final exam review packet
... C- Periodic Table-2301. I can differentiate between groups and periods on the periodic table and what is common about elements within a group. C- Periodic Table-2302. I can locate metals, non-metals and metalloids on the periodic table. C- Periodic Table-2303. I can list properties of metals, non me ...
... C- Periodic Table-2301. I can differentiate between groups and periods on the periodic table and what is common about elements within a group. C- Periodic Table-2302. I can locate metals, non-metals and metalloids on the periodic table. C- Periodic Table-2303. I can list properties of metals, non me ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... what are the other ligands which can show some pi bonding affinity which is dominating also to the metal centre. So when we consider the sigma bonding parameter we must have some head on overlap. So, we should have the corresponding metal ligand overlap which can be considered as a head on overlap ...
... what are the other ligands which can show some pi bonding affinity which is dominating also to the metal centre. So when we consider the sigma bonding parameter we must have some head on overlap. So, we should have the corresponding metal ligand overlap which can be considered as a head on overlap ...
200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
200things2know
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... (E) 84 Which element contains 3 half-filled orbitals? 37. (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 38. Which element has the highest electronegativity? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 39. Which element is a metalloid? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 40. Which element does not form compounds? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) ...
... (E) 84 Which element contains 3 half-filled orbitals? 37. (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 38. Which element has the highest electronegativity? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 39. Which element is a metalloid? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 40. Which element does not form compounds? (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) ...
200 Things to Know to Pass the Chemistry Regents
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
Topic 1 Test - A-Level Chemistry
... State how krypton is ionised in the mass spectrometer. Write an equation, including state symbols, to show the reaction that occurs when the first ionisation energy of Kr is measured. Sometimes the mass spectrum of Kr has a very small peak with an m/z value of 42. Explain the occurrence of this peak ...
... State how krypton is ionised in the mass spectrometer. Write an equation, including state symbols, to show the reaction that occurs when the first ionisation energy of Kr is measured. Sometimes the mass spectrum of Kr has a very small peak with an m/z value of 42. Explain the occurrence of this peak ...
Final Exam - Dawson College
... A transition metal ion with a charge of 1+ having 5 unpaired “4d” electrons The element with the highest first ionization energy in period 4 The excited electron configuration is 1s22s22p63s13p1 The halogen with the smallest electron affinity (less exothermic) The noble gas with electrons occupying ...
... A transition metal ion with a charge of 1+ having 5 unpaired “4d” electrons The element with the highest first ionization energy in period 4 The excited electron configuration is 1s22s22p63s13p1 The halogen with the smallest electron affinity (less exothermic) The noble gas with electrons occupying ...
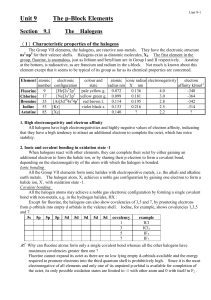
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
... All the halogen atoms may achieve a noble gas electronic configuration by forming a single covalent bond with non-metals, e.g. in the hydrogen halides, HX : Except for fluorine, the halogens can also show covalencies of 3,5 and 7, by promoting electrons from p orbitals into empty d orbitals in the v ...
... All the halogen atoms may achieve a noble gas electronic configuration by forming a single covalent bond with non-metals, e.g. in the hydrogen halides, HX : Except for fluorine, the halogens can also show covalencies of 3,5 and 7, by promoting electrons from p orbitals into empty d orbitals in the v ...
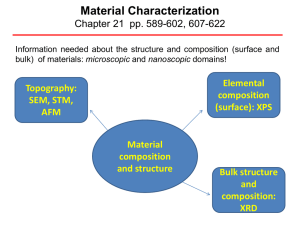
Material Characterization
... X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its "as received" state, or after some treatment XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot detect hyd ...
... X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its "as received" state, or after some treatment XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot detect hyd ...
- Aboriginal Access to Engineering
... Not all electrons orbit at the same distance from the nucleus. In fact, electrons orbit the nucleus at several distinct energy levels, each of which can hold a different number of electrons. The first energy level can hold up to 2 electrons, the second up to 8. As you get further from the nucleus th ...
... Not all electrons orbit at the same distance from the nucleus. In fact, electrons orbit the nucleus at several distinct energy levels, each of which can hold a different number of electrons. The first energy level can hold up to 2 electrons, the second up to 8. As you get further from the nucleus th ...
UNIT NUM="1" ID="UN
... in the center of the field. Moreover, the electrons would be like two tiny gnats buzzing around the stadium. Atoms are mostly empty space. When two atoms approach each other during a chemical reaction, their nuclei do not come close enough to interact. Of the three kinds of subatomic particles we ha ...
... in the center of the field. Moreover, the electrons would be like two tiny gnats buzzing around the stadium. Atoms are mostly empty space. When two atoms approach each other during a chemical reaction, their nuclei do not come close enough to interact. Of the three kinds of subatomic particles we ha ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
key concepts of matter
... protons located in its nucleus. Key Concept 2: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. Key Concept 3: Electrons located in the outermost shell of the electron cloud are ...
... protons located in its nucleus. Key Concept 2: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. Key Concept 3: Electrons located in the outermost shell of the electron cloud are ...
Key Concept 1: An atom is the smallest unit of an element that
... Key Concept 7: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. ...
... Key Concept 7: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. ...
PVS103 - unit 6 notes
... We have already seen how electronegativity increases on moving across the periodic table. Can you remember why? As a result electronegativity is a periodic property, so for example, the halogens (Group 7a elements) are all highly electronegative. ...
... We have already seen how electronegativity increases on moving across the periodic table. Can you remember why? As a result electronegativity is a periodic property, so for example, the halogens (Group 7a elements) are all highly electronegative. ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.