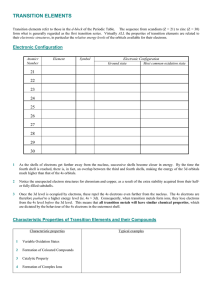
6.7 – Ionic Compounds
... valence electrons in order to achieve the octet rule (have 0 valence electrons). Fluorine is in Group 7A and therefore has 7 valence electrons. So Fluorine will gain 1 valence electron in order to achieve the octet rule (have 8 valence electrons). Cation – A metal that has lost its valence electrons ...
... valence electrons in order to achieve the octet rule (have 0 valence electrons). Fluorine is in Group 7A and therefore has 7 valence electrons. So Fluorine will gain 1 valence electron in order to achieve the octet rule (have 8 valence electrons). Cation – A metal that has lost its valence electrons ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam 3 (2015)
... 12) Which of the following states that the pressure and volume are inversely proportional for a gas at constant temperature? A) Boyle's law ...
... 12) Which of the following states that the pressure and volume are inversely proportional for a gas at constant temperature? A) Boyle's law ...
Chapter 7 The Quantum- Mechanical Model of the Atom
... • Energies are defined as being negative. – An electron would have E = 0 when it escapes the atom. ...
... • Energies are defined as being negative. – An electron would have E = 0 when it escapes the atom. ...
Chapter 7
... • Energies are defined as being negative. – An electron would have E = 0 when it escapes the atom. ...
... • Energies are defined as being negative. – An electron would have E = 0 when it escapes the atom. ...
ppt Lewis Dot Diagram Rules
... When compounds are formed they tend to follow the Octet Rule. Octet Rule: An atom will gain or loose e-(s) until it is surrounded by eight valence electrons. (Seek a full octet) ...
... When compounds are formed they tend to follow the Octet Rule. Octet Rule: An atom will gain or loose e-(s) until it is surrounded by eight valence electrons. (Seek a full octet) ...
9/6/12 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... Compounds are Pure Substances - Pure substances that are not elements are compounds. Compounds are composed of more than one kind of atom. o Example: carbon dioxide - There may be easier ways of preparing them, but compounds can be made from their elements. - Compounds can be broken down into their ...
... Compounds are Pure Substances - Pure substances that are not elements are compounds. Compounds are composed of more than one kind of atom. o Example: carbon dioxide - There may be easier ways of preparing them, but compounds can be made from their elements. - Compounds can be broken down into their ...
Grades 9-12 Chemistry California Content Standards
... 8. Chemical reaction rates depend on factors that influence the frequency of collision of reactant molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. the rate of reaction is the decrease in concentration of reactants or the increase in concentration of products with time. b. how ...
... 8. Chemical reaction rates depend on factors that influence the frequency of collision of reactant molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. the rate of reaction is the decrease in concentration of reactants or the increase in concentration of products with time. b. how ...
The Atom - Effingham County Schools
... of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers ...
... of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers ...
1 Course Code– CH1141 Semester – I Credit
... concepts - orbitals, radial and angular probability distribution curves, shapes of orbitals. Particle in a one-dimensional box. eigen functions and eigen values. Particle in three dimensional box. Module II - Electronic Configuration and Periodicity ...
... concepts - orbitals, radial and angular probability distribution curves, shapes of orbitals. Particle in a one-dimensional box. eigen functions and eigen values. Particle in three dimensional box. Module II - Electronic Configuration and Periodicity ...
Chemistry -- Oxidation
... most compounds. Exceptions are O2 (where O = 0) and peroxides, such as H2O2 or Na2O2, where O = -1. • For other elements, you can usually use If no other rules apply, assume ON is the same as the charge taken on in an ionic compound (“the charge it would like to be) ...
... most compounds. Exceptions are O2 (where O = 0) and peroxides, such as H2O2 or Na2O2, where O = -1. • For other elements, you can usually use If no other rules apply, assume ON is the same as the charge taken on in an ionic compound (“the charge it would like to be) ...
Chemistry
... 9 – 7 Know how to apply solution concentration, the gas laws and percent composition in order to carry out stoichiometrical calculations in a variety of experimental situations. 9 – 8 Know that chemical reactions can take place at different rates and that reaction rates depend on a variety of factor ...
... 9 – 7 Know how to apply solution concentration, the gas laws and percent composition in order to carry out stoichiometrical calculations in a variety of experimental situations. 9 – 8 Know that chemical reactions can take place at different rates and that reaction rates depend on a variety of factor ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... nature as a diatomic molecule? b. 3 a. Nitrogen c. 4 b. Helium d. 2 c. Hydrogen 11. In the correct Lewis structure for the methane d. oxygen molecule, how many unshared electron pairs 2. Ionic compounds generally form: surround the carbon? a. Liquids a. 2 b. Gases b. 0 c. Crystals c. 8 d. molecules ...
... nature as a diatomic molecule? b. 3 a. Nitrogen c. 4 b. Helium d. 2 c. Hydrogen 11. In the correct Lewis structure for the methane d. oxygen molecule, how many unshared electron pairs 2. Ionic compounds generally form: surround the carbon? a. Liquids a. 2 b. Gases b. 0 c. Crystals c. 8 d. molecules ...
1994–PTAS, Inc - mvhs
... 4a) XII, b) VIII, c) VII, d) V, e) I, f) II, g) X 5) D 6) C 7) D 8) A 9) D 10) B 11) D 12) C WORKSHEET 5 1) Energy is quantized: electrons can only have certain energies. When an electron makes a transition from a higher energy level to a lower energy level, the excess energy may be released in the ...
... 4a) XII, b) VIII, c) VII, d) V, e) I, f) II, g) X 5) D 6) C 7) D 8) A 9) D 10) B 11) D 12) C WORKSHEET 5 1) Energy is quantized: electrons can only have certain energies. When an electron makes a transition from a higher energy level to a lower energy level, the excess energy may be released in the ...
Chapter-2
... 8. Draw molecular orbital diagrams for HF, CO, NO, NO+. Calculate their bond order and predict magnetic properties. ...
... 8. Draw molecular orbital diagrams for HF, CO, NO, NO+. Calculate their bond order and predict magnetic properties. ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... with its charge? (1) A neutron has a negative charge. (2) A proton has a negative charge. (3) A neutron has no charge. (4) A proton has no charge. ...
... with its charge? (1) A neutron has a negative charge. (2) A proton has a negative charge. (3) A neutron has no charge. (4) A proton has no charge. ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.