal atoms, which may be arranged either octahedrally or trigonal prismatically around a central carbon atom. Each of these clusters has a welldefined electron count. Fo ...
The structure of Matter
... O Compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. O Two of the simplest hydrocarbons are methane and ethane. O Many hydrocarbons are used as fuels. ...
... O Compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. O Two of the simplest hydrocarbons are methane and ethane. O Many hydrocarbons are used as fuels. ...
end of year review
... Which of the following is an accurate comparison of the atomic number and mass of copper and gold? a. Au has a smaller atomic mass and fewer electrons than Cu b. Au has the same atomic mass as Cu but a greater atomic number c. Au has the same atomic number as Cu but a much greater atomic mass d. Au ...
... Which of the following is an accurate comparison of the atomic number and mass of copper and gold? a. Au has a smaller atomic mass and fewer electrons than Cu b. Au has the same atomic mass as Cu but a greater atomic number c. Au has the same atomic number as Cu but a much greater atomic mass d. Au ...
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding
... octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if all of its single electrons are used in a covalent bond, and there are sur ...
... octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if all of its single electrons are used in a covalent bond, and there are sur ...
Chemical Bonding - The Free Information Society
... actually required to break the chemical bond; the difference is the very small zero-point energy as explained inFig. 3. Bond energies are usually determined indirectly from thermodynamic data, but there are two main experimental ways of measuring them directly: 1. The direct thermochemical method in ...
... actually required to break the chemical bond; the difference is the very small zero-point energy as explained inFig. 3. Bond energies are usually determined indirectly from thermodynamic data, but there are two main experimental ways of measuring them directly: 1. The direct thermochemical method in ...
Practice exam - Dynamic Science
... Atom “Y” will give one electron away. Atom “Y” will take one electron away. Atom “Y” will share one electron with another atom. Atom “Y” will share two electrons with another atom. ...
... Atom “Y” will give one electron away. Atom “Y” will take one electron away. Atom “Y” will share one electron with another atom. Atom “Y” will share two electrons with another atom. ...
homework-11th-chem
... electrons will experience more effective nuclear charge from the nucleus? 43 The bromine atom possesses 35 electrons. It contains 6 electrons in 2p orbital, 6 electrons in 3p orbital and 5 electrons in 4p orbital. Which of these electron experiences the lowest effective nuclear charge? 44 Draw the s ...
... electrons will experience more effective nuclear charge from the nucleus? 43 The bromine atom possesses 35 electrons. It contains 6 electrons in 2p orbital, 6 electrons in 3p orbital and 5 electrons in 4p orbital. Which of these electron experiences the lowest effective nuclear charge? 44 Draw the s ...
Chapter 2 Expanded Notes
... Ion = an atom or molecule with an electrical charge resulting from the gain or loss of 1 or more electrons. Ionic bond: attraction of opposite charges, fairly strong, most common, found in metals and salts. Ionic bonds are formed by the mutual attraction of opposite charges of positive and negative ...
... Ion = an atom or molecule with an electrical charge resulting from the gain or loss of 1 or more electrons. Ionic bond: attraction of opposite charges, fairly strong, most common, found in metals and salts. Ionic bonds are formed by the mutual attraction of opposite charges of positive and negative ...
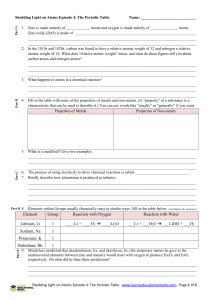
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In the 1810s and 1820s, carbon w ...
... Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In the 1810s and 1820s, carbon w ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... 4. When the Earth formed, nonmetals were the "limiting reactants." What would the Earth's structure be like if, instead, metals had been the limiting reactants and nonmetals were present in excess? In this case, there would be no native (elemental) metals. The three kinds of substances would be che ...
... 4. When the Earth formed, nonmetals were the "limiting reactants." What would the Earth's structure be like if, instead, metals had been the limiting reactants and nonmetals were present in excess? In this case, there would be no native (elemental) metals. The three kinds of substances would be che ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.